模版:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
const int Times = 10;
const int N = 5500;
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL ct, cnt;
LL fac[N], num[N];
LL gcd(LL a, LL b)
{
return b? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
LL multi(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 0;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = (ans + a) % m;
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = (a + a) % m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 1;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = multi(ans, a, m);
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = multi(a, a, m);
}
return ans;
}
bool Miller_Rabin(LL n)
{
if(n == 2) return true;
if(n < 2 || !(n & 1)) return false;
LL m = n - 1;
int k = 0;
while((m & 1) == 0)
{
k++;
m >>= 1;
}
for(int i=0; i<Times; i++)
{
LL a = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL x = quick_mod(a, m, n);
LL y = 0;
for(int j=0; j<k; j++)
{
y = multi(x, x, n);
if(y == 1 && x != 1 && x != n - 1) return false;
x = y;
}
if(y != 1) return false;
}
return true;
}
LL pollard_rho(LL n, LL c)
{
LL i = 1, k = 2;
LL x = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL y = x;
while(true)
{
i++;
x = (multi(x, x, n) + c) % n;
LL d = gcd((y - x + n) % n, n);
if(1 < d && d < n) return d;
if(y == x) return n;
if(i == k)
{
y = x;
k <<= 1;
}
}
}
void find(LL n, int c)
{
if(n == 1) return;
if(Miller_Rabin(n))
{
fac[ct++] = n;
return ;
}
LL p = n;
LL k = c;
while(p >= n) p = pollard_rho(p, c--);
find(p, k);
find(n / p, k);
}
int main()
{
LL n;
while(cin>>n)
{
ct = 0;
find(n, 120);
sort(fac, fac + ct);
num[0] = 1;
int k = 1;
for(int i=1; i<ct; i++)
{
if(fac[i] == fac[i-1])
++num[k-1];
else
{
num[k] = 1;
fac[k++] = fac[i];
}
}
cnt = k;
for(int i=0; i<cnt; i++)
cout<<fac[i]<<"^"<<num[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=2429
题意:给出两个数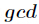
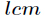
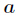
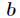
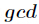
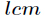
多个,则输出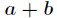
分析:我们可以知道如果把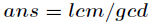
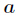
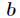
因子的问题,这个由于数据范围太大,用pollard-rho大数分解即可,然后用dfs找因子。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
const int Times = 10;
const LL INF = (LL)1<<61;
const int N = 550;
LL n, m, ct, cnt;
LL mini, mina, minb, ans;
LL fac[N], num[N];
LL gcd(LL a, LL b)
{
return b? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
LL multi(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 0;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = (ans + a) % m;
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = (a + a) % m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 1;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = multi(ans, a, m);
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = multi(a, a, m);
}
return ans;
}
bool Miller_Rabin(LL n)
{
if(n == 2) return true;
if(n < 2 || !(n & 1)) return false;
LL m = n - 1;
int k = 0;
while((m & 1) == 0)
{
k++;
m >>= 1;
}
for(int i=0; i<Times; i++)
{
LL a = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL x = quick_mod(a, m, n);
LL y = 0;
for(int j=0; j<k; j++)
{
y = multi(x, x, n);
if(y == 1 && x != 1 && x != n - 1) return false;
x = y;
}
if(y != 1) return false;
}
return true;
}
LL pollard_rho(LL n, LL c)
{
LL i = 1, k = 2;
LL x = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL y = x;
while(true)
{
i++;
x = (multi(x, x, n) + c) % n;
LL d = gcd((y - x + n) % n, n);
if(1 < d && d < n) return d;
if(y == x) return n;
if(i == k)
{
y = x;
k <<= 1;
}
}
}
void find(LL n, int c)
{
if(n == 1) return;
if(Miller_Rabin(n))
{
fac[ct++] = n;
return ;
}
LL p = n;
LL k = c;
while(p >= n) p = pollard_rho(p, c--);
find(p, k);
find(n / p, k);
}
void dfs(LL dept, LL product = 1)
{
if(dept == cnt)
{
LL a = product;
LL b = ans / a;
if(gcd(a, b) == 1)
{
a *= n;
b *= n;
if(a + b < mini)
{
mini = a + b;
mina = a;
minb = b;
}
}
return ;
}
for(int i=0; i<=num[dept]; i++)
{
if(product > mini) return;
dfs(dept + 1, product);
product *= fac[dept];
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%llu %llu", &n, &m))
{
if(n == m)
{
printf("%llu %llu\n",n,m);
continue;
}
mini = INF;
ct = cnt = 0;
ans = m / n;
find(ans, 120);
sort(fac, fac + ct);
num[0] = 1;
int k = 1;
for(int i=1; i<ct; i++)
{
if(fac[i] == fac[i-1])
++num[k-1];
else
{
num[k] = 1;
fac[k++] = fac[i];
}
}
cnt = k;
dfs(0, 1);
if(mina > minb) swap(mina, minb);
printf("%llu %llu\n",mina, minb);
}
return 0;
}
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4344
题意:给一个数,求这个数的所有因子中组成的最大的一个子集,其中1和它本身除外,使得在这个子集中元素两两
互素,求最大子集的元素个数,并且求出和最大的值。
分析:直接素因子分解,然后每一个素因子的k次方是一个元素,元素个数就是素因子个数。注意如果只有一个素因
子,那么由于不能包含本身,所以多除一个素因子。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
const int Times = 10;
const int N = 5500;
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL ct, cnt;
LL fac[N], num[N];
LL gcd(LL a, LL b)
{
return b? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
LL multi(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 0;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = (ans + a) % m;
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = (a + a) % m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 1;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = multi(ans, a, m);
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = multi(a, a, m);
}
return ans;
}
bool Miller_Rabin(LL n)
{
if(n == 2) return true;
if(n < 2 || !(n & 1)) return false;
LL m = n - 1;
int k = 0;
while((m & 1) == 0)
{
k++;
m >>= 1;
}
for(int i=0; i<Times; i++)
{
LL a = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL x = quick_mod(a, m, n);
LL y = 0;
for(int j=0; j<k; j++)
{
y = multi(x, x, n);
if(y == 1 && x != 1 && x != n - 1) return false;
x = y;
}
if(y != 1) return false;
}
return true;
}
LL pollard_rho(LL n, LL c)
{
LL i = 1, k = 2;
LL x = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL y = x;
while(true)
{
i++;
x = (multi(x, x, n) + c) % n;
LL d = gcd((y - x + n) % n, n);
if(1 < d && d < n) return d;
if(y == x) return n;
if(i == k)
{
y = x;
k <<= 1;
}
}
}
void find(LL n, int c)
{
if(n == 1) return;
if(Miller_Rabin(n))
{
fac[ct++] = n;
return ;
}
LL p = n;
LL k = c;
while(p >= n) p = pollard_rho(p, c--);
find(p, k);
find(n / p, k);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
LL n;
scanf("%I64d",&n);
ct = 0;
find(n, 120);
sort(fac, fac + ct);
num[0] = 1;
int k = 1;
for(int i=1; i<ct; i++)
{
if(fac[i] == fac[i-1])
++num[k-1];
else
{
num[k] = 1;
fac[k++] = fac[i];
}
}
cnt = k;
LL ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
{
LL t = 1;
for(int j=0;j<num[i];j++)
t *= fac[i];
ans += t;
}
if(cnt == 1) ans /= fac[0];
printf("%I64d %I64d\n", cnt, ans);
}
return 0;
}
题目:http://icpc.njust.edu.cn/Problem/Local/1722/
题意:给定一个数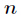
其中对任意的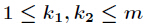
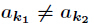
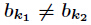
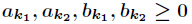
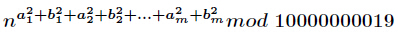
分析:当然是素因子分解了,然后注意乘法要改为二分形式,因为10000000019很大。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
const LL Times = 10;
const LL N = 555;
const LL MOD = 10000000018;
LL ct, cnt, c, n;
LL fac[N], num[N];
LL arr[N];
LL gcd(LL a, LL b)
{
return b? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
LL multi(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 0;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = (ans + a) % m;
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = (a + a) % m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 1;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = multi(ans, a, m);
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = multi(a, a, m);
}
return ans;
}
bool Miller_Rabin(LL n)
{
if(n == 2) return true;
if(n < 2 || !(n & 1)) return false;
LL m = n - 1;
int k = 0;
while((m & 1) == 0)
{
k++;
m >>= 1;
}
for(int i=0; i<Times; i++)
{
LL a = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL x = quick_mod(a, m, n);
LL y = 0;
for(int j=0; j<k; j++)
{
y = multi(x, x, n);
if(y == 1 && x != 1 && x != n - 1) return false;
x = y;
}
if(y != 1) return false;
}
return true;
}
LL pollard_rho(LL n, LL c)
{
LL i = 1, k = 2;
LL x = rand() % (n - 1) + 1;
LL y = x;
while(true)
{
i++;
x = (multi(x, x, n) + c) % n;
LL d = gcd((y - x + n) % n, n);
if(1 < d && d < n) return d;
if(y == x) return n;
if(i == k)
{
y = x;
k <<= 1;
}
}
}
void find(LL n, int c)
{
if(n == 1) return;
if(Miller_Rabin(n))
{
fac[ct++] = n;
return ;
}
LL p = n;
LL k = c;
while(p >= n) p = pollard_rho(p, c--);
find(p, k);
find(n / p, k);
}
void dfs(int dept, LL product = 1)
{
if(dept == cnt)
{
if(product <= (LL)sqrt(1.0*n) && (product + n / product) % 2 == 0 && (n / product - product)% 2 == 0)
arr[c++] = product;
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<=num[dept]; i++)
{
dfs(dept + 1, product);
product *= fac[dept];
}
}
int main()
{
int T, tt = 1;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>n;
printf("Case %d: ",tt++);
if(n == 1)
{
puts("1");
continue;
}
ct = c = 0;
find(n, 120);
sort(fac, fac + ct);
num[0] = 1;
LL k = 1;
for(int i=1; i<ct; i++)
{
if(fac[i] == fac[i-1])
++num[k-1];
else
{
num[k] = 1;
fac[k++] = fac[i];
}
}
cnt = k;
dfs(0, 1);
sort(arr, arr + c);
LL ans = 0;
for(int i=0; i<c; i++)
{
LL x = (n / arr[i] + arr[i]) / 2;
LL y = (n / arr[i] - arr[i]) / 2;
ans += multi(x, x, MOD) + multi(y, y, MOD);
ans %= MOD;
}
if(c > 0) cout<<quick_mod(n, ans, MOD + 1)<<endl;
else puts("-1");
}
return 0;
}





 本文通过几个具体的编程竞赛题目,详细介绍了素因子分解算法及其在解决特定数学问题中的应用,包括大数分解、求解互素子集等问题。
本文通过几个具体的编程竞赛题目,详细介绍了素因子分解算法及其在解决特定数学问题中的应用,包括大数分解、求解互素子集等问题。
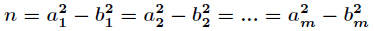
















 9969
9969

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








