Authors
Kaiming He Xiangyu Zhang Shaoqing Ren Jian Sun
Abstract
Residual Networks are easier to optimize and gain accuracy from considerably increased depth, but it have lower complexity than VGGnets.
1 Introduction
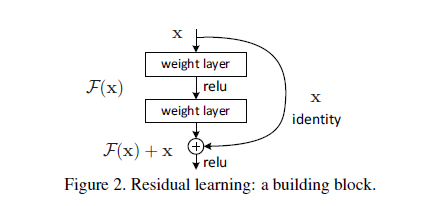
We denote the desired underlying mapping as H(x)=F(x)+x, We hypothesize that it is easier to optimize the residual mapping than to optimize original, unreferenced mapping. To the extreme, if an identity mapping were optimal, it would be easier to push the residual to zero than to fit an identity mapping by a stack of nonlinear layers.
2 relate work
2.1 Residual representation
F. Perronnin and C. Dance. Fisher kernels on visual vocabularies for
image categorization. In CVPR, 2007.
H. Jegou, F. Perronnin, M. Douze, J. Sanchez, P. Perez, and
C. Schmid. Aggregating local image descriptors into compact codes.
TPAMI, 2012.
W. L. Briggs, S. F. McCormick, et al. A Multigrid Tutorial. Siam,
2000.2.2 shortcut connections
#highway
R. K. Srivastava, K. Greff, and J. Schmidhuber. Highway networks.
arXiv:1505.00387, 2015
R. K. Srivastava, K. Greff, and J. Schmidhuber. Training very deep
networks. 1507.06228, 2015.
#LSTM
S. Hochreiter and J. Schmidhuber. Long short-term memory. Neural
computation, 9(8):1735–1780, 19973 Deep residual learning
3.1 residual learning
The degradation problem suggests that the solver might have difficults in approximating identity mappings by multiple layers.
3.2 Identity Mapping by Shortcuts
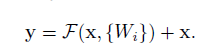
we can perform a linear projection by the shortcut connetions to match the dimensions.
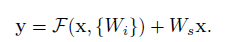
In this exprements, the F has 2-3 layers , but cannot only 1 layer, that will similar to a linear year.
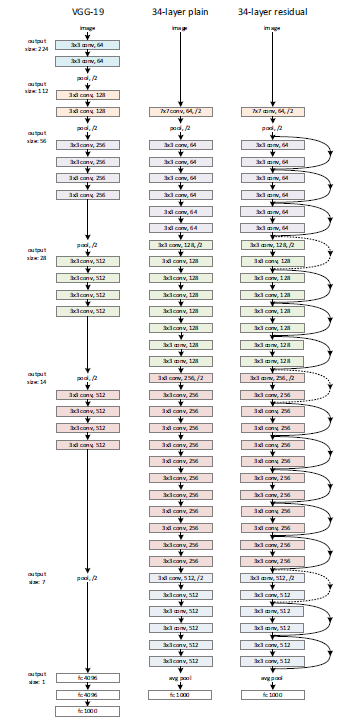
Plain Network The convolutional layer mostly have 3x3 filters and follow two simple design rules:1) for the same output feature map size, the layers have the same number of filters;2) if the feature map size is halved, the number of filters is doubled so as to preserve the time complexity per layer.
Residual Network: when the dimensions increase(dotted line shortcuts), there are two options:1) zeros pads for increaseing dimensions 2)1x1 convolutions(slightly better)
4 Experments
BN ensures forward propagated signals to have non-zero variances.
S. Ioffe and C. Szegedy. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep
network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In ICML, 2015ResNet eases the optimization by providing faster convergence at the early stage.
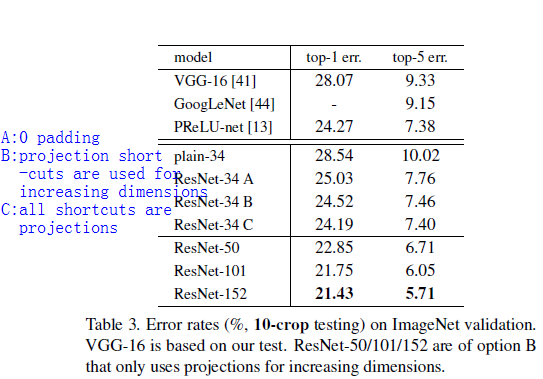
shortcut : identity or projection?
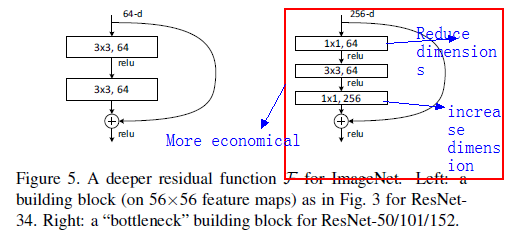
deep bottleneck architectures
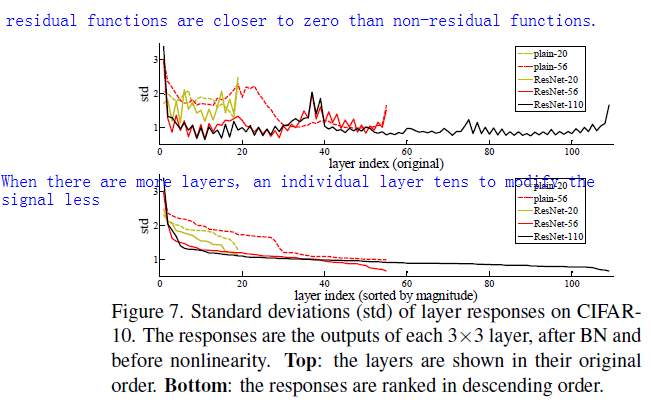
Analysis of layer responses
Object detection Improvement
box refinement:
S. Gidaris and N. Komodakis. Object detection via a multi-region &
semantic segmentation-aware cnn model. In ICCV, 2015.global context:
RoI–add a global feature SPP






















 1030
1030

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








