一、概述
对于加载图片,大家都不陌生,一般为了尽可能避免OOM都会按照如下做法:
- 对于图片显示:根据需要显示图片控件的大小对图片进行压缩显示。
- 如果图片数量非常多:则会使用LruCache等缓存机制,将所有图片占据的内容维持在一个范围内。
其实对于图片加载还有种情况,就是单个图片非常巨大,并且还不允许压缩。比如显示:世界地图、清明上河图、微博长图等。
那么对于这种需求,该如何做呢?
首先不压缩,按照原图尺寸加载,那么屏幕肯定是不够大的,并且考虑到内存的情况,不可能一次性整图加载到内存中,所以肯定是局部加载,那么就需要用到一个类:
BitmapRegionDecoder
其次,既然屏幕显示不完,那么最起码要添加一个上下左右拖动的手势,让用户可以拖动查看。
那么综上,本篇博文的目的就是去自定义一个显示巨图的View,支持用户去拖动查看,大概的效果图如下:
好吧,这清明上河图太长了,想要观看全图,文末下载,图片在assets目录。当然如果你的图,高度也很大,肯定也是可以上下拖动的。
二、初识BitmapRegionDecoder
BitmapRegionDecoder主要用于显示图片的某一块矩形区域,如果你需要显示某个图片的指定区域,那么这个类非常合适。
对于该类的用法,非常简单,既然是显示图片的某一块区域,那么至少只需要一个方法去设置图片;一个方法传入显示的区域即可;详见:
BitmapRegionDecoder提供了一系列的newInstance方法来构造对象,支持传入文件路径,文件描述符,文件的inputstrem等。
例如:
BitmapRegionDecoder bitmapRegionDecoder = BitmapRegionDecoder.newInstance(inputStream, false);- 1
- 2
- 3
上述解决了传入我们需要处理的图片,那么接下来就是显示指定的区域。
bitmapRegionDecoder.decodeRegion(rect, options);- 1
参数一很明显是一个rect,参数二是BitmapFactory.Options,你可以控制图片的
inSampleSize,inPreferredConfig等。
那么下面看一个超级简单的例子:
package com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.BitmapRegionDecoder;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import com.zhy.blogcodes.R;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class LargeImageViewActivity extends AppCompatActivity
{
private ImageView mImageView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_large_image_view);
mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_imageview);
try
{
InputStream inputStream = getAssets().open("tangyan.jpg");
//获得图片的宽、高
BitmapFactory.Options tmpOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();
tmpOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(inputStream, null, tmpOptions);
int width = tmpOptions.outWidth;
int height = tmpOptions.outHeight;
//设置显示图片的中心区域
BitmapRegionDecoder bitmapRegionDecoder = BitmapRegionDecoder.newInstance(inputStream, false);
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
Bitmap bitmap = bitmapRegionDecoder.decodeRegion(new Rect(width / 2 - 100, height / 2 - 100, width / 2 + 100, height / 2 + 100), options);
mImageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
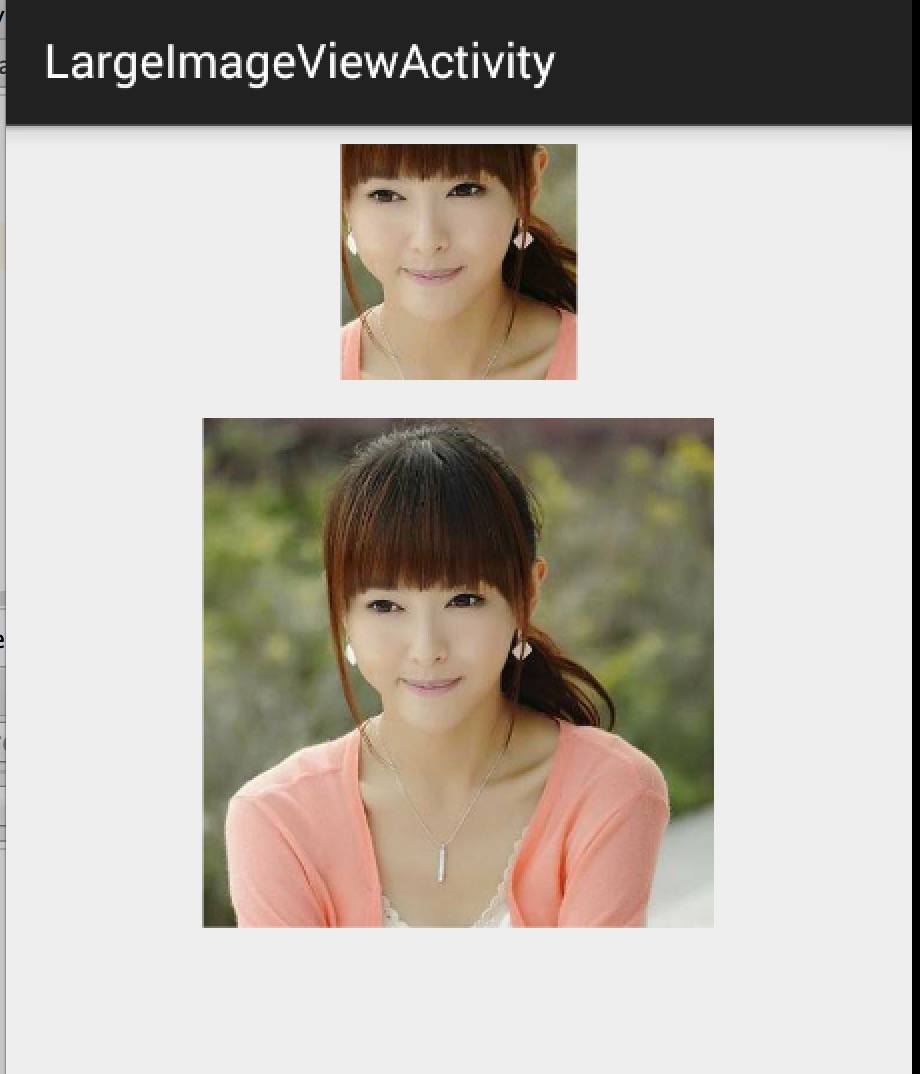
上述代码,就是使用BitmapRegionDecoder去加载assets中的图片,调用bitmapRegionDecoder.decodeRegion解析图片的中间矩形区域,返回bitmap,最终显示在ImageView上。
效果图:
上面的小图显示的即为下面的大图的中间区域。
ok,那么目前我们已经了解了BitmapRegionDecoder的基本用户,那么往外扩散,我们需要自定义一个控件去显示巨图就很简单了,首先Rect的范围就是我们View的大小,然后根据用户的移动手势,不断去更新我们的Rect的参数即可。
三、自定义显示大图控件
根据上面的分析呢,我们这个自定义控件思路就非常清晰了:
- 提供一个设置图片的入口
- 重写onTouchEvent,在里面根据用户移动的手势,去更新显示区域的参数
- 每次更新区域参数后,调用invalidate,onDraw里面去regionDecoder.decodeRegion拿到bitmap,去draw
理清了,发现so easy,下面上代码:
package com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.BitmapRegionDecoder;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Created by zhy on 15/5/16.
*/
public class LargeImageView extends View
{
private BitmapRegionDecoder mDecoder;
/**
* 图片的宽度和高度
*/
private int mImageWidth, mImageHeight;
/**
* 绘制的区域
*/
private volatile Rect mRect = new Rect();
private MoveGestureDetector mDetector;//手势探测
private static final BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
static
{
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
}
public void setInputStream(InputStream is)
{
try
{
mDecoder = BitmapRegionDecoder.newInstance(is, false);
BitmapFactory.Options tmpOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();
// Grab the bounds for the scene dimensions
tmpOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is, null, tmpOptions);
mImageWidth = tmpOptions.outWidth;
mImageHeight = tmpOptions.outHeight;
requestLayout();//!!!!!
invalidate();//!!!!!!
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
} finally
{
try
{
if (is != null) is.close();
} catch (Exception e)
{
}
}
}
public void init()
{
mDetector = new MoveGestureDetector(getContext(), new MoveGestureDetector.SimpleMoveGestureDetector()
{
@Override
public boolean onMove(MoveGestureDetector detector)
{
int moveX = (int) detector.getMoveX();
int moveY = (int) detector.getMoveY();
if (mImageWidth > getWidth())
{
mRect.offset(-moveX, 0);
checkWidth();
invalidate();
}
if (mImageHeight > getHeight())
{
mRect.offset(0, -moveY);
checkHeight();
invalidate();
}
return true;
}
});
}
private void checkWidth()
{
Rect rect = mRect;
int imageWidth = mImageWidth;
int imageHeight = mImageHeight;
if (rect.right > imageWidth)
{
rect.right = imageWidth;
rect.left = imageWidth - getWidth();
}
if (rect.left < 0)
{
rect.left = 0;
rect.right = getWidth();
}
}
private void checkHeight()
{
Rect rect = mRect;
int imageWidth = mImageWidth;
int imageHeight = mImageHeight;
if (rect.bottom > imageHeight)
{
rect.bottom = imageHeight;
rect.top = imageHeight - getHeight();
}
if (rect.top < 0)
{
rect.top = 0;
rect.bottom = getHeight();
}
}
public LargeImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{//构造方法
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{//touch方法被手势探测器消费
mDetector.onToucEvent(event);
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
{//bitmapRegionDecoder加载区域画面
Bitmap bm = mDecoder.decodeRegion(mRect, options);
canvas.drawBitmap(bm, 0, 0, null);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
int imageWidth = mImageWidth;
int imageHeight = mImageHeight;
//默认直接显示图片的中心区域,可以自己去调节
mRect.left = imageWidth / 2 - width / 2;
mRect.top = imageHeight / 2 - height / 2;
mRect.right = mRect.left + width;
mRect.bottom = mRect.top + height;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
根据上述源码:
- setInputStream里面去获得图片的真实的宽度和高度,以及初始化我们的mDecoder
- onMeasure里面为我们的显示区域的rect赋值,大小为view的尺寸
- onTouchEvent里面我们监听move的手势,在监听的回调里面去改变rect的参数,以及做边界检查,最后invalidate
- 在onDraw里面就是根据rect拿到bitmap,然后draw了
ok,上面并不复杂,不过大家有没有注意到,这个监听用户move手势的代码写的有点奇怪,恩,这里模仿了系统的ScaleGestureDetector,编写了MoveGestureDetector,代码如下:
MoveGestureDetector
package com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage.view; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.PointF; import android.view.MotionEvent; public class MoveGestureDetector extends BaseGestureDetector { private PointF mCurrentPointer; private PointF mPrePointer; //仅仅为了减少创建内存 private PointF mDeltaPointer = new PointF(); //用于记录最终结果,并返回 private PointF mExtenalPointer = new PointF(); private OnMoveGestureListener mListenter; public MoveGestureDetector(Context context, OnMoveGestureListener listener) {//构造方法 super(context); mListenter = listener; } @Override protected void handleInProgressEvent(MotionEvent event) { int actionCode = event.getAction() & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK; switch (actionCode) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: mListenter.onMoveEnd(this); resetState(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: updateStateByEvent(event); boolean update = mListenter.onMove(this); if (update) { mPreMotionEvent.recycle(); mPreMotionEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(event); } break; } } @Override protected void handleStartProgressEvent(MotionEvent event) { int actionCode = event.getAction() & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK; switch (actionCode) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: resetState();//防止没有接收到CANCEL or UP ,保险起见 mPreMotionEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(event); updateStateByEvent(event); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: mGestureInProgress = mListenter.onMoveBegin(this); break; } } protected void updateStateByEvent(MotionEvent event) { final MotionEvent prev = mPreMotionEvent; mPrePointer = caculateFocalPointer(prev); mCurrentPointer = caculateFocalPointer(event); //Log.e("TAG", mPrePointer.toString() + " , " + mCurrentPointer); boolean mSkipThisMoveEvent = prev.getPointerCount() != event.getPointerCount(); //Log.e("TAG", "mSkipThisMoveEvent = " + mSkipThisMoveEvent); mExtenalPointer.x = mSkipThisMoveEvent ? 0 : mCurrentPointer.x - mPrePointer.x; mExtenalPointer.y = mSkipThisMoveEvent ? 0 : mCurrentPointer.y - mPrePointer.y; } /** * 根据event计算多指中心点 * * @param event * @return */ private PointF caculateFocalPointer(MotionEvent event) { final int count = event.getPointerCount(); float x = 0, y = 0; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { x += event.getX(i); y += event.getY(i); } x /= count; y /= count; return new PointF(x, y); } public float getMoveX() { return mExtenalPointer.x; } public float getMoveY() { return mExtenalPointer.y; } public interface OnMoveGestureListener { public boolean onMoveBegin(MoveGestureDetector detector); public boolean onMove(MoveGestureDetector detector); public void onMoveEnd(MoveGestureDetector detector); } public static class SimpleMoveGestureDetector implements OnMoveGestureListener { @Override public boolean onMoveBegin(MoveGestureDetector detector) { return true; } @Override public boolean onMove(MoveGestureDetector detector) { return false; } @Override public void onMoveEnd(MoveGestureDetector detector) { } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
BaseGestureDetector
package com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage.view; import android.content.Context; import android.view.MotionEvent; public abstract class BaseGestureDetector { protected boolean mGestureInProgress; protected MotionEvent mPreMotionEvent; protected MotionEvent mCurrentMotionEvent; protected Context mContext; public BaseGestureDetector(Context context) { mContext = context; } public boolean onToucEvent(MotionEvent event) { if (!mGestureInProgress) { handleStartProgressEvent(event); } else { handleInProgressEvent(event); } return true; } protected abstract void handleInProgressEvent(MotionEvent event); protected abstract void handleStartProgressEvent(MotionEvent event); protected abstract void updateStateByEvent(MotionEvent event); protected void resetState() { if (mPreMotionEvent != null) { mPreMotionEvent.recycle(); mPreMotionEvent = null; } if (mCurrentMotionEvent != null) { mCurrentMotionEvent.recycle(); mCurrentMotionEvent = null; } mGestureInProgress = false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
你可能会说,一个move手势搞这么多代码,太麻烦了。的确是的,move手势的检测非常简单,那么之所以这么写呢,主要是为了可以复用,比如现在有一堆的
XXXGestureDetector,当我们需要监听什么手势,就直接拿个detector来检测多方便。我相信大家肯定也郁闷过Google,为什么只有ScaleGestureDetector而没有RotateGestureDetector呢。
根据上述,大家应该理解了为什么要这么做,当时不强制,每个人都有个性。
不过值得一提的是:上面这个手势检测的写法,不是我想的,而是一个开源的项目https://github.com/rharter/android-gesture-detectors,里面包含很多的手势检测。对应的博文是:http://code.almeros.com/android-multitouch-gesture-detectors#.VibzzhArJXg那面上面两个类就是我偷学了的~ 哈
四、测试
测试其实没撒好说的了,就是把我们的LargeImageView放入布局文件,然后Activity里面去设置inputstream了。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage.view.LargeImageView
android:id="@+id/id_largetImageview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</RelativeLayout>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
然后在Activity里面去设置图片:
package com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.zhy.blogcodes.R;
import com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage.view.LargeImageView;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class LargeImageViewActivity extends AppCompatActivity
{
private LargeImageView mLargeImageView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_large_image_view);
mLargeImageView = (LargeImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_largetImageview);
try
{
InputStream inputStream = getAssets().open("world.jpg");
mLargeImageView.setInputStream(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
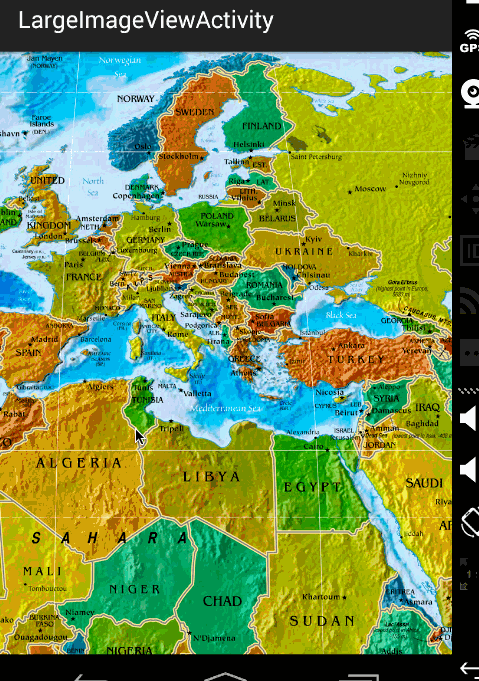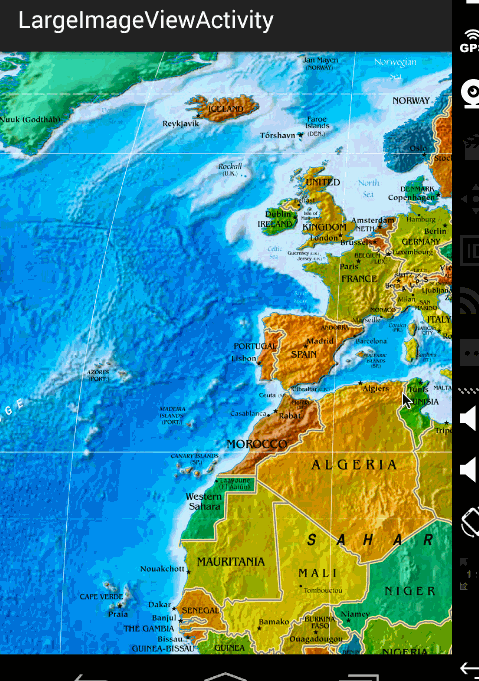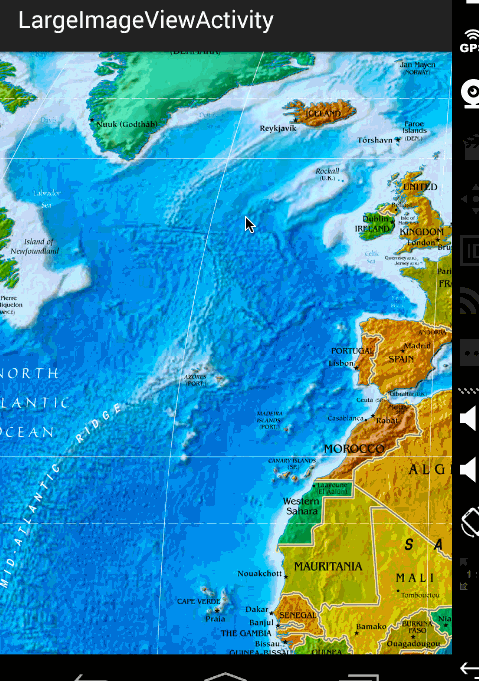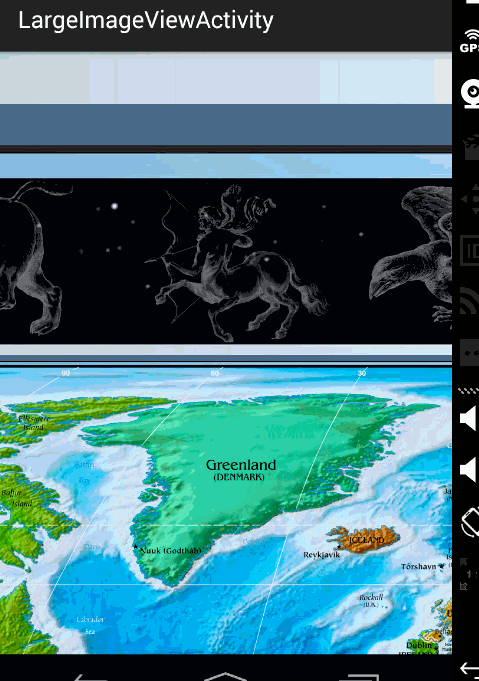
效果图:
ok,那么到此,显示巨图的方案以及详细的代码就描述完成了,总体还是非常简单的。
但是,在实际的项目中,可能会有更多的需求,比如增加放大、缩小;增加快滑手势等等,那么大家可以去参考这个库:https://github.com/johnnylambada/WorldMap,该库基本实现了绝大多数的需求,大家根据本文这个思路再去看这个库,也会简单很多,定制起来也容易。我这个地图的图就是该库里面提供的。
哈,掌握了这个,以后面试过程中也可以悄悄的装一把了,当你优雅的答完android加载图片的方案以后,然后接一句,其实还有一种情况,就是高清显示巨图,那么我们应该…相信面试官对你的印象会好很多~ have a nice day ~
源码链接:https://github.com/hongyangAndroid/Android_Blog_Demos
参考链接
- http://code.almeros.com/android-multitouch-gesture-detectors#.VibzzhArJXg
- https://github.com/rharter/android-gesture-detectors
- https://github.com/johnnylambada/WorldMap
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/49300989






















 3166
3166











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








