gson可能大部分程序员都不熟悉,简言之就是一个json工具,可实现对象和json字符串之间的转换;有人可能会说了用json-lib就可以了啊,之前我也是用json-lib的但是总是觉得很麻烦,生成json还OK但是解析就要费九牛二虎之力了,权衡之下还是选择使用gson.这次就使用gson配合百度API来实现天气预报的查询功能。
一 gson的下载地址
Gson是Google提供的用于在Java对象和JSON字符串之间进行转换的Java类库。
下载地址1:https://code.google.com/p/google-gson/downloads/list
下载地址2:http://download.csdn.net/detail/lyq8479/8451103
二 代码实现
1 先来体验下gson的简单使用
先搞个pojo类:
package org.lxh;
public class UserInfo {
private String name;
private String address;
private String email;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
接下来直接上测试类:
package org.lxh;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class UseGson {
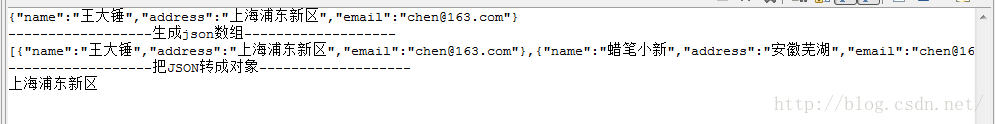
public static void main(String args[]){
UserInfo u1=new UserInfo();
u1.setAddress("上海浦东新区");
u1.setEmail("chen@163.com");
u1.setName("王大锤");
Gson gson=new Gson();
String jsonStr=gson.toJson(u1);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
UserInfo u2=new UserInfo();
u2.setAddress("安徽芜湖");
u2.setEmail("chen@163.com");
u2.setName("蜡笔小新");
List<UserInfo> all=new ArrayList<UserInfo>();
all.add(u1);
all.add(u2);
String jsonArrStr=gson.toJson(all);
System.out.println("------------------生成json数组-------------------");
System.out.println(jsonArrStr);
System.out.println("------------------把JSON转成对象-------------------");
List<UserInfo> obj=gson.fromJson(jsonArrStr, new TypeToken<List<UserInfo>>(){}.getType());
System.out.println(obj.get(0).getAddress());
}
}
来看下运行效果:
2 封装天气预报工具类
百度API地址:http://developer.baidu.com/map/index.php?title=car/api/weather
使用之前要先注册个开发者账号,之后创建应用就能得到ak了,这些操作就自己搞了,你们都懂的。
(1)封装WeatherData类
package org.lxh;
public class WeatherData {
private String date;
private String weather;
private String dayPictureUrl;
private String nightPictureUrl;
private String wind;
private String temperature;
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getDayPictureUrl() {
return dayPictureUrl;
}
public void setDayPictureUrl(String dayPictureUrl) {
this.dayPictureUrl = dayPictureUrl;
}
public String getNightPictureUrl() {
return nightPictureUrl;
}
public void setNightPictureUrl(String nightPictureUrl) {
this.nightPictureUrl = nightPictureUrl;
}
public String getWind() {
return wind;
}
public void setWind(String wind) {
this.wind = wind;
}
public String getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(String temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public String getWeather() {
return weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
}
(2)封装WeatherResult
package org.lxh;
import java.util.List;
public class WeatherResult {
private String currentCity;
private String pm25;
private List<WeatherData> weather_data;
public String getCurrentCity() {
return currentCity;
}
public void setCurrentCity(String currentCity) {
this.currentCity = currentCity;
}
public String getPm25() {
return pm25;
}
public void setPm25(String pm25) {
this.pm25 = pm25;
}
public List<WeatherData> getWeather_data() {
return weather_data;
}
public void setWeather_data(List<WeatherData> weatherData) {
weather_data = weatherData;
}
}
(3)封装WeatherResp
package org.lxh;
import java.util.List;
public class WeatherResp {
private int error;
private String status;
private String date;
private List<WeatherResult> results;
public int getError() {
return error;
}
public void setError(int error) {
this.error = error;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public List<WeatherResult> getResults() {
return results;
}
public void setResults(List<WeatherResult> results) {
this.results = results;
}
}
(4)HttpURLConnection操作工具类
package org.lxh;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ConnectException;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class CommonUtil {
public static String httpRequest(String requestUrl, String requestMethod, String outputStr) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
try {
URL url = new URL(requestUrl);
HttpURLConnection httpUrlConn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
httpUrlConn.setDoOutput(true);
httpUrlConn.setDoInput(true);
httpUrlConn.setUseCaches(false);
// 设置请求方式(GET/POST)
httpUrlConn.setRequestMethod(requestMethod);
httpUrlConn.connect();
// 当有数据需要提交时
if (null != outputStr) {
OutputStream outputStream = httpUrlConn.getOutputStream();
// 注意编码格式,防止中文乱码
outputStream.write(outputStr.getBytes("UTF-8"));
outputStream.close();
}
// 将返回的输入流转换成字符串
InputStream inputStream = httpUrlConn.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "utf-8");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String str = null;
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
buffer.append(str);
}
bufferedReader.close();
inputStreamReader.close();
// 释放资源
inputStream.close();
inputStream = null;
} catch (ConnectException ce) {
ce.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return buffer.toString();
}
}
(5)天气预报获取工具类
package org.lxh;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class WeatherUtil {
public static String getWeatherResult(String cityName) throws Exception{
String requestUrl="http://api.map.baidu.com/telematics/v3/weather?location={LOCATION}&output=json&ak={KEY}";
String requestWeatherUrl=requestUrl.replace("{LOCATION}", URLEncoder.encode(cityName, "UTF-8")).replace("{KEY}", "你的AK");
String result=CommonUtil.httpRequest(requestWeatherUrl, "POST", null);
//System.out.println(result);
Gson gson=new Gson();
WeatherResp wresp=gson.fromJson(result, WeatherResp.class);
StringBuffer buf=new StringBuffer();
buf.append(cityName+"天气预报"+"\n\n");
List<WeatherData> wdata=wresp.getResults().get(0).getWeather_data();
Iterator<WeatherData> it=wdata.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
WeatherData w=it.next();
buf.append(w.getDate()+","+w.getWeather()+","+w.getTemperature()+","+w.getWind());
buf.append("\n\n");
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
System.out.println(getWeatherResult("苏州"));
}
}
来看下运行效果截图:
天气预报的接口来源还是挺多的,数据交互方式也不尽相同,选择合适的就行,不一定局限于百度的API.gson的使用关键在于json数据的分析,按结构提取出合适的pojo类能很好的降低解析难度。

























 2597
2597











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








