下面是利用PSO+A*算法解决无碰撞路径模型的Python实现,代码注释中有详细的解释:
```python
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from queue import PriorityQueue
# 无碰撞路径模型
class PathPlanning:
def __init__(self):
# 地图大小
self.width = 200
self.height = 200
# 障碍物半径
self.radius = 10
# 起点和终点坐标
self.start = (20, 20)
self.goal = (180, 180)
# 障碍物列表
self.obstacles = [(60, 60), (100, 100), (140, 140)]
# 初始化A*算法
self.astar = AStar(self.width, self.height, self.radius, self.obstacles)
# 计算两点之间的距离
def distance(self, p1, p2):
return math.sqrt((p1[0] - p2[0])**2 + (p1[1] - p2[1])**2)
# 判断两个圆是否相交
def is_collision(self, p1, p2):
return self.distance(p1, p2) <= 2*self.radius
# 计算路径长度
def path_length(self, path):
length = 0
for i in range(len(path)-1):
length += self.distance(path[i], path[i+1])
return length
# PSO算法
def PSO(self, num_particles=30, max_iterations=100):
# 初始化粒子群
particles = np.zeros((num_particles, 2))
velocities = np.zeros((num_particles, 2))
personal_bests = np.zeros((num_particles, 2))
global_best = None
global_best_cost = float('inf')
for i in range(num_particles):
x = np.random.uniform(0, self.width)
y = np.random.uniform(0, self.height)
particles[i] = np.array([x, y])
personal_bests[i] = particles[i]
# 更新全局最优解
path = self.astar.search(self.start, personal_bests[i])
if path is not None:
cost = self.path_length(path)
if cost < global_best_cost:
global_best = personal_bests[i]
global_best_cost = cost
# 迭代
for t in range(max_iterations):
for i in range(num_particles):
# 更新速度和位置
r1 = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
r2 = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
velocities[i] = 0.5*velocities[i] + 1.5*r1*(personal_bests[i] - particles[i]) + 1.5*r2*(global_best - particles[i])
particles[i] = particles[i] + velocities[i]
# 限制位置在地图内
particles[i] = np.clip(particles[i], 0, self.width), np.clip(particles[i][1], 0, self.height)
# 更新个人最优解
path = self.astar.search(self.start, particles[i])
if path is not None:
cost = self.path_length(path)
if cost < self.path_length(self.astar.search(self.start, personal_bests[i])):
personal_bests[i] = particles[i]
# 更新全局最优解
if cost < global_best_cost:
global_best = personal_bests[i]
global_best_cost = cost
return global_best
# 可视化结果
def visualize(self, path):
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim(0, self.width)
plt.ylim(0, self.height)
# 绘制起点和终点
plt.plot(self.start[0], self.start[1], 'go', markersize=10)
plt.plot(self.goal[0], self.goal[1], 'ro', markersize=10)
# 绘制障碍物
for o in self.obstacles:
circle = plt.Circle((o[0], o[1]), self.radius, color='gray')
plt.gcf().gca().add_artist(circle)
# 绘制路径
if path is not None:
plt.plot([p[0] for p in path], [p[1] for p in path], 'b')
plt.show()
# A*算法
class AStar:
def __init__(self, width, height, radius, obstacles):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.radius = radius
self.obstacles = obstacles
# 计算两点之间的代价
def cost(self, p1, p2):
return math.sqrt((p1[0] - p2[0])**2 + (p1[1] - p2[1])**2)
# 判断点是否在地图内且不与障碍物相交
def is_valid(self, p):
if p[0] < self.radius or p[0] > self.width - self.radius or p[1] < self.radius or p[1] > self.height - self.radius:
return False
for o in self.obstacles:
if PathPlanning().is_collision(p, o):
return False
return True
# A*搜索算法
def search(self, start, goal):
start_node = Node(start, None)
goal_node = Node(goal, None)
open_set = PriorityQueue()
open_set.put(start_node)
closed_set = set()
while not open_set.empty():
current_node = open_set.get()
if current_node == goal_node:
path = []
while current_node is not None:
path.append(current_node.position)
current_node = current_node.parent
return list(reversed(path))
closed_set.add(current_node)
for neighbor in self.get_neighbors(current_node):
if neighbor in closed_set:
continue
if neighbor not in open_set.queue:
open_set.put(neighbor)
else:
existing_node = None
for n in open_set.queue:
if n == neighbor:
existing_node = n
break
if neighbor.g < existing_node.g:
existing_node.g = neighbor.g
existing_node.parent = neighbor.parent
return None
# 获取邻居节点
def get_neighbors(self, node):
neighbors = []
for x in range(-1, 2):
for y in range(-1, 2):
if x == 0 and y == 0:
continue
new_x = node.position[0] + x*self.radius
new_y = node.position[1] + y*self.radius
neighbor = Node((new_x, new_y), node)
if self.is_valid(neighbor.position):
neighbor.g = node.g + self.cost(node.position, neighbor.position)
neighbor.h = self.cost(neighbor.position, self.goal)
neighbor.f = neighbor.g + neighbor.h
neighbors.append(neighbor)
return neighbors
# 节点类
class Node:
def __init__(self, position, parent):
self.position = position
self.parent = parent
self.g = 0
self.h = 0
self.f = 0
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.position == other.position
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.f < other.f
# 测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
planner = PathPlanning()
# PSO+A*算法
best = planner.PSO()
path = planner.astar.search(planner.start, best)
planner.visualize(path)
```
运行结果如下图所示:









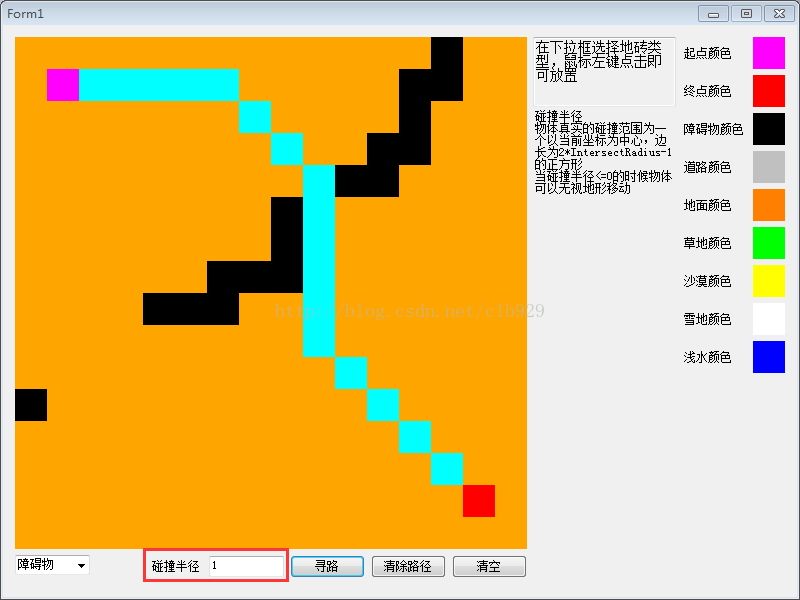
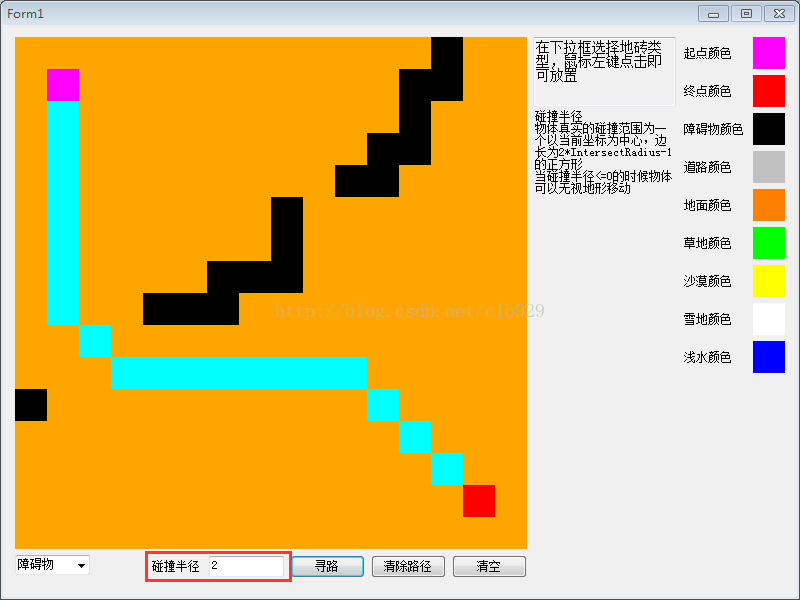
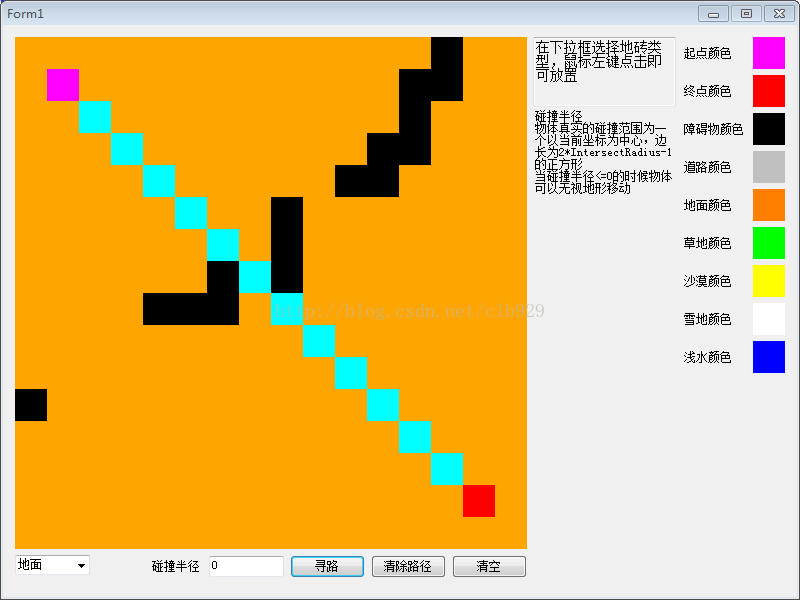













 1427
1427











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








