一.EventBus概述
1.EventBus的三要素
EventBus有三个主要的元素需要我们先了解一下:
Event:事件,可以是任意类型的对象。
Subscriber:事件订阅者,在EventBus3.0之前消息处理的方法只能限定于onEvent、onEventMainThread、onEventBackgroundThread和onEventAsync,他们分别代表四种线程模型。而在EventBus3.0之后,事件处理的方法可以随便取名,但是需要添加一个注解@Subscribe,并且要指定线程模型(默认为POSTING),四种线程模型下面会讲到。
Publisher:事件发布者,可以在任意线程任意位置发送事件,直接调用EventBus的post(Object)方法。可以自己实例化EventBus对象,但一般使用EventBus.getDefault()就好了,根据post函数参数的类型,会自动调用订阅相应类型事件的函数。
2.EventBus的四种ThreadMode(线程模型)
EventBus3.0有以下四种ThreadMode:
POSTING(默认):如果使用事件处理函数指定了线程模型为POSTING,那么该事件在哪个线程发布出来的,事件处理函数就会在这个线程中运行,也就是说发布事件和接收事件在同一个线程。在线程模型为POSTING的事件处理函数中尽量避免执行耗时操作,因为它会阻塞事件的传递,甚至有可能会引起ANR。
MAIN:
事件的处理会在UI线程中执行。事件处理时间不能太长,长了会ANR的。
BACKGROUND:如果事件是在UI线程中发布出来的,那么该事件处理函数就会在新的线程中运行,如果事件本来就是子线程中发布出来的,那么该事件处理函数直接在发布事件的线程中执行。在此事件处理函数中禁止进行UI更新操作。
ASYNC:无论事件在哪个线程发布,该事件处理函数都会在新建的子线程中执行,同样,此事件处理函数中禁止进行UI更新操作。
二.EventBus的基本用法
1.自定义一个事件类(相当于我们平常所用的bean类)
public class MessageEvent {
...
}2.在需要订阅的地方注册
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);3.发送事件
第一种.普通事件
EventBus.getDefault().post(messageEvent);
第二种.粘性事件
EventBus.getDefault().postSticky(messageEvent);4.处理事件(eg.刷新UI)
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN)
public void XXX(MessageEvent messageEvent) {
...
}5.取消事件订阅
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
super.onDestroy();
}三.EventBus的实际应用(模拟登陆传值)
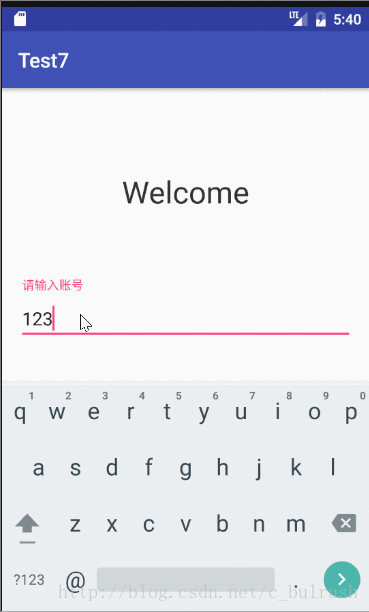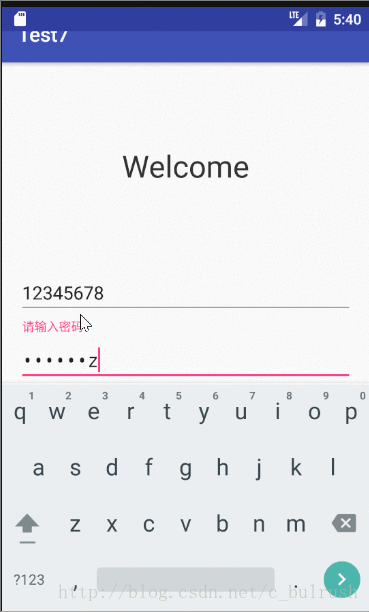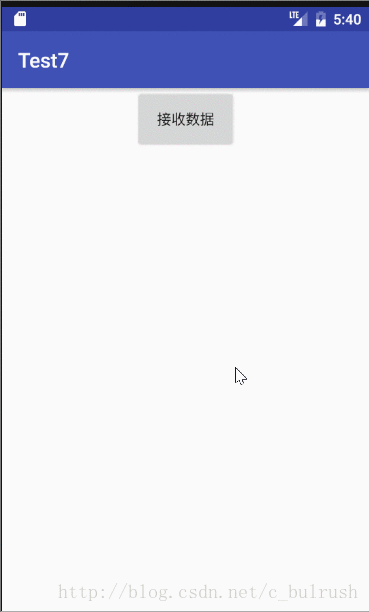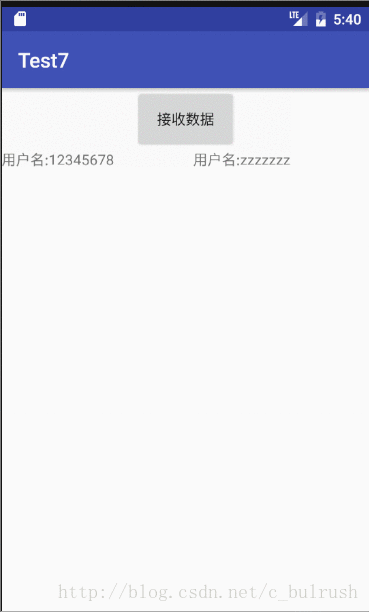
1.导入3.0依赖
compile 'org.greenrobot:eventbus:3.0.0'2.定义消息事件类
public class MessageEvent {
public final String uname;
public final String upass;
public MessageEvent(String name,String pass) {
this.uname = name;
this.upass = pass;
}
}3.发送事件(粘性事件)
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private String username;
private String password;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final TextInputLayout usernameWrapper = (TextInputLayout) findViewById(R.id.usernameWrapper);
final TextInputLayout passwordWrapper = (TextInputLayout) findViewById(R.id.passwordWrapper);
Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn);
usernameWrapper.setHint("请输入账号");
passwordWrapper.setHint("请输入密码");
//点击事件
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
hideKeyboard();
username = usernameWrapper.getEditText().getText().toString();
password = passwordWrapper.getEditText().getText().toString();
if (!validateEmail(username)) {
usernameWrapper.setError("Not a valid email address!");
} else if (!validatePassword(password)) {
passwordWrapper.setError("Not a valid password!");
} else {
usernameWrapper.setErrorEnabled(false);
passwordWrapper.setErrorEnabled(false);
//发送粘性事件//
EventBus.getDefault().postSticky(new MessageEvent(username,password));
startActivity(new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class));
}
}
});
}
private void hideKeyboard() {
View view = getCurrentFocus();
if (view != null) {
((InputMethodManager) getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE)).
hideSoftInputFromWindow(view.getWindowToken(), InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS);
}
}
//邮箱验证
public boolean validateEmail(String email) {
return email.length() > 5;
}
// 密码验证
public boolean validatePassword(String password) {
return password.length() > 5;
}
}4.注册和取消订阅事件
public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView name,pass;
private Button button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_second);
name= (TextView) findViewById(R.id.uname);
pass= (TextView) findViewById(R.id.upass);
button= (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
//注册EventBus
EventBus.getDefault().register(SecondActivity.this);
}
});
}
//事件订阅者处理事件
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.POSTING,sticky = true)
public void onUserEvent(MessageEvent event) {
name.setText("用户名:" + event.uname);
pass.setText("用户名:" + event.upass);
}
//取消注册
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
super.onDestroy();
}
}
布局
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Welcome"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:textColor="#333333"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:orientation="vertical">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/usernameWrapper"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/username"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress"
android:hint="Username"/>
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/passwordWrapper"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/usernameWrapper"
android:layout_marginTop="4dp">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:hint="Password"/>
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_marginTop="4dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Login"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
activity_second.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_second"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:gravity="center">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="接收数据" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/uname"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/upass"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>




















 922
922











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








