买了大神关爱民与何红辉所著书籍《设计模式解析与实战》,观后有所感、有所悟。
单例模式之饿汉式:
public class Person {
/**
* 在课堂上不同身份的人说不通的话
*/
public void say(){
}
}定义教导主任:
public class Director extends Person {
private static final Director mDirector=new Director();
public static Director getDirector(){
return mDirector;
}
@Override
public void say() {
super.say();
System.out.println("Director:"+"准备开始上课吧");
}
}
定义上课老师:
public class Teacher extends Person {
@Override
public void say() {
super.say();
System.out.println("Teacher:"+"Stand up");
}
}
定义上课学生:
public class Student extends Person {
@Override
public void say() {
super.say();
System.out.println("Student:"+"老师好");
}
}
定义学校:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class School {
private ArrayList<Person> mPersonList=new ArrayList<>();
public void addPerson(Person mPerson){
mPersonList.add(mPerson);
}
public void showEveryOneSay(){
for(Person mPerson:mPersonList){
mPerson.say();
}
}
}下面是测试代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
School mSchool =new School();
mSchool.addPerson(new Director());
mSchool.addPerson(new Teacher());
mSchool.addPerson(new Student());
mSchool.addPerson(new Student());
mSchool.showEveryOneSay();
}
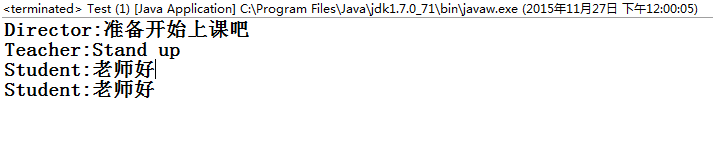
}测试输出结果:
单例模式之懒汉式(synchronized 保证单例对象的唯一性):
public class Person {
private static Person instance;
public Person() {
}
public static synchronized Person getInstance(){
if(instance==null){
instance=new Person();
}
return instance;
}
}
DCL 实现单例,DCL的闪光点在getInstance方法上,两次判断为空,具体原因想知道更多详情请购买《设计模式解析与实战》自行了解吧,打字麻烦!!当然如果你耐不住性子可以通过以下博客内容找到答案:http://blog.csdn.net/liguangzhenghi/article/details/8076361(个人最喜欢用的方式):
public class Person {
private static Person instance;
public Person() {
}
public static Person getInstance(){
if(instance==null){
synchronized (Person.class) {
if(instance==null){
instance=new Person();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
}DCL优点:资源利用率高,缺点:第一次加载稍慢(基本可以忽略)。下面是静态内部类单例模式:
public class Person {
public Person() {
}
public static Person getInstance(){
return SingleHolder.instance;
}
private static class SingleHolder{
private static final Person instance=new Person();
}
}
枚举单列(与其他单例模式不同,在反序列时不会重新new ):
public enum PersonEnum {
student,teacher,director;
public void say(){
}
}通过容器实现单例(下面是对象为例的):
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PersonManager {
private static Map<String ,Object> map=new HashMap<String, Object>();
public PersonManager() {
}
public static <T> T putPersonService(T t){
map.put(t.getClass().getName(),t);
return t;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T getPersonService(T t){
t=(T)map.get(t.getClass().getName());
return t;
}
}再补充一个特别的单例(Application,每个应用都有一个Application,应用启动就会创建,会调用onCreate方法,此时可以给instance赋值):
import android.app.Application;
public class MyApplication extends Application{
public static MyApplication instance;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
instance=this;
}
}
<application
android:name="com.example.MyApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >在android 源码中的运用例举如下:
WindowManager manager=(WindowManager)getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);而Context.WINDOW_SERVICE只是在常量类Context里面定义的键:
/**
* Use with {@link #getSystemService} to retrieve a
* {@link android.view.WindowManager} for accessing the system's window
* manager.
*
* @see #getSystemService
* @see android.view.WindowManager
*/
public static final String WINDOW_SERVICE = "window";继续跟进Activity..
@Override
public Object getSystemService(@ServiceName @NonNull String name) {
if (getBaseContext() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"System services not available to Activities before onCreate()");
}
if (WINDOW_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
return mWindowManager;
} else if (SEARCH_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
ensureSearchManager();
return mSearchManager;
}
return super.getSystemService(name);
}
Activity继承ContextThemeWrapper,这里调用父类getSystemService,继续跟进..
@Override public Object getSystemService(String name) {
if (LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
if (mInflater == null) {
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(getBaseContext()).cloneInContext(this);
}
return mInflater;
}
return getBaseContext().getSystemService(name);
}
不断然而还没看到我想看的,只看到了一个抽象的Context对象,根据何红辉大神说的,我从Activity的ActivityThread入手(Activity的入口是ActivityThread的main函数):
public static void main(String[] args) {
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}创建ActivityThread后调用attach函数传入参数fasle(非系统应用),会通过Binder机制与ActivityManagerService通信,最终调用performLaunchActivity,然后调用createBaseContextForActivity方法:
private Context createBaseContextForActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, final Activity activity) {
int displayId = Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY;
try {
displayId = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().getActivityDisplayId(r.token);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createActivityContext(
this, r.packageInfo, displayId, r.overrideConfig);
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
Context baseContext = appContext;
.....................此处略...................
}
上面代码分析到Context实现类ContextImpl,Eclipse开发可能没法继续跟进了,android.jar里面也找不到,这时候需要https://github.com/android这里面去找源码了(framework层),换了Android Studio继续跟踪到了ContextImpl实现类,发现 ServiceManager.getService(key)方法的,没法跟进ServiceManager,只好github上https://github.com/android/platform_frameworks_base/blob/master/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java继续跟踪:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package android.os;
import com.android.internal.os.BinderInternal;
import android.util.Log;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/** @hide */
public final class ServiceManager {
private static final String TAG = "ServiceManager";
private static IServiceManager sServiceManager;
private static HashMap<String, IBinder> sCache = new HashMap<String, IBinder>();
private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;
}
// Find the service manager
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative.asInterface(BinderInternal.getContextObject());
return sServiceManager;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name.
*
* @param name the name of the service to get
* @return a reference to the service, or <code>null</code> if the service doesn't exist
*/
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
return getIServiceManager().getService(name);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Place a new @a service called @a name into the service
* manager.
*
* @param name the name of the new service
* @param service the service object
*/
public static void addService(String name, IBinder service) {
try {
getIServiceManager().addService(name, service, false);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in addService", e);
}
}
/**
* Place a new @a service called @a name into the service
* manager.
*
* @param name the name of the new service
* @param service the service object
* @param allowIsolated set to true to allow isolated sandboxed processes
* to access this service
*/
public static void addService(String name, IBinder service, boolean allowIsolated) {
try {
getIServiceManager().addService(name, service, allowIsolated);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in addService", e);
}
}
/**
* Retrieve an existing service called @a name from the
* service manager. Non-blocking.
*/
public static IBinder checkService(String name) {
try {
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
return getIServiceManager().checkService(name);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in checkService", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* Return a list of all currently running services.
*/
public static String[] listServices() throws RemoteException {
try {
return getIServiceManager().listServices();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in listServices", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* This is only intended to be called when the process is first being brought
* up and bound by the activity manager. There is only one thread in the process
* at that time, so no locking is done.
*
* @param cache the cache of service references
* @hide
*/
public static void initServiceCache(Map<String, IBinder> cache) {
if (sCache.size() != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("setServiceCache may only be called once");
}
sCache.putAll(cache);
}
}折腾这么久最后还是找到了想要的源码中单例模式的实战,继续拜读大神著作!!




















 288
288











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








