- 一 android基本架构
- 二 android dialog
- 三 图片
- 四 开启通知栏权限
- 五 android60程序在运行时申请权限
- 六 获取项目参数
- 七 Android四大启动模式
- 八 android中的dppx深度解析
- 九 时间相关
- 十 截屏监听OcrService
- 十一 android在Service中弹出提示
- 十二 android性能优化
- 十三 Android 判断是开发debug模式还是发布release模式
- 十四 暂停1s
- 十五 部分Android手机拍照后照片被旋转的解决方案
- 十六 Android中显示照片的Exif信息
- 十七 Activity继承自 androidsupportv7appAppCompatActivity而不是 androidappActivity时要注意的事
- 十八 用Base64加密数据解决json传输数据中特殊字符问题
- 十九 Json
- 二十 浅谈Android XML中的tools属性
- 二十一 android 项目Gradle配置
- 二十二 android方法
- 二十三 java继承作用
- 二十四 EditText总结
- 二十五 TextView
- 二十六 遍历 Map
- 二十七 bugly渠道
一 android基本架构
1.1 架构图直观
下面这张图展示了Android系统的主要组成部分:
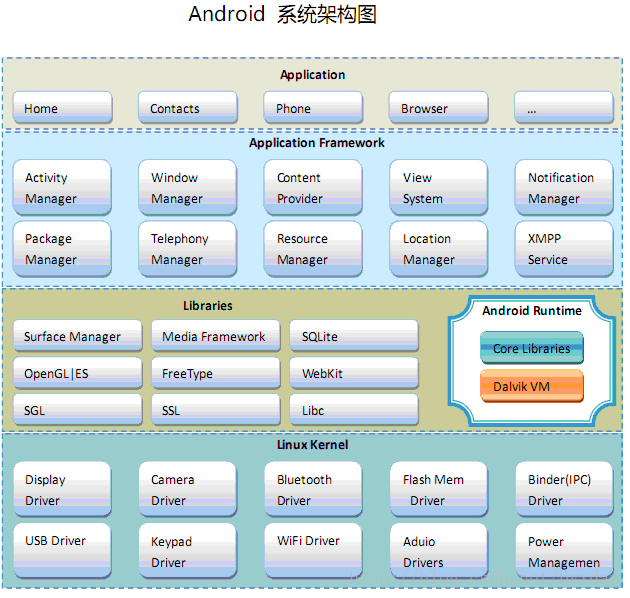
可以很明显看出,Android系统架构由5部分组成,分别是:Linux Kernel、Android Runtime、Libraries、Application Framework、Applications。第二部分将详细介绍这5个部分。
1.2 架构详解
现在我们拿起手术刀来剖析各个部分。其实这部分SDK文档已经帮我们做得很好了,我们要做的就是拿来主义,然后再加上自己理解。下面自底向上分析各层。
1.2.1 Linux Kernel
Android基于Linux 2.6提供核心系统服务,例如:安全、内存管理、进程管理、网络堆栈、驱动模型。Linux Kernel也作为硬件和软件之间的抽象层,它隐藏具体硬件细节而为上层提供统一的服务。
如果你学过计算机网络知道OSI/RM,就会知道分层的好处就是使用下层提供的服务而为上层提供统一的服务,屏蔽本层及以下层的差异,当本层及以下层发生了变化不会影响到上层。也就是说各层各司其职,各层提供固定的SAP(Service Access Point),专业点可以说是高内聚、低耦合。
如果你只是做应用开发,就不需要深入了解Linux Kernel层。
1.2.2 Android Runtime
Android包含一个核心库的集合,提供大部分在Java编程语言核心类库中可用的功能。每一个Android应用程序是Dalvik虚拟机中的实例,运行在他们自己的进程中。Dalvik虚拟机设计成,在一个设备可以高效地运行多个虚拟机。Dalvik虚拟机可执行文件格式是.dex,dex格式是专为Dalvik设计的一种压缩格式,适合内存和处理器速度有限的系统。
大多数虚拟机包括JVM都是基于栈的,而Dalvik虚拟机则是基于寄存器的。两种架构各有优劣,一般而言,基于栈的机器需要更多指令,而基于寄存器的机器指令更大。dx 是一套工具,可以將 Java .class 转换成 .dex 格式。一个dex文件通常会有多个.class。由于dex有時必须进行最佳化,会使文件大小增加1-4倍,以ODEX结尾。
Dalvik虚拟机依赖于Linux 内核提供基本功能,如线程和底层内存管理。
1.2.3 Libraries
Android包含一个C/C++库的集合,供Android系统的各个组件使用。这些功能通过Android的应用程序框架(application framework)暴露给开发者。下面列出一些核心库:
- 系统C库——标准C系统库(libc)的BSD衍生,调整为基于嵌入式Linux设备
- 媒体库——基于PacketVideo的OpenCORE。这些库支持播放和录制许多流行的音频和视频格式,以及静态图像文件,包括MPEG4、 H.264、 MP3、 AAC、 AMR、JPG、 PNG
- 界面管理——管理访问显示子系统和无缝组合多个应用程序的二维和三维图形层
- LibWebCore——新式的Web浏览器引擎,驱动Android 浏览器和内嵌的web视图
- SGL——基本的2D图形引擎
- 3D库——基于OpenGL ES 1.0 APIs的实现。库使用硬件3D加速或包含高度优化的3D软件光栅
- FreeType ——位图和矢量字体渲染
- SQLite ——所有应用程序都可以使用的强大而轻量级的关系数据库引擎
1.2.4 Application Framework
通过提供开放的开发平台,Android使开发者能够编制极其丰富和新颖的应用程序。开发者可以自由地利用设备硬件优势、访问位置信息、运行后台服务、设置闹钟、向状态栏添加通知等等,很多很多。
开发者可以完全使用核心应用程序所使用的框架APIs。应用程序的体系结构旨在简化组件的重用,任何应用程序都能发布他的功能且任何其他应用程序可以使用这些功能(需要服从框架执行的安全限制)。这一机制允许用户替换组件。
所有的应用程序其实是一组服务和系统,包括:
- 视图(View)——丰富的、可扩展的视图集合,可用于构建一个应用程序。包括包括列表、网格、文本框、按钮,甚至是内嵌的网页浏览器
- 内容提供者(Content Providers)——使应用程序能访问其他应用程序(如通讯录)的数据,或共享自己的数据
- 资源管理器(Resource Manager)——提供访问非代码资源,如本地化字符串、图形和布局文件
- 通知管理器(Notification Manager)——使所有的应用程序能够在状态栏显示自定义警告
- 活动管理器(Activity Manager)——管理应用程序生命周期,提供通用的导航回退功能
1.2.5 Applications
Android装配一个核心应用程序集合,包括电子邮件客户端、SMS程序、日历、地图、浏览器、联系人和其他设置。所有应用程序都是用Java编程语言写的。更加丰富的应用程序有待我们去开发!
1.3 总结
从上面我们知道Android的架构是分层的,非常清晰,分工很明确。Android本身是一套软件堆叠(Software Stack),或称为「软件叠层架构」,叠层主要分成三层:操作系统、中间件、应用程序。从上面我们也看到了开源的力量,一个个熟悉的开源软件在这里贡献了自己的一份力量。
二 android dialog
public void showBluetoothCheckDialog(final Context context) {
dialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(context).create();// 创建一个AlertDialog对象
viewReconnectBluetooth = ((Activity) context).getLayoutInflater()
.inflate(R.layout.dialog_confirm_bluetooth, null);// 自定义布局
messagetext = (TextView) viewReconnectBluetooth.findViewById(R.id.message);
dialog.setCancelable(false);// dialog弹出后会点击屏幕或物理返回键,dialog不消失
messagetext.setText("当前是蓝牙模式,但是蓝牙设备已断开连接,请选择操作。");
View reconnect = viewReconnectBluetooth.findViewById(R.id.reconnect);
reconnect.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context,
DeviceListActivity.class);
context.startActivity(intent);
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
View cancel = viewReconnectBluetooth.findViewById(R.id.cancel);
cancel.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// nothing to do
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
View shutdown = viewReconnectBluetooth.findViewById(R.id.shutdown);
shutdown.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// Auto-generated method stub
Util.savePreferences(Constants.BLUE_TOOTH, 0, context);
bluetoothAdapter.disable();
app.setVersion(app.getVersion() + 1);
dialog.dismiss();
Toast.makeText(context, "蓝牙模式已关闭", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
dialog.setView(viewReconnectBluetooth, 0, 0, 0, 0);// 把自定义的布局设置到dialog中,注意,布局设置一定要在show之前。从第二个参数分别填充内容与边框之间左、上、右、下、的像素
// Service&Application弹出对话框或WindowManager添加view时,要设置window type为TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT
dialog.getWindow().setType(WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT);
dialog.show();// 一定要先show出来再设置dialog的参数,不然就不会改变dialog的大小了
}三 图片
3.1 使用 MediaStore.Images.Media.getBitmap从Uri中获得bitmap以及其缺陷与优化
MediaStore.Images.Media.getBitmap(ContentResolver cr,Uri url)方法可以从一个已知的图片Uri中获得图片的bitmap对象,其中ContentResolver通常可以通过在Activity中调用的getContentResolver()方法中获取。Uri地址就是类似 content://media/external/images/media/2 的地址,也就是Content Provider定义的地址形式。但是这种获取bitmap的方式在图片较大的时候并不可取。为什么呢?
从getBitmap的参数可以看出,我们没有传递所要得到的bitmap大小信息,那么getBitmap的返回的bitmap究竟有多大我们就无从知晓,完全取决于getBitmap本身,最乐观的结果是getBitmap能智能的判断我们的需求,返回一个合适的bitmap,但是可能性很小。到底getBitmap中做了什么还是直接去看他的实现源码吧:
android.provider.MediaStore中找到Images.Media的getBitmap方法:
public static final Bitmap getBitmap(ContentResolver cr, Uri url)
throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
InputStream input = cr.openInputStream(url);
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(input);
input.close();
return bitmap;
}其实它很简单很粗暴,返回的是原始大小的bitmap。
MediaStore.Images.Media自身的getBitmap不是很可靠。那我们来自定义一个getBitmap吧:
取名叫getThumbnail,他能返回一个指定大小的bitmap:
public static Bitmap getThumbnail(Uri uri,int size) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{
InputStream input = this.getContentResolver().openInputStream(uri);
BitmapFactory.Options onlyBoundsOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();
onlyBoundsOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
onlyBoundsOptions.inDither=true;//optional
onlyBoundsOptions.inPreferredConfig=Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888;//optional
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(input, null, onlyBoundsOptions);
input.close();
if ((onlyBoundsOptions.outWidth == -1) || (onlyBoundsOptions.outHeight == -1))
return null;
int originalSize = (onlyBoundsOptions.outHeight > onlyBoundsOptions.outWidth) ? onlyBoundsOptions.outHeight : onlyBoundsOptions.outWidth;
double ratio = (originalSize > size) ? (originalSize / size) : 1.0;
BitmapFactory.Options bitmapOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();
bitmapOptions.inSampleSize = getPowerOfTwoForSampleRatio(ratio);
bitmapOptions.inDither=true;//optional
bitmapOptions.inPreferredConfig=Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888;//optional
input = this.getContentResolver().openInputStream(uri);
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(input, null, bitmapOptions);
input.close();
return bitmap;
}
private static int getPowerOfTwoForSampleRatio(double ratio){
int k = Integer.highestOneBit((int)Math.floor(ratio));
if(k==0) return 1;
else return k;
}3.2 uri,file,path互转
3.2.1 uri转path
private String getPath(Uri uri) {
String[] projection = {MediaStore.Video.Media.DATA};
Cursor cursor = managedQuery(uri, projection, null, null, null);
int column_index = cursor
.getColumnIndexOrThrow(MediaStore.Audio.Media.DATA);
cursor.moveToFirst();
return cursor.getString(column_index);
} 3.2.2 path转uri
Uri uri = Uri.parse(path);3.2.3 file转path
String path = file.getPath()3.2.4 path转file
File file = new File(path) 3.3 Bitmap、file互转(Bitmap转file即保存图片到本地),Bitmap、Uri互转,Bitmap、path互转
3.3.1 Bitmap转file即保存图片到本地
3.3.1.1 Bitmap转file
/**
* 将图片Bitmap保存到本地返回File
* @param bmp
*/
public File saveBmpToFile(Bitmap bmp) {
// 将图片保存到本地时进行压缩开始时间
Log.v("TakePhoteActivity.this","将图片保存到本地时进行压缩开始时间"+getTime());
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int options = 100;
bmp.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, options, baos);
// 系统时间
long dateTaken = System.currentTimeMillis();
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH.mm.ss.SSS");
String formatStr =formatter.format(dateTaken);
// 图像名称
String filename = formatStr + ".JPEG";
File parent =new File(PATH);
if (!parent.exists()) {
parent.mkdirs();
}
File file = new File(PATH, filename);
if(file.exists()){
file.delete();
}
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(baos.toByteArray());
fos.flush();
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return file;
}
3.3.1.2 Bitmap转file即保存图片到本地,并将图片信息添加入媒体数据库
3.3.1.2.1算法定义
/**
* 存储图像并将信息添加入媒体数据库
*/
private Uri insertImage(ContentResolver cr, String name, long dateTaken,
String directory, String filename, Bitmap source, byte[] jpegData) {
OutputStream outputStream = null;
String filePath = directory + filename;
try {
File dir = new File(directory);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
File file = new File(directory, filename);
if (file.createNewFile()) {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
if (source != null) {








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 2163
2163











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








