本篇文章的项目地址基于Core Text实现的TXT电子书阅读器。
最近花了一点时间学习了iOS的底层文字处理的框架Core Text。在网上也参考很多资料,具体的资料在文章最后列了出来,有兴趣的可参考一下。
本篇主要介绍实现TXT电子书阅读器设计用到的Core Text相关的用法与实现。
关于Core Text
Core Text是iOS底层的文字处理框架,只提供一套C函数接口,使用Core Text对象时要注意手动管理内存以避免发生内存泄漏。之前写了一篇iOS富文本(二)初识Text Kit是介绍iOS的另一个文字处理框架Text Kit,Text Kit是封装Core Text函数提供一套Objective-C的接口,使用起来也比较友好。高度的封装意味着可定制性差,灵活性低。所以如果需要实现更多的功能最好还是用Core Text。
关于文字的相关知识参考文章最后列出的资料,因为涉及到字体大小的计算。例如在算字体高度时应该是baseline+ascent+descent的总和,了解这些知识对理解Core Text相关函数很有帮助
Core Text运行时的层次
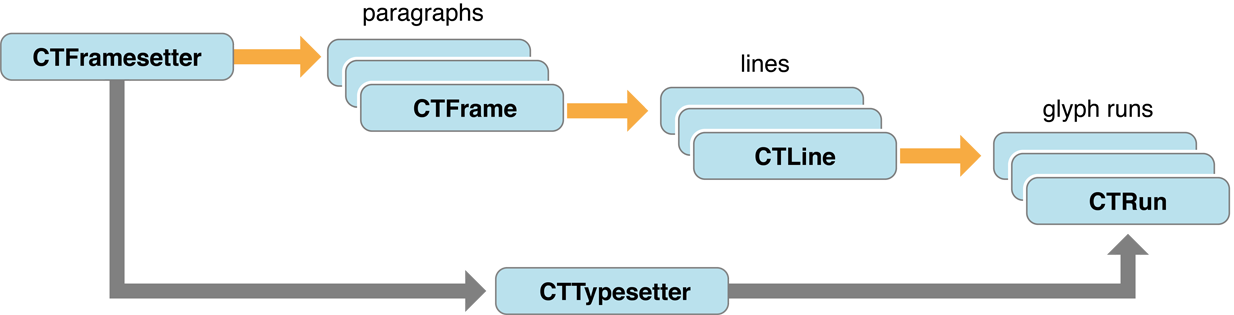
介绍一下这个层级。framesetter对象(CTFramesetterRef)最为顶层接收一个属性化字符串(attributedString)作为输入,一个framesetter对象生成一个或多个文本中的帧(CTFrameRef)每一个CTFrame都代表一个段落。
要生成帧(CTFrameRef)时,framesetter调用一个typesetter对象(CTTypesetterRef),它放置文本在frame中,framesetter设置段落样式给typesetter对象,包括属性对齐方式,制表位,行间距,缩进和换行模式,typesetter对象用这些属性转换每个字符成字形,然后在每行中填充这些字型,再用这些行填满整个绘制区间。
每个CTFrame对象包含段落线(CTLine)对象。每个(CTLine)对象代表段落中的每一行,一个CTFrame可以包含一个或者多个CTLine对象。CTLine由typesetter对象操作期间被创建。
每个CTLine是包含字形管理(CTRun)对象的数组,一个CTRun对象是一组共享相同属性,方向的连续字形。
基于Core Text实现的电子书阅读器
根据配置文件得到文字显示的属性。
+(NSDictionary *)parserAttribute:(LSYReadConfig *)config
{
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[NSForegroundColorAttributeName] = config.fontColor;
dict[NSFontAttributeName] = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:config.fontSize];
NSMutableParagraphStyle *paragraphStyle = [[NSMutableParagraphStyle alloc] init];
paragraphStyle.lineSpacing = config.lineSpace;
paragraphStyle.alignment = NSTextAlignmentJustified;
dict[NSParagraphStyleAttributeName] = paragraphStyle;
return [dict copy];
}根据属性生成属性化字符串,然后属性化字符串作为输入得到CTFrame对象
+(CTFrameRef)parserContent:(NSString *)content config:(LSYReadConfig *)parser bouds:(CGRect)bounds
{
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedString = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:content];
NSDictionary *attribute = [self parserAttribute:parser];
[attributedString setAttributes:attribute range:NSMakeRange(0, content.length)];
CTFramesetterRef setterRef = CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((__bridge CFAttributedStringRef)attributedString);
CGPathRef pathRef = CGPathCreateWithRect(bounds, NULL);
CTFrameRef frameRef = CTFramesetterCreateFrame(setterRef, CFRangeMake(0, 0), pathRef, NULL);
CFRelease(setterRef);
CFRelease(pathRef);
return frameRef;
}生成的CTFrame在要View的drawRect方法中调用CTFrameDraw就可以进行绘制。
因为我们不仅要绘制出文字还要和文字进行交互所以仅仅这两个函数是不够的。
还需要以下函数
//根据触摸点获取当前文字的索引
+(CFIndex)parserIndexWithPoint:(CGPoint)point frameRef:(CTFrameRef)frameRef
{
CFIndex index = -1;
CGPathRef pathRef = CTFrameGetPath(frameRef); //获取绘制的路径
CGRect bounds = CGPathGetBoundingBox(pathRef); //获取绘制的区间
NSArray *lines = (__bridge NSArray *)CTFrameGetLines(frameRef); //获取绘制区间内所有的行数
if (!lines) {
return index;
}
NSInteger lineCount = [lines count];
CGPoint *origins = malloc(lineCount * sizeof(CGPoint)); //给每行的起始点开辟内存
if (lineCount) {
CTFrameGetLineOrigins(frameRef, CFRangeMake(0, 0), origins); //获取每行的坐标
for (int i = 0; i<lineCount; i++) {
CGPoint baselineOrigin = origins[i];
CTLineRef line = (__bridge CTLineRef)[lines objectAtIndex:i];
CGFloat ascent,descent,linegap; //声明字体的上行高度和下行高度和行距
CGFloat lineWidth = CTLineGetTypographicBounds(line, &ascent, &descent, &linegap); //获取每行的宽度
CGRect lineFrame = CGRectMake(baselineOrigin.x, CGRectGetHeight(bounds)-baselineOrigin.y-ascent, lineWidth, ascent+descent+linegap+[LSYReadConfig shareInstance].lineSpace); //没有转换坐标系左下角为坐标原点 字体高度为上行高度加下行高度
if (CGRectContainsPoint(lineFrame,point)){
index = CTLineGetStringIndexForPosition(line, point); //得到当前文字的索引
break;
}
}
}
free(origins); 释放内存
return index;
}长按文字会默认选中两个文字这样就要计算选中的区间
+(CGRect)parserRectWithPoint:(CGPoint)point frameRef:(CTFrameRef)frameRef
{
CFIndex index = -1;
CGPathRef pathRef = CTFrameGetPath(frameRef);
CGRect bounds = CGPathGetBoundingBox(pathRef);
CGRect rect = CGRectZero;
NSArray *lines = (__bridge NSArray *)CTFrameGetLines(frameRef);
if (!lines) {
return rect;
}
NSInteger lineCount = [lines count];
CGPoint *origins = malloc(lineCount * sizeof(CGPoint)); //给每行的起始点开辟内存
if (lineCount) {
CTFrameGetLineOrigins(frameRef, CFRangeMake(0, 0), origins);
for (int i = 0; i<lineCount; i++) {
CGPoint baselineOrigin = origins[i];
CTLineRef line = (__bridge CTLineRef)[lines objectAtIndex:i];
CGFloat ascent,descent,linegap; //声明字体的上行高度和下行高度和行距
CGFloat lineWidth = CTLineGetTypographicBounds(line, &ascent, &descent, &linegap);
CGRect lineFrame = CGRectMake(baselineOrigin.x, CGRectGetHeight(bounds)-baselineOrigin.y-ascent, lineWidth, ascent+descent+linegap+[LSYReadConfig shareInstance].lineSpace); //没有转换坐标系左下角为坐标原点 字体高度为上行高度加下行高度加行间距 注:[LSYReadConfig shareInstance].lineSpace为配置文件中设置的行间距
if (CGRectContainsPoint(lineFrame,point)){
CFRange stringRange = CTLineGetStringRange(line);
index = CTLineGetStringIndexForPosition(line, point);
CGFloat xStart = CTLineGetOffsetForStringIndex(line, index, NULL); //获取当前索引在当前行的偏移量
CGFloat xEnd;
//默认选中两个单位
if (index > stringRange.location+stringRange.length-2) {
xEnd = xStart;
xStart = CTLineGetOffsetForStringIndex(line,index-2,NULL);
}
else{
xEnd = CTLineGetOffsetForStringIndex(line,index+2,NULL);
}
rect = CGRectMake(origins[i].x+xStart,baselineOrigin.y-descent,fabs(xStart-xEnd), ascent+descent);
break;
}
}
}
free(origins);
return rect;
}上面就是实现这个项目使用的大部分关于Core Text代码,实际项目实现起来远比这要复杂的多。具体实现请参考这个项目基于Core Text实现的TXT电子书阅读器
参考资料
Core Text 入门
基于 CoreText 的排版引擎:基础
Core Text Tutorial for iOS: Making a Magazine App
NIAttributedLabel.m
WFCoretext





















 8597
8597











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








