目录:
1.Binary Tree Level Order Traversal - 二叉树层次遍历 BFS
2.Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II - 二叉树层次遍历从低往高输出 BFS
3.Maximum Depth of Binary Tree - 求二叉树的深度 DFS
4.Balanced Binary Tree - 判断平衡二叉树 DFS
5.Path Sum - 二叉树路径求和判断DFS
题目概述:
Given a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left to right, level by level).
For example:
Given binary tree {3,9,20,#,#,15,7},
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its level order traversal as:
[ [3], [9,20], [15,7] ]
Here's an example:
1
/ \
2 3
/
4
\
5
The above binary tree is serialized as "{1,2,3,#,#,4,#,#,5}".
题目分析:
本题考查的就是二叉树的层次遍历,需要注意的是二叉树用数组的表示方法,二叉树的每层是从左到右存入数组的。方法包括:
1.层次遍历。二维数组存储数字和深度,输出二维数组即可,过于复杂。
2.通过队列BFS广度优先搜索。
3.通过DFS深度优先搜索实现。
我的代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//二叉树层次遍历 通过队列BFS广度优先搜索
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
queue<TreeNode*>q;
vector<int> level; //每层结果
int size,i;
TreeNode* p;
if(root==NULL) return result;
q.push(root); //入队
while(!q.empty()) {
//队列中有几个元素就依次遍历每个元素的左右结点
level.clear();
size=q.size();
for(i=0; i<size; i++) {
p=q.front(); //队首元素值赋给p
q.pop(); //出队
level.push_back(p->val);
if(p->left) { //依次压入左右结点元素
q.push(p->left);
}
if(p->right) {
q.push(p->right);
}
}
result.push_back(level); //添加每层数据
}
return result;
}
};
代码详解:
该题目你如果采用C语言二维数组过于复杂,故采用C++的容器vector实现。同时BFS广度优先搜索采用队列queue实现,常见方法如下(参考地址):
1.栈操作
#include<stack> 头文件
stack<int> s 定义栈
s.empty() 如果栈为空返回true,否则返回false
s.size() 返回栈中元素的个数
s.pop() 删除栈顶元素但不返回其值
s.top() 返回栈顶的元素,但不删除该元素
s.push() 在栈顶压入新元素 #include<queue> 头文件
queue<int> q 定义队列
q.empty() 如果队列为空返回true,否则返回false
q.size() 返回队列中元素的个数
q.pop() 删除队列首元素但不返回其值
q.front() 返回队首元素的值,但不删除该元素
q.push() 在队尾压入新元素
q.back() 返回队列尾元素的值,但不删除该元素 由于二叉树是从左至右进行输入,故层次遍历通过队列存储每层的结点,它存储的顺序也是前一个结点的左孩子结点、右孩子结点,依次顺序进出队列。
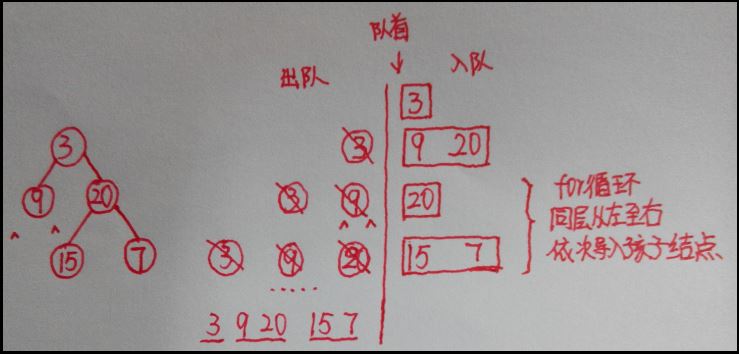
其他题目:
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
层次遍历从低往root结点输出,如 Given binary tree {3,9,20,#,#,15,7},
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its level order traversal as:
[ [15,7], [9,20], [3] ]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> level;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root==NULL)
return result;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
//层次遍历
level.clear();
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) { //注意:不能i<q.size() 当入队时它会变换
TreeNode* p=q.front();
q.pop();
level.push_back(p->val);
if(p->left)
q.push(p->left);
if(p->right)
q.push(p->right);
}
//每层结果存入容器
result.push_back(level);
}
/*
* 逆序输出 倒置容器调用函数
* reverse(result.begin(),result.end());
* return result;
*/
vector<vector<int>>::iterator iter; //迭代器
vector<vector<int>> res;
for(iter=result.end()-1; iter!=result.begin()-1; iter--)
{
level.clear();
for(int i=0; i<(*iter).size(); i++) //复制每层内容
{
level.push_back((*iter)[i]);
}
res.push_back(level);
}
return res;
}
};Maximum Depth of Binary Tree - 求二叉树的深度
常见方法通过BFS层次遍历计算二叉树层数及深度或通过DFS计算二叉树从root到leaf结点最长路径及深度,在采用BSF代码中可通过前面代码进行修改,但错误:
[0,2,4,1,null,3,-1,5,1,null,6,null,8] output=5 Excepted=4
故采用DFS进行深度递归搜索。代码如下:
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return (left >= right ? left : right) + 1;
}
Balanced Binary Tree - 判断平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树是一 棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。参考前面的计算深度方法完成。
int DFS(struct TreeNode* p) {
if(p==NULL)
return 0;
int left=DFS(p->left);
int right=DFS(p->right);
return (left>=right?left:right)+1;
}
//递归判断左右子树结点是否符合平衡二叉树
bool isBalancedNode(struct TreeNode* L,struct TreeNode* R) {
if(!L&&!R)
return true;
//自定义DFS函数计算结点的深度
int left=DFS(L);
int right=DFS(R);
//平衡二叉树左右结点深度相差0或1
if(abs(left-right)>1)
return false;
else if(L&&R) //必须存在 否则会报错RE [1,2]时R->left不存在
return isBalancedNode(L->left,L->right) && isBalancedNode(R->left,R->right);
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root&&!root->left&&!root->right)
return true;
else
return isBalancedNode(root->left,root->right);
}/**
* Definition for binary tree
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool checkBalance(TreeNode *node, int &dep)
{
if (node == NULL)
{
dep = 0;
return true;
}
int leftDep, rightDep;
bool leftBalance = checkBalance(node->left, leftDep);
bool rightBalance = checkBalance(node->right, rightDep);
dep = max(leftDep, rightDep)+1;
return leftBalance && rightBalance && (abs(rightDep - leftDep) <= 1);
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode *root) {
int dep;
return checkBalance(root, dep);
}
};Path Sum - 二叉树路径求和判断
Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.For example:
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path 5->4->11->2 which sum is 22.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
//思路:通过DFS计算root-to-leaf的结果
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(root==NULL)
return false;
else if(root&&!root->left&&!root->right&&root->val==sum) //仅root结点
return true;
else if(root&&!root->left&&!root->right&&root->val!=sum)
return false;
else //包括子结点
return hasPathSum(root->left,(sum - root->val)) ||
hasPathSum(root->right,(sum - root->val));
}(By:Eastmount 2015-9-11 凌晨3点半 http://blog.csdn.net/eastmount/)






















 1363
1363











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










