一、前言
今天是元旦,也是Single Dog的嚎叫之日,只能写博客来祛除寂寞了,今天我们继续来看一下Android中的签名机制的姊妹篇:android中是如何验证一个Apk的签名。在前一篇文章中我们介绍了,Android中是如何对程序进行签名的,不了解的同学可以转战:
http://blog.csdn.net/jiangwei0910410003/article/details/50402000
当然在了解我们今天说到的知识点,这篇文章也是需要了解的,不然会有些知识点有些困惑的。
二、知识摘要
在我们没有开始这篇文章之前,我们回顾一下之前说到的签名机制流程:
1、对Apk中的每个文件做一次算法(数据摘要+Base64编码),保存到MANIFEST.MF文件中
2、对MANIFEST.MF整个文件做一次算法(数据摘要+Base64编码),存放到CERT.SF文件的头属性中,在对MANIFEST.MF文件中各个属性块做一次算法(数据摘要+Base64编码),存到到一个属性块中。
3、对CERT.SF文件做签名,内容存档到CERT.RSA中
所以通过上面的流程可以知道,我们今天来验证签名流程也是这三个步骤
三、代码分析
我们既然要了解Android中的应用程序的签名验证过程的话,那么我们肯定需要从一个类来开始看起,那就是PackageManagerService.Java,因为这个类是Apk在安装的过程中核心类:frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\pm\PackageManagerService.java
- private void installPackageLI(InstallArgs args, PackageInstalledInfo res) {
- ……
- PackageParser pp = new PackageParser();
- ……
- try {
- pp.collectCertificates(pkg, parseFlags);
- pp.collectManifestDigest(pkg);
- } catch (PackageParserException e) {
- res.setError("Failed collect during installPackageLI", e);
- return;
- }
- ……
我们可以看到,有一个核心类:PackageParser
frameworks\base\core\java\android\content\pm\PackageParser.java
这个类也是见名知意,就是需要解析Apk包,那么就会涉及到签名信息了,下面我们就从这个类开始入手:
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST;
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_PACKAGE_NAME;
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_CERTIFICATE_ENCODING;
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_INCONSISTENT_CERTIFICATES;
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NOT_APK;
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NO_CERTIFICATES;
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_UNEXPECTED_EXCEPTION;
我们看到了几个我们很熟悉的信息:
- import static android.content.pm.PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NO_CERTIFICATES;
这个是在安装apk包的时候出现的错误,没有证书:
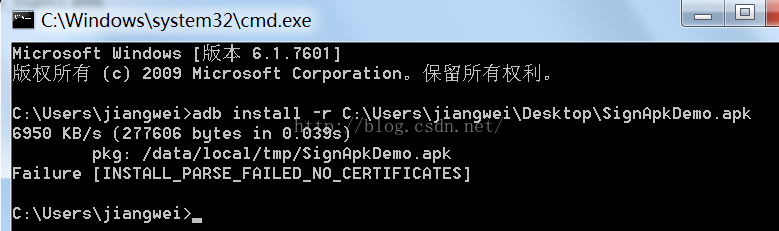
那么我们就先来查找一下这个字段:
- private static void collectCertificates(Package pkg, File apkFile, int flags)
- throws PackageParserException {
- final String apkPath = apkFile.getAbsolutePath();
-
- StrictJarFile jarFile = null;
- try {
- jarFile = new StrictJarFile(apkPath);
-
-
- final ZipEntry manifestEntry = jarFile.findEntry(ANDROID_MANIFEST_FILENAME);
- if (manifestEntry == null) {
- throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST,
- "Package " + apkPath + " has no manifest");
- }
-
- final List<ZipEntry> toVerify = new ArrayList<>();
- toVerify.add(manifestEntry);
-
-
- if ((flags & PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) == 0) {
- final Iterator<ZipEntry> i = jarFile.iterator();
- while (i.hasNext()) {
- final ZipEntry entry = i.next();
-
- if (entry.isDirectory()) continue;
- if (entry.getName().startsWith("META-INF/")) continue;
- if (entry.getName().equals(ANDROID_MANIFEST_FILENAME)) continue;
-
- toVerify.add(entry);
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
- for (ZipEntry entry : toVerify) {
- final Certificate[][] entryCerts = loadCertificates(jarFile, entry);
- if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(entryCerts)) {
- throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NO_CERTIFICATES,
- "Package " + apkPath + " has no certificates at entry "
- + entry.getName());
- }
- final Signature[] entrySignatures = convertToSignatures(entryCerts);
-
- if (pkg.mCertificates == null) {
- pkg.mCertificates = entryCerts;
- pkg.mSignatures = entrySignatures;
- pkg.mSigningKeys = new ArraySet<PublicKey>();
- for (int i=0; i < entryCerts.length; i++) {
- pkg.mSigningKeys.add(entryCerts[i][0].getPublicKey());
- }
- } else {
- if (!Signature.areExactMatch(pkg.mSignatures, entrySignatures)) {
- throw new PackageParserException(
- INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_INCONSISTENT_CERTIFICATES, "Package " + apkPath
- + " has mismatched certificates at entry "
- + entry.getName());
- }
- }
- }
- } catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
- throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_CERTIFICATE_ENCODING,
- "Failed to collect certificates from " + apkPath, e);
- } catch (IOException | RuntimeException e) {
- throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NO_CERTIFICATES,
- "Failed to collect certificates from " + apkPath, e);
- } finally {
- closeQuietly(jarFile);
- }
- }
这里看到了,当有异常的时候就会提示这个信息,我们在跟进去看看:
-
-
-
- for (ZipEntry entry : toVerify) {
- final Certificate[][] entryCerts = loadCertificates(jarFile, entry);
- if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(entryCerts)) {
- throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NO_CERTIFICATES,
- "Package " + apkPath + " has no certificates at entry "
- + entry.getName());
- }
- final Signature[] entrySignatures = convertToSignatures(entryCerts);
-
- if (pkg.mCertificates == null) {
- pkg.mCertificates = entryCerts;
- pkg.mSignatures = entrySignatures;
- pkg.mSigningKeys = new ArraySet<PublicKey>();
- for (int i=0; i < entryCerts.length; i++) {
- pkg.mSigningKeys.add(entryCerts[i][0].getPublicKey());
- }
- } else {
- if (!Signature.areExactMatch(pkg.mSignatures, entrySignatures)) {
- throw new PackageParserException(
- INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_INCONSISTENT_CERTIFICATES, "Package " + apkPath
- + " has mismatched certificates at entry "
- + entry.getName());
- }
- }
- }
这里有一个重要的方法:loadCertificates
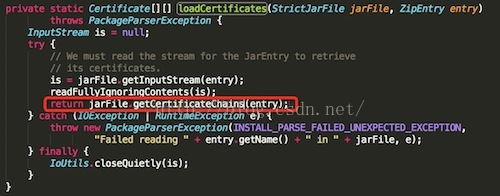
- private static Certificate[][] loadCertificates(StrictJarFile jarFile, ZipEntry entry)
- throws PackageParserException {
- InputStream is = null;
- try {
-
-
- is = jarFile.getInputStream(entry);
- readFullyIgnoringContents(is);
- return jarFile.getCertificateChains(entry);
- } catch (IOException | RuntimeException e) {
- throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_UNEXPECTED_EXCEPTION,
- "Failed reading " + entry.getName() + " in " + jarFile, e);
- } finally {
- IoUtils.closeQuietly(is);
- }
- }
这个方法是加载证书内容的
1、验证Apk中的每个文件的算法(数据摘要+Base64编码)和MANIFEST.MF文件中的对应属性块内容是否配对
首先获取StrictJarFile文件中的InputStream对象
StrictJarFile这个类:libcore\luni\src\main\java\java\util\jar\StrictJarFile.java
- public InputStream getInputStream(ZipEntry ze) {
- final InputStream is = getZipInputStream(ze);
-
- if (isSigned) {
- JarVerifier.VerifierEntry entry = verifier.initEntry(ze.getName());
- if (entry == null) {
- return is;
- }
-
- return new JarFile.JarFileInputStream(is, ze.getSize(), entry);
- }
-
- return is;
- }
1》获取到VerifierEntry对象entry
在JarVerifier.java:libcore\luni\src\main\java\java\util\jar\JarVerifier.java
- VerifierEntry initEntry(String name) {
-
-
-
- if (manifest == null || signatures.isEmpty()) {
- return null;
- }
- Attributes attributes = manifest.getAttributes(name);
-
- if (attributes == null) {
- return null;
- }
- ArrayList<Certificate[]> certChains = new ArrayList<Certificate[]>();
- Iterator<Map.Entry<String, HashMap<String, Attributes>>> it = signatures.entrySet().iterator();
- while (it.hasNext()) {
- Map.Entry<String, HashMap<String, Attributes>> entry = it.next();
- HashMap<String, Attributes> hm = entry.getValue();
- if (hm.get(name) != null) {
-
- String signatureFile = entry.getKey();
- Certificate[] certChain = certificates.get(signatureFile);
- if (certChain != null) {
- certChains.add(certChain);
- }
- }
- }
-
- if (certChains.isEmpty()) {
- return null;
- }
- Certificate[][] certChainsArray = certChains.toArray(new Certificate[certChains.size()][]);
- for (int i = 0; i < DIGEST_ALGORITHMS.length; i++) {
- final String algorithm = DIGEST_ALGORITHMS[i];
- final String hash = attributes.getValue(algorithm + "-Digest");
- if (hash == null) {
- continue;
- }
- byte[] hashBytes = hash.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
- try {
- return new VerifierEntry(name, MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm), hashBytes,
- certChainsArray, verifiedEntries);
- } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException ignored) {
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
就是构造一个VerifierEntry对象:
-
-
-
-
- static class VerifierEntry extends OutputStream {
- private final String name;
- private final MessageDigest digest;
- private final byte[] hash;
- private final Certificate[][] certChains;
- private final Hashtable<String, Certificate[][]> verifiedEntries;
- VerifierEntry(String name, MessageDigest digest, byte[] hash,
- Certificate[][] certChains, Hashtable<String, Certificate[][]> verifedEntries) {
- this.name = name;
- this.digest = digest;
- this.hash = hash;
- this.certChains = certChains;
- this.verifiedEntries = verifedEntries;
- }
-
-
-
- @Override
- public void write(int value) {
- digest.update((byte) value);
- }
-
-
-
- @Override
- public void write(byte[] buf, int off, int nbytes) {
- digest.update(buf, off, nbytes);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- void verify() {
- byte[] d = digest.digest();
- if (!MessageDigest.isEqual(d, Base64.decode(hash))) {
- throw invalidDigest(JarFile.MANIFEST_NAME, name, name);
- }
- verifiedEntries.put(name, certChains);
- }
- }
要构造这个对象,必须事先准备好参数。第一个参数很简单,就是要验证的文件名,直接将name传进来就好了。第二个参数是计算摘要的对象,可以通过MessageDigest.getInstance获得,不过要先告知到底要用哪个摘要算法,同样也是通过查看MANIFEST.MF文件中对应名字的属性值来决定的:
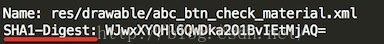
所以可以知道所用的摘要算法是SHA1。第三个参数是对应文件的摘要值,这是通过读取MANIFEST.MF文件获得的:
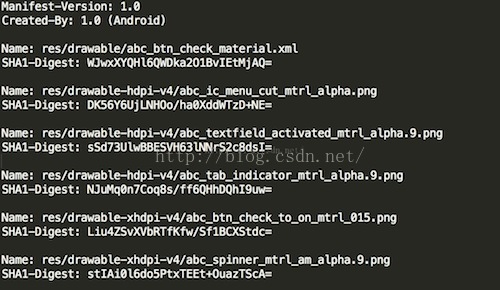
第四个参数是证书链,即对该apk文件签名的所有证书链信息。为什么是二维数组呢?这是因为Android允许用多个证书对apk进行签名,但是它们的证书文件名必须不同,这个知识点,我在之前的一篇文章中:签名过程详解 中有提到。
最后一个参数是已经验证过的文件列表,VerifierEntry在完成了对指定文件的摘要验证之后会将该文件的信息加到其中。
2》再去JarFile的JarFileInputStream类中看看:
- static final class JarFileInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
- private long count;
-
- private ZipEntry zipEntry;
-
- private JarVerifier.VerifierEntry entry;
-
- private boolean done = false;
-
- JarFileInputStream(InputStream is, ZipEntry ze,
- JarVerifier.VerifierEntry e) {
- super(is);
- zipEntry = ze;
- count = zipEntry.getSize();
- entry = e;
- }
-
- @Override
- public int read() throws IOException {
- if (done) {
- return -1;
- }
- if (count > 0) {
- int r = super.read();
- if (r != -1) {
- entry.write(r);
- count--;
- } else {
- count = 0;
- }
- if (count == 0) {
- done = true;
- entry.verify();
- }
- return r;
- } else {
- done = true;
- entry.verify();
- return -1;
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int read(byte[] buf, int off, int nbytes) throws IOException {
- if (done) {
- return -1;
- }
- if (count > 0) {
- int r = super.read(buf, off, nbytes);
- if (r != -1) {
- int size = r;
- if (count < size) {
- size = (int) count;
- }
- entry.write(buf, off, size);
- count -= size;
- } else {
- count = 0;
- }
- if (count == 0) {
- done = true;
- entry.verify();
- }
- return r;
- } else {
- done = true;
- entry.verify();
- return -1;
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int available() throws IOException {
- if (done) {
- return 0;
- }
- return super.available();
- }
-
- @Override
- public long skip(long byteCount) throws IOException {
- return Streams.skipByReading(this, byteCount);
- }
- }
3》PackageParser的readFullyIgnoringContents方法:
- public static long readFullyIgnoringContents(InputStream in) throws IOException {
- byte[] buffer = sBuffer.getAndSet(null);
- if (buffer == null) {
- buffer = new byte[4096];
- }
-
- int n = 0;
- int count = 0;
- while ((n = in.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1) {
- count += n;
- }
-
- sBuffer.set(buffer);
- return count;
- }
得到第二步之后的一个InputStream对象,然后就开始read操作,这里我没发现什么猫腻,但是我们从第一件事做完之后可以发现,这里的InputStream对象其实是JarInputStream,所以我们可以去看一下他的read方法的实现:
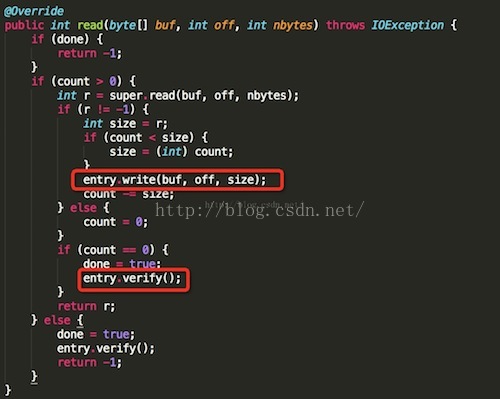
玄机原来在这里,这里的JarFileInputStream.read确实会调用其父类的read读取指定的apk内文件的内容,并且将其传给JarVerifier.VerifierEntry.write函数。当文件读完后,会接着调用JarVerifier.VerifierEntry.verify函数对其进行验证。JarVerifier.VerifierEntry.write函数非常简单:
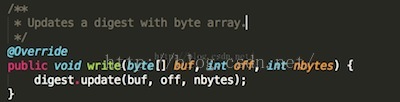
就是将读到的文件的内容传给digest,这个digest就是前面在构造JarVerifier.VerifierEntry传进来的,对应于在MANIFEST.MF文件中指定的摘要算法。万事具备,接下来想要验证就很简单了:
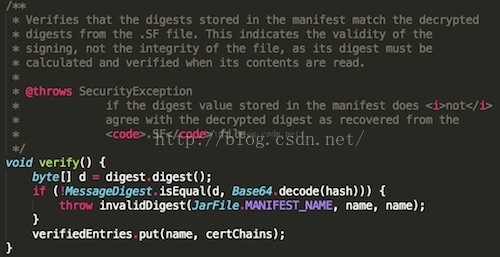
通过digest就可以算出apk内指定文件的真实摘要值。而记录在MANIFEST.MF文件中对应该文件的摘要值,也在构造JarVerifier.VerifierEntry时传递给了hash变量。不过这个hash值是经过Base64编码的。所以在比较之前,必须通过Base64解码。如果不一致的话,会抛出SecurityException异常:
- private static SecurityException invalidDigest(String signatureFile, String name,
- String jarName) {
- throw new SecurityException(signatureFile + " has invalid digest for " + name +
- " in " + jarName);
- }
到这里我们就分析了,Android中是如何验证MANIFEST.MF文件中的内容的,我们这里再来看一下,这里抛出异常出去:
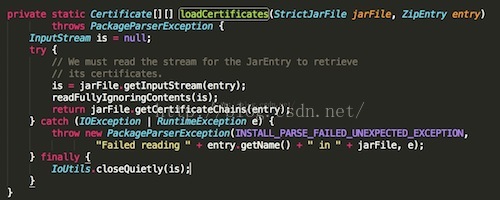
这里捕获到异常之后,会在抛异常出去:
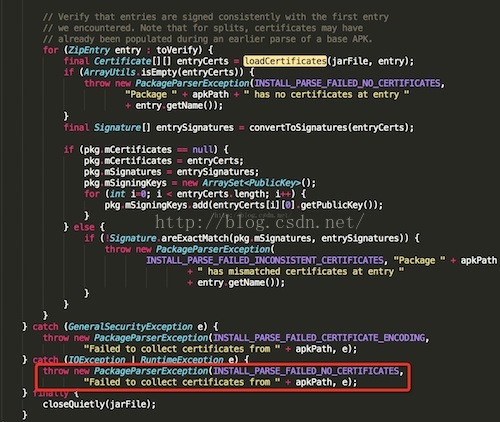
在这里就会抛出异常信息,所以如果我们修改了一个Apk中的一个文件内容的话,这里肯定是安装不上的。
2、验证CERT.SF文件的签名信息和CERT.RSA中的内容是否一致
1》我们就来看看StrictJarFile中的getCertificateChains方法:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public Certificate[][] getCertificateChains(ZipEntry ze) {
- if (isSigned) {
- return verifier.getCertificateChains(ze.getName());
- }
-
- return null;
- }
这里有一个变量判断:isSigned,他是在构造方法中赋值的:
- public StrictJarFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
- this.nativeHandle = nativeOpenJarFile(fileName);
- this.raf = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "r");
-
- try {
-
-
-
- HashMap<String, byte[]> metaEntries = getMetaEntries();
- this.manifest = new Manifest(metaEntries.get(JarFile.MANIFEST_NAME), true);
- this.verifier = new JarVerifier(fileName, manifest, metaEntries);
-
- isSigned = verifier.readCertificates() && verifier.isSignedJar();
- } catch (IOException ioe) {
- nativeClose(this.nativeHandle);
- throw ioe;
- }
-
- guard.open("close");
- }
去verifier中看看这两个方法:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- synchronized boolean readCertificates() {
- if (metaEntries.isEmpty()) {
- return false;
- }
- Iterator<String> it = metaEntries.keySet().iterator();
- while (it.hasNext()) {
- String key = it.next();
- if (key.endsWith(".DSA") || key.endsWith(".RSA") || key.endsWith(".EC")) {
- verifyCertificate(key);
- it.remove();
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
这个方法其实很简单,就是判断metaEntries中是否为空,说白了,就是判断Apk中的META-INF文件夹中是否为空,只有文件就返回true。再来看看isSignedJar方法:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- boolean isSignedJar() {
- return certificates.size() > 0;
- }
这个方法直接判断certificates这个集合是否为空。我们全局搜索一下这个集合在哪里存入的数据的地方,找到了verifyCertificate方法,同时我们发现,在上面的readCertificates方法中,就调用了这个方法,其实这个方法就是读取证书信息的。
下面来看一下verifyCertificate方法:
-
-
-
- private void verifyCertificate(String certFile) {
-
- String signatureFile = certFile.substring(0, certFile.lastIndexOf('.')) + ".SF";
- byte[] sfBytes = metaEntries.get(signatureFile);
- if (sfBytes == null) {
- return;
- }
- byte[] manifestBytes = metaEntries.get(JarFile.MANIFEST_NAME);
-
- if (manifestBytes == null) {
- return;
- }
- byte[] sBlockBytes = metaEntries.get(certFile);
- try {
- Certificate[] signerCertChain = JarUtils.verifySignature(
- new ByteArrayInputStream(sfBytes),
- new ByteArrayInputStream(sBlockBytes));
- if (signerCertChain != null) {
- certificates.put(signatureFile, signerCertChain);
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- return;
- } catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
- throw failedVerification(jarName, signatureFile);
- }
-
- Attributes attributes = new Attributes();
- HashMap<String, Attributes> entries = new HashMap<String, Attributes>();
- try {
- ManifestReader im = new ManifestReader(sfBytes, attributes);
- im.readEntries(entries, null);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- return;
- }
-
- if (attributes.get(Attributes.Name.SIGNATURE_VERSION) == null) {
- return;
- }
- boolean createdBySigntool = false;
- String createdBy = attributes.getValue("Created-By");
- if (createdBy != null) {
- createdBySigntool = createdBy.indexOf("signtool") != -1;
- }
-
-
-
-
- if (mainAttributesEnd > 0 && !createdBySigntool) {
- String digestAttribute = "-Digest-Manifest-Main-Attributes";
- if (!verify(attributes, digestAttribute, manifestBytes, 0, mainAttributesEnd, false, true)) {
- throw failedVerification(jarName, signatureFile);
- }
- }
-
- String digestAttribute = createdBySigntool ? "-Digest" : "-Digest-Manifest";
- if (!verify(attributes, digestAttribute, manifestBytes, 0, manifestBytes.length, false, false)) {
- Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Attributes>> it = entries.entrySet().iterator();
- while (it.hasNext()) {
- Map.Entry<String, Attributes> entry = it.next();
- Manifest.Chunk chunk = manifest.getChunk(entry.getKey());
- if (chunk == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (!verify(entry.getValue(), "-Digest", manifestBytes,
- chunk.start, chunk.end, createdBySigntool, false)) {
- throw invalidDigest(signatureFile, entry.getKey(), jarName);
- }
- }
- }
- metaEntries.put(signatureFile, null);
- signatures.put(signatureFile, entries);
- }
2》获取证书信息,并且验证CERT.SF文件的签名信息和CERT.RSA中的内容是否一致。
-
- String signatureFile = certFile.substring(0, certFile.lastIndexOf('.')) + ".SF";
- byte[] sfBytes = metaEntries.get(signatureFile);
- if (sfBytes == null) {
- return;
- }
- byte[] manifestBytes = metaEntries.get(JarFile.MANIFEST_NAME);
-
- if (manifestBytes == null) {
- return;
- }
- byte[] sBlockBytes = metaEntries.get(certFile);
- try {
- Certificate[] signerCertChain = JarUtils.verifySignature(
- new ByteArrayInputStream(sfBytes),
- new ByteArrayInputStream(sBlockBytes));
- if (signerCertChain != null) {
- certificates.put(signatureFile, signerCertChain);
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- return;
- } catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
- throw failedVerification(jarName, signatureFile);
- }
这里首先获取到,签名文件。我们在之前的一篇文章中说到了,签名文件和证书文件的名字是一样的。
同时这里还调用了JarUtils类:libcore\luni\src\main\java\org\apache\harmony\security\utils\JarUtils.java
中的verifySignature方法来获取证书,这里就不做太多的解释了,如何从一个RSA文件中获取证书,这样的代码网上也是有的,而且后面我会演示一下,如何获取。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public static Certificate[] verifySignature(InputStream signature, InputStream
- signatureBlock) throws IOException, GeneralSecurityException {
-
- BerInputStream bis = new BerInputStream(signatureBlock);
- ContentInfo info = (ContentInfo)ContentInfo.ASN1.decode(bis);
- SignedData signedData = info.getSignedData();
- if (signedData == null) {
- throw new IOException("No SignedData found");
- }
- Collection<org.apache.harmony.security.x509.Certificate> encCerts
- = signedData.getCertificates();
- if (encCerts.isEmpty()) {
- return null;
- }
- X509Certificate[] certs = new X509Certificate[encCerts.size()];
- int i = 0;
- for (org.apache.harmony.security.x509.Certificate encCert : encCerts) {
- certs[i++] = new X509CertImpl(encCert);
- }
-
- List<SignerInfo> sigInfos = signedData.getSignerInfos();
- SignerInfo sigInfo;
- if (!sigInfos.isEmpty()) {
- sigInfo = sigInfos.get(0);
- } else {
- return null;
- }
-
-
- X500Principal issuer = sigInfo.getIssuer();
-
-
- BigInteger snum = sigInfo.getSerialNumber();
-
-
- int issuerSertIndex = 0;
- for (i = 0; i < certs.length; i++) {
- if (issuer.equals(certs[i].getIssuerDN()) &&
- snum.equals(certs[i].getSerialNumber())) {
- issuerSertIndex = i;
- break;
- }
- }
- if (i == certs.length) {
- return null;
- }
-
- if (certs[issuerSertIndex].hasUnsupportedCriticalExtension()) {
- throw new SecurityException("Can not recognize a critical extension");
- }
-
-
- Signature sig = null;
- String da = sigInfo.getDigestAlgorithm();
- String dea = sigInfo.getDigestEncryptionAlgorithm();
- String alg = null;
- if (da != null && dea != null) {
- alg = da + "with" + dea;
- try {
- sig = Signature.getInstance(alg, OpenSSLProvider.PROVIDER_NAME);
- } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {}
- }
- if (sig == null) {
- alg = da;
- if (alg == null) {
- return null;
- }
- try {
- sig = Signature.getInstance(alg, OpenSSLProvider.PROVIDER_NAME);
- } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
- return null;
- }
- }
- sig.initVerify(certs[issuerSertIndex]);
- ......
这里返回的是一个证书的数组。
3、MANIFEST.MF整个文件签名在CERT.SF文件中头属性中的值是否匹配以及验证MANIFEST.MF文件中的各个属性块的签名在CERT.SF文件中是否匹配
1》第一件事是:验证MANIFEST.MF整个文件签名在CERT.SF文件中头属性中的值是否匹配
-
-
-
-
- if (mainAttributesEnd > 0 && !createdBySigntool) {
- String digestAttribute = "-Digest-Manifest-Main-Attributes";
- if (!verify(attributes, digestAttribute, manifestBytes, 0, mainAttributesEnd, false, true)) {
- throw failedVerification(jarName, signatureFile);
- }
- }
这里的manifestBytes:
- byte[] manifestBytes = metaEntries.get(JarFile.MANIFEST_NAME);
就是MANIFEST.MF文件内容。继续看一下verify方法:
- private boolean verify(Attributes attributes, String entry, byte[] data,
- int start, int end, boolean ignoreSecondEndline, boolean ignorable) {
- for (int i = 0; i < DIGEST_ALGORITHMS.length; i++) {
- String algorithm = DIGEST_ALGORITHMS[i];
- String hash = attributes.getValue(algorithm + entry);
- if (hash == null) {
- continue;
- }
- MessageDigest md;
- try {
- md = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
- } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
- continue;
- }
- if (ignoreSecondEndline && data[end - 1] == '\n' && data[end - 2] == '\n') {
- md.update(data, start, end - 1 - start);
- } else {
- md.update(data, start, end - start);
- }
- byte[] b = md.digest();
- byte[] hashBytes = hash.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
- return MessageDigest.isEqual(b, Base64.decode(hashBytes));
- }
- return ignorable;
- }
这个方法其实很简单,就是验证传入的data数据块的数据摘要算法和传入的attributes中的算法块的值是否匹配,比如这里:
- String algorithm = DIGEST_ALGORITHMS[i];
- String hash = attributes.getValue(algorithm + entry);
这里的algorithm是算法:
- private static final String[] DIGEST_ALGORITHMS = new String[] {
- "SHA-512",
- "SHA-384",
- "SHA-256",
- "SHA1",
- };
这里的entry也是传入的,我们看到传入的是:-Digest
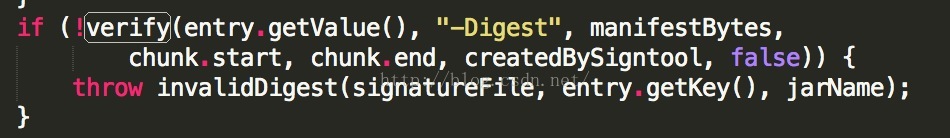
这样就是CERT.SF文件中的一个条目:

2》第二件事是:验证MANIFEST.MF文件中的各个属性块的签名在CERT.SF文件中是否匹配
-
- String digestAttribute = createdBySigntool ? "-Digest" : "-Digest-Manifest";
- if (!verify(attributes, digestAttribute, manifestBytes, 0, manifestBytes.length, false, false)) {
- Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Attributes>> it = entries.entrySet().iterator();
- while (it.hasNext()) {
- Map.Entry<String, Attributes> entry = it.next();
- Manifest.Chunk chunk = manifest.getChunk(entry.getKey());
- if (chunk == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (!verify(entry.getValue(), "-Digest", manifestBytes,
- chunk.start, chunk.end, createdBySigntool, false)) {
- throw invalidDigest(signatureFile, entry.getKey(), jarName);
- }
- }
- }
这里我们可以看到也是同样调用verify方法来验证CERT.SF中的条目信息的。
最后我们再看一下是如何配对签名信息的,在PackageParser中的collectCertificates方法:
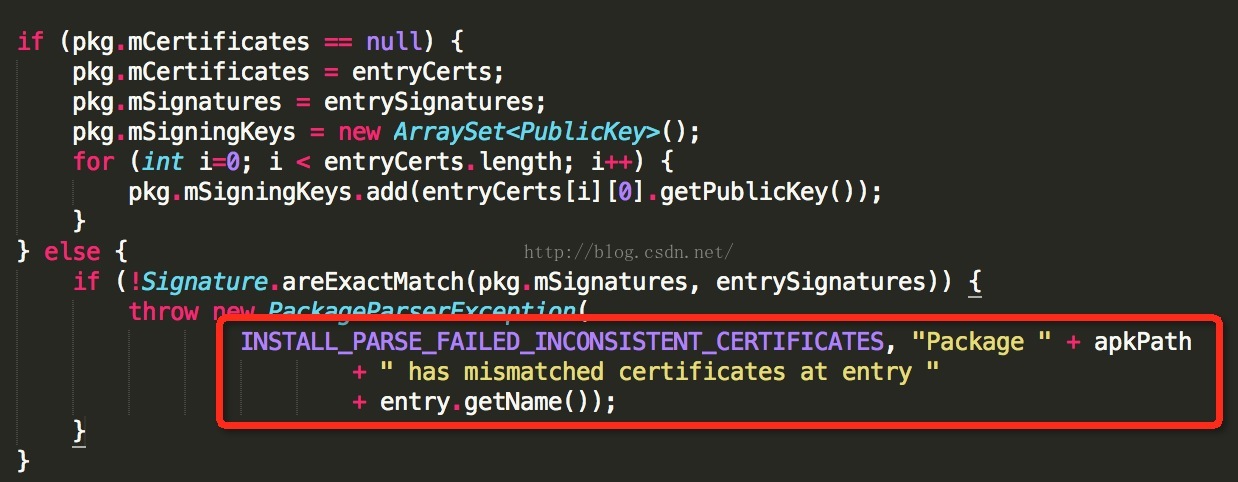
这里会比对已经安装的apk的签名和准备要安装的apk的签名是否一致,如果不一致的话,就会报错:
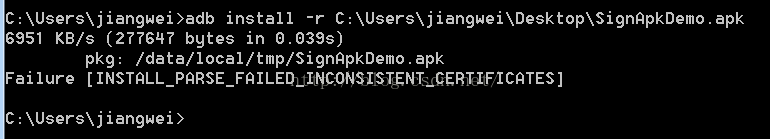
这个错,也是我们经常会遇到的,就是同样的apk,签名不一致导致的问题。
我们从上面的分析代码中可以看到,这里的Signature比对签名,其实就是比对证书中的公钥信息:
上面我们就看完了Android中验证签名信息的流程,下面我们再来梳理一下流程吧:
所有有关apk文件的签名验证工作都是在JarVerifier里面做的,一共分成三步:
1、JarVerifier.VerifierEntry.verify做了验证,即保证apk文件中包含的所有文件,对应的摘要值与MANIFEST.MF文件中记录的一致。
2、JarVeirifer.verifyCertificate使用证书文件(在META-INF目录下,以.DSA、.RSA或者.EC结尾的文件)检验签名文件(在META-INF目录下,和证书文件同名,但扩展名为.SF的文件)是没有被修改过的。这里我们可以注意到,Android中在验证的过程中对SF喝RSA文件的名字并不关心,这个在之前的 签名过程 文章中介绍到了。
3、JarVeirifer.verifyCertificate中使用签名文件CERT.SF,检验MANIFEST.MF文件中的内容也没有被篡改过
综上所述:
首先,如果你改变了apk包中的任何文件,那么在apk安装校验时,改变后的文件摘要信息与MANIFEST.MF的检验信息不同,于是验证失败,程序就不能成功安装。
其次,如果你对更改的过的文件相应的算出新的摘要值,然后更改MANIFEST.MF文件里面对应的属性值,那么必定与CERT.SF文件中算出的摘要值不一样,照样验证失败。
这里都会提示安装失败信息:

如果你还不死心,继续计算MANIFEST.MF的摘要值,相应的更改CERT.SF里面的值.
那么数字签名值必定与CERT.RSA文件中记录的不一样,还是失败。
这里的失败信息:

那么能不能继续伪造数字签名呢?不可能,因为没有数字证书对应的私钥。
所以,如果要重新打包后的应用程序能再Android设备上安装,必须对其进行重签名。
从上面的分析可以得出,只要修改了Apk中的任何内容,就必须重新签名,不然会提示安装失败,当然这里不会分析,后面一篇文章会注重分析为何会提示安装失败。
总结
到这里我们就介绍完了Android中的apk的签名验证过程,再结合之前的一篇文章,我们可以了解到了Android中的签名机制了。这个也是对Android中的安全机制的一个深入了解吧,新年快乐~~

































 3748
3748











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








