1 线性表定义
线性表(list)是零个或多个数据元素的集合,线性表中的数据元素之间是有顺序的,线性表中的数据元素个数是有限的,线性表中数据元素的类型必须相同。
2 线性表数学定义
线性表(linear list)也称为有序表(
order list
)。每一个实例都是元素的一个有序集合。每一个实例的形式为(e
1
,e
2
,e
3
,...,e
n-1
),其中n为又穷自然数,e
i
是线性表的元素,i是元素e
i
的索引,n是线性表的大小。元素可以被看做原子,它们本身的结构与线性表的结构无关。当n = 0时,线性表为空;当n>0时,e
0
是线性表的第0个元素,e
n-1
是线性表的最后一个元素。
3 线性表的性质
e0为线性表的第一个元素,只有一个后继, en为线性表的最后一个元素,只有一个前驱。除e0和en外的其它元素ei,既有前驱,又有后继线性表能够逐项访问和顺序存取。
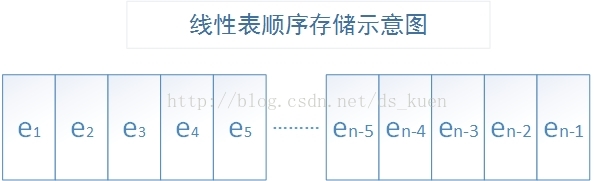
4线性表顺序存储的设计与实现
(1)顺序表节点的定义
//用数组来模拟线性表
typedef struct _tag_SeqList
{
int capacity;
int length;
int **node;
}TSeqList;
(2)顺序表的创建(返回链表)
//链表 创建
SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity) //O(1)
{
int ret;
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
tmp = (TSeqList *)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
ret = 1;
printf("func SeqList_Create() err :%d \n", ret);
return NULL;
}
memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(TSeqList));
tmp->capacity = capacity;
tmp->length = 0;
tmp->node = (int **)malloc(sizeof(void *) * capacity);
if (tmp->node == NULL)
{
ret = 2;
printf("func SeqList_Create() malloc err :%d \n", ret);
return NULL;
}
memset(tmp->node, 0, sizeof(void *) * capacity);
return tmp;
}
//链表 创建
int SeqList_Create2(int capacity, SeqList**handle)
{
int ret = 0;
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
tmp = (TSeqList *)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
ret = 1;
printf("func SeqList_Create2() err :%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(TSeqList));
tmp->capacity = capacity;
tmp->length = 0;
tmp->node = (int **)malloc(sizeof(void *) * capacity);
if (tmp->node == NULL)
{
ret = 2;
printf("func SeqList_Create2() malloc err :%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
*handle = tmp;
return ret;
}
//链表 销毁
void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
if (tmp->node != NULL)
{
free(tmp->node);
}
free(tmp);
return;
}
(5)顺序表清空
链表 清空
void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
tmp->length = 0;
memset(tmp->node, 0, (tmp->capacity * sizeof(void *)));
return;
}
(6)顺序表的长度
//链表 长度
int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
return tmp->length;
}
(7)顺序表的容量
//链表 容量
int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
return tmp->capacity;
}
(8)顺序表在某一个位置插入元素
//链表 在某一个位置 插入元素
int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos) //O(n)
{
TSeqList *tList = NULL;
int i = 0;
if (list == NULL || node == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
tList = (TSeqList *)list;
//如果满了
if (tList->length >= tList->capacity)
{
return -2;
}
//pos位置的容错处理
if (pos > tList->length)
{
pos = tList->length;
}
for (i = tList->length; i>pos; i--) //n
{
tList->node[i] = tList->node[i - 1];
}
tList->node[i] = (int*)node; //ok
tList->length++;
return 0;
}//获取某一个位置的链表结点
SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tList = NULL;
SeqListNode *tmp = NULL;
tList = (TSeqList *)list;
if (list == NULL || pos<0 || pos >= tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
tmp = tList->node[pos];
return tmp;
}
//删除某一个位置的结点
SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos) O(n)
{
int i = 0;
TSeqList *tList = NULL;
SeqListNode *tmp = NULL;
tList = (TSeqList *)list;
if (list == NULL || pos <0 || pos >= tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
tmp = tList->node[pos];
// pos = 3
for (i = pos + 1; i<tList->length; i++)
{
tList->node[i - 1] = tList->node[i];
}
tList->length--;
return tmp;
}//SeqList.h
#ifndef __MY_SEQLIST_H__
#define __MY_SEQLIST_H__
typedef void SeqList;
typedef void SeqListNode;
//链表 创建
SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity);
//链表 销毁
void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list);
链表 清空
void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list);
//链表 长度
int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list);
//链表 容量
int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list);
//链表 在某一个位置 插入元素
int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos);//获取某一个位置元素SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos);
//删除某一个位置的结点
SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos);
#endif //__MY_SEQLIST_H__//SeqList.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "seqlist.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
//用数组来模拟线性表
typedef struct _tag_SeqList
{
int capacity;
int length;
int **node;
}TSeqList;
//链表 创建
SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity) //O(1)
{
int ret;
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
tmp = (TSeqList *)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
ret = 1;
printf("func SeqList_Create() err :%d \n", ret);
return NULL;
}
memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(TSeqList));
tmp->capacity = capacity;
tmp->length = 0;
tmp->node = (int **)malloc(sizeof(void *) * capacity);
if (tmp->node == NULL)
{
ret = 2;
printf("func SeqList_Create() malloc err :%d \n", ret);
return NULL;
}
memset(tmp->node, 0, sizeof(void *) * capacity);
return tmp;
}
//链表 创建
int SeqList_Create2(int capacity, SeqList**handle)
{
int ret = 0;
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
tmp = (TSeqList *)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
ret = 1;
printf("func SeqList_Create2() err :%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(TSeqList));
tmp->capacity = capacity;
tmp->length = 0;
tmp->node = (int **)malloc(sizeof(void *) * capacity);
if (tmp->node == NULL)
{
ret = 2;
printf("func SeqList_Create2() malloc err :%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
*handle = tmp;
return ret;
}
//链表 销毁
void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
if (tmp->node != NULL)
{
free(tmp->node);
}
free(tmp);
return;
}
链表 清空
void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
tmp->length = 0;
memset(tmp->node, 0, (tmp->capacity * sizeof(void *)));
return;
}
//链表 长度
int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
return tmp->length;
}
//链表 容量
int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tmp = NULL;
if (list == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
tmp = (TSeqList *)list;
return tmp->capacity;
}
//链表 在某一个位置 插入元素
int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos) //O(n)
{
TSeqList *tList = NULL;
int i = 0;
if (list == NULL || node == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
tList = (TSeqList *)list;
//如果满了
if (tList->length >= tList->capacity)
{
return -2;
}
//pos位置的容错处理
if (pos > tList->length)
{
pos = tList->length;
}
for (i = tList->length; i>pos; i--) //n
{
tList->node[i] = tList->node[i - 1];
}
tList->node[i] = (int*)node; //ok
tList->length++;
return 0;
}
//获取某一个位置的链表结点
SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos) //O(1)
{
TSeqList *tList = NULL;
SeqListNode *tmp = NULL;
tList = (TSeqList *)list;
if (list == NULL || pos<0 || pos >= tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
tmp = tList->node[pos];
return tmp;
}
//删除某一个位置的结点
SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos) O(n)
{
int i = 0;
TSeqList *tList = NULL;
SeqListNode *tmp = NULL;
tList = (TSeqList *)list;
if (list == NULL || pos <0 || pos >= tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
tmp = tList->node[pos];
// pos = 3
for (i = pos + 1; i<tList->length; i++)
{
tList->node[i - 1] = tList->node[i];
}
tList->length--;
return tmp;
}
//test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "seqlist.h"
typedef struct _Teacher
{
char name[32];
int age ;
}Teacher;
void main()
{
int ret = 0, i = 0;
SeqList * list;
Teacher t1, t2, t3;
t1.age = 31;
t2.age = 32;
t3.age = 33;
list = SeqList_Create(10);
//思考1: 如何实现 链表的api(链表的算法) 和 具体的数据分离
//思考2: 链表库(业务逻辑) 测试程序的业务逻辑 结点的生命周期 归谁管?
ret = SeqList_Insert(list, (SeqListNode *)&t1, 0); //头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list, (SeqListNode *)&t2, 0); //头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list, (SeqListNode *)&t3, 0); //头插法
//遍历链表
for (i=0; i<SeqList_Length(list); i++ )
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(list, i); //获取链表结点
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("func SeqList_Get() err:%d \n ", ret);
return ;
}
printf("age:%d \n", tmp->age);
}
//销毁链表
while (SeqList_Length(list) > 0)
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Delete(list, 0);//
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("func SeqList_Get() err:%d \n ", ret);
return ;
}
printf("age:%d \n", tmp->age);
}
SeqList_Destroy(list);
system("pause");
return ;
}




















 868
868











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








