Java容器复习
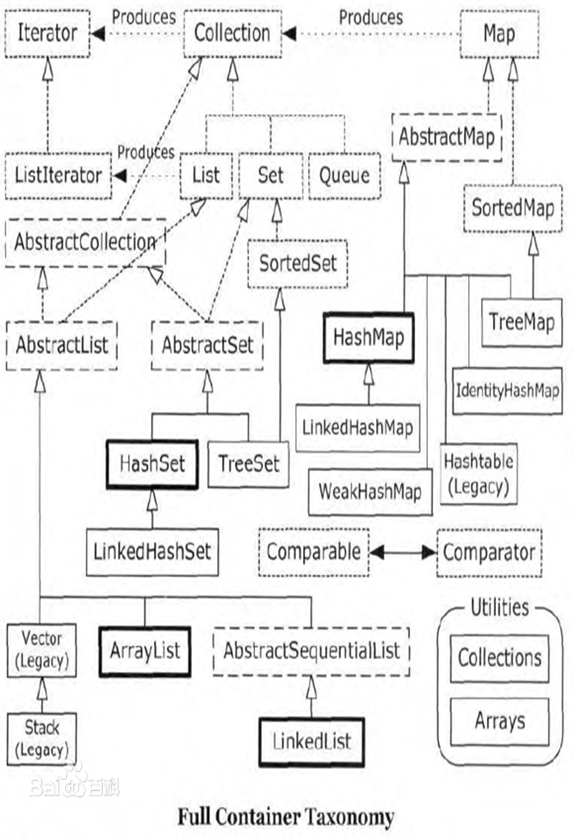
前言:在java开发中我们肯定会大量的使用集合,在这里我将总结常见的集合类,每个集合类的优点和缺点,以便我们能更好的使用集合。下面我用一幅图来表示
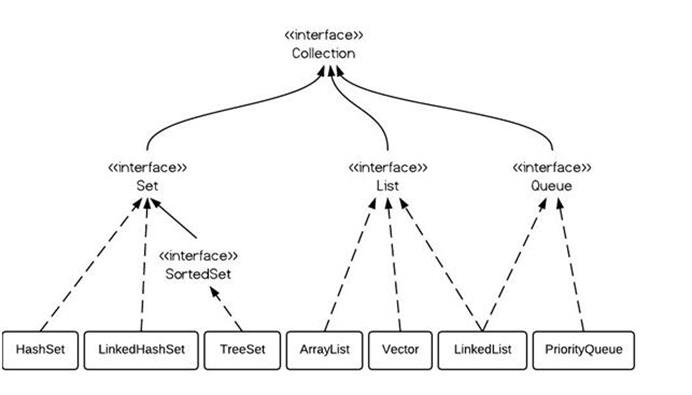
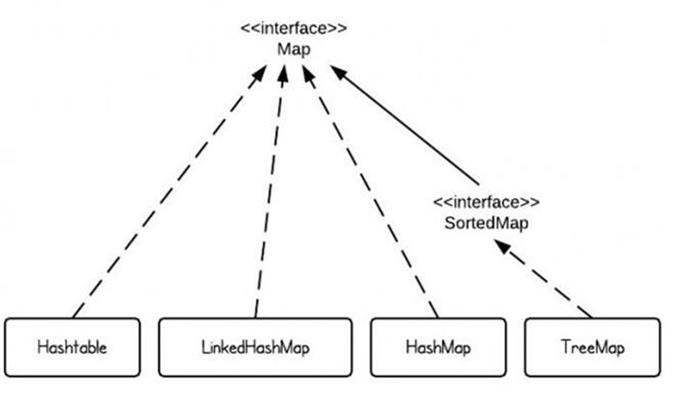
常用的容器如下
Collection和map都实现了一个规范的接口Iterable<T> ,它的作用API
Implementing this interface allows an object to be the target of the "for-each loop" statement
Target : n.目标; 目的; (服务的) 对象; (射击的) 靶子;vt. 瞄准; 把…作为攻击目标;
Loop n. 回路; 圈,环; [医] 宫内避孕环; 弯曲部分; vt. (使) 成环,(使)成圈; 以环连结; 使翻筋斗;
-
Collection : The root interface in the collection hierarchy. A collection represents(代表) a group of objects, known as its elements. Some collections allow duplicate(重复的) elements and others do not. Some are ordered and others unordered. The JDK does not provide any direct implementations of this interface: it provides implementations of more specific ( 特性,特殊的 )subinterfaces ( 子接口 )like Set and List. This interface is typically( 代表性地;作为特色地 ) used to pass collections around and manipulate( 操纵;操作 ) them where maximum ( 最大限度 )generality( 一般性 ) is desired.
-
Set: A collection that contains no duplicate elements. More formally, sets contain no pair of elements e1 and e2 such that e1.equals(e2), and at most one null element. As implied by its name, this interface models the mathematical set abstraction.
-
Hashset : This class implements the Set interface, backed( 支持 , 有背的;有财力支持的 ) by a hash table (actually a HashMap instance). It makes no guarantees ( 保证 )as to the iteration order of the set; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant( 常数;恒量,不变的 ) over time( 随着时间 ). This class permits( 许可 )the null element.
-
Hashset的实现不是同步的,namely,线程不安全的 因此用的时候要在外部加synchronizedset 关键字(Note that this implementation is not synchronized.)
-
spliterator() J2SE 8 新特性,
-
Spliterator(splitable iterator可分割迭代器)接口是Java为了并行遍历数据源中的元素而设计的迭代器,这个可以类比最早Java提供的顺序遍历迭代器Iterator,但一个是顺序遍历,一个是并行遍历 详细https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000007087438
-
-
Note that里面维护了一个a HashMap instance ,减少了equals方法的执行,通过hashcode大大增加的效率。
-
只允许一个null element
-
迭代器规则:它生成的迭代器一旦确定,就不允许再修改原容器里的元素,一旦修改其中元素,再使用原来迭代器进行遍历时,就会报出异常,当然java也禁用了其add 之类的方法(但有listIterator允许add)
-
J2SE 1.8 说明如下fail-fast
-
The iterators returned by this class's iterator and (listIterator list中有) methods are fail-fast: if the list is structurally(在结构上) modified (修改,改进的)at any time after the iterator is created, in any way except through the Iterator's own remove or (add listIterator的方法) methods, the iterator will throw a ConcurrentModificationException. Thus, in the face of concurrent (并发的,一致发生的)modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking arbitrary(任意的), non-deterministic (不确定的)behavior at an undetermined(待定的) time in the future.
-
-
-
LinkedHashSet : Hash table and linked list implementation of the Set interface, with predictable( 可预言的 ) iteration order. This implementation differs ( 不同 )from HashSet in that it maintains(维持,主张) a doubly-linked (双链表)list running through all of its entries(入口). This linked list defines the iteration ordering, which is the order in which elements were inserted into the set (insertion-order). Note that insertion order is not affected if an element is re-inserted into the set. (An element e is reinserted into a set s if s.add(e) is invoked when s.contains(e) would return true immediately prior to the invocation.)
-
维护着一个运行于所有条目的双重链接列表,此链接列表定义了迭代顺序,这样才实现了混沌有序
-
也有spliterator(),和迭代器规则
-
-
TreeSet A NavigableSet implementation based on a TreeMap. The elements are ordered using their natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at set creation time, depending on which constructor is used.
-
注意,此实现不是同步的 (Note that this implementation is not synchronized.)
-
迭代器规则
-
自然有序,且其判断相同是根据compareto方法,也可据此来决定顺序
-
-
-
List An ordered collection (also known as a sequence(序列)). The user of this interface has precise(精确的) control over where in the list each element is inserted. The user can access(n进入,使用,存取) elements by their integer index (position (方位)in the list), and search for elements in the list.
-
ArrayList :Resizable(可变的)-array implementation of the List interface. Implements all optional(可选的) list operations, and permits all elements, including null. In addition to (除什么之外)implementing the List interface, this class provides methods to manipulate(操纵) the size of the array that is used internally(内部的) to store(存储) the list. (This class is roughly equivalent to Vector, except that it is unsynchronized.)
-
内部有一个object对象的数组,自动增长,增长策略看源码
-
因为是随机存储的数组,故get 和set 为固定时间,add 和remove效率低
-
线程不安全
-
listIterator() 返回一个ListIterator 对象, 可以通过修改原来list的元素,可知原list绑定,实际上是一个arraylist的一个内部类,当然共用一个Object[] elementData
-
也有spliterator()
-
-
Vector The Vector class implements a growable array of objects. Like an array, it contains components(组件,成分) that can be accessed using an integer index. However, the size of a Vector can grow or shrink(缩小,畏缩) as needed to accommodate(适应) adding and removing items after the Vector has been created.
-
与ArraList不同的是它是线程安全的
-
其他大致相同
-
-
LinkedList Doubly-linked list implementation of the List and Deque(双队列) interfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements (including null ).
-
内部实现是一个node结点的双链表
-
故插入删除操作效率较高
-
线程不安全
-
listIterator() 返回一个ListIterator 对象, 可以通过修改原来list的元素,可知原list绑定,实际上是一个arraylist的一个内部类,当然共用一个Object[] elementData
-
也有spliterator()
-
-
PriorityQueue An unbounded(无限的,不受控制的) priority queue(队列) based on a priority(优先权) heap. The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to their natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is used. A priority queue does not permit null elements. A priority queue relying on natural ordering also does not permit insertion of non-comparable objects (doing so may result in ClassCastException).
-
有顺序的队列 每次从队列中取出的是具有最高优先权的元素。
-
线程不安全
-
没有listiterator
-
Iterator fail-fast
-
Compareto方法来实现顺序
-
-
-
Map An object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value.(至多一个值) This interface takes the place of the Dictionary class, which was a totally abstract class rather than an interface.
-
迭代方法
-
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 返回一个 Set映射的视图包含在这个Map
-
keySet() 返回一个 Set查看键包含在这个Map
-
values() 返回一个 Collection的价值观包含在这个Map。
-
-
是否Null
-
是否线程同步
-
是否有序
-
HashTable This class implements a hash table(哈希表), which maps keys to values. Anynon-null object can be used as a key or as a value. To successfully store (存储)and retrieve(检索) objects from a hashtable, the objects used as keys must implement the hashCode method and the equals method.
-
线程安全
-
存储的是键值对
-
不允许null
-
-
LinkedHashMap Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable(可预测的) iteration order. This implementation differs from HashMap in that it maintains(维持) a doubly-linked list running through all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering, which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map (insertion-order). Note that insertion order is not affected if a key is re-inserted into the map. (A key k is reinserted into a map m if m.put(k, v) is invoked when m.containsKey(k) would return true immediately prior to the invocation.)
-
线程不安全
-
Maintain 一个双链表,混沌有序
-
允许null
-
其他与HashTable一样
-
迭代方法通用
-
-
HashMap Hash table based implementation of the Map interface. This implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits null values and the null key. (The HashMap class is roughly (粗糙的)equivalent(等价物) to Hashtable, except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees(保证) as to the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time.
-
线程不安全
-
和HashSet,LinkedHashMap类似
-
允许null
-
没有顺序
-
迭代方法通用
-
-
TreeMap A Red-Black tree based NavigableMap(可执行的map) implementation. The map is sorted according to the natural ordering of its keys, or by a Comparator provided at map creation time, depending on which constructor is used.
-
线程不安全
-
有自然顺序,实现compareto方法,类似TreeSet
-
不允许null
-
迭代方法通用
-
-
-
-
Vector和ArrayList
1,vector是线程同步的,所以它也是线程安全的,而arraylist是线程异步的,是不安全的。如果不考虑到线程的安全因素,一般用arraylist效率比较高。
2,如果集合中的元素的数目大于目前集合数组的长度时,vector增长率为目前数组长度的100%,而arraylist增长率为目前数组长度的50%.如过在集合中使用数据量比较大的数据,用vector有一定的优势。
3,如果查找一个指定位置的数据,vector和arraylist使用的时间是相同的,都是0(1),这个时候使用vector和arraylist都 可以。而如果移动一个指定位置的数据花费的时间为0(n-i)n为总长度,这个时候就应该考虑到使用linklist,因为它移动一个指定位置的数据所花 费的时间为0(1),而查询一个指定位置的数据时花费的时间为0(i)。
ArrayList 和Vector是采用数组方式存储数据,此数组元素数大于实际存储的数据以便增加和插入元素,都允许直接序号索引元素,但是插入数据要设计到数组元素移动 等内存操作,所以索引数据快插入数据慢,Vector由于使用了synchronized方法(线程安全)所以性能上比ArrayList要 差,LinkedList使用双向链表实现存储,按序号索引数据需要进行向前或向后遍历,但是插入数据时只需要记录本项的前后项即可,所以插入数度较快!
Aarraylist和Linkedlist
1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList基于链表的数据结构。
2.对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针。
3.对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
这一点要看实际情况的。若只对单条数据插入或删除,ArrayList的速度反而优于LinkedList。但若是批量随机的插入删除数 据,LinkedList的速度大大优于ArrayList. 因为ArrayList每插入一条数据,要移动插入点及之后的所有数据。
HashMap与TreeMap
1、HashMap通过hashcode对其内容进行快速查找,而TreeMap中所有的元素都保持着某种固定的顺序,如果你需要得到一个有序的结果你就 应该使用TreeMap(HashMap中元素的排列顺序是不固定的)。HashMap中元素的排列顺序是不固定的)。
2、 HashMap通过hashcode对其内容进行快速查找,而TreeMap中所有的元素都保持着某种固定的顺序,如果你需要得到一个有序的结果你就应该 使用TreeMap(HashMap中元素的排列顺序是不固定的)。集合框架"提供两种常规的Map实现:HashMap和TreeMap (TreeMap实现SortedMap接口)。
3、在Map 中插入、删除和定位元素,HashMap 是最好的选择。但如果您要按自然顺序或自定义顺序遍历键,那么TreeMap会更好。使用HashMap要求添加的键类明确定义了hashCode()和 equals()的实现。 这个TreeMap没有调优选项,因为该树总处于平衡状态。
hashtable与hashmap
1、历史原因:Hashtable是基于陈旧的Dictionary类的,HashMap是Java 1.2引进的Map接口的一个实现 。
2、同步性:Hashtable是线程安全的,也就是说是同步的,而HashMap是线程序不安全的,不是同步的 。
3、值:只有HashMap可以让你将空值作为一个表的条目的key或value 。






















 323
323

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








