前面两次的自定义注解,都只是解析了一个注解,今天要讲的junit需要三个注解,而且解析框架中反射激活方法时要根据Before、Test、After的顺序来执行,需要注意的是Test注解可能会有多个,所以我们在外面定义一个数组,用来存储所有由@Test标注的方法。下面来看一下具体实现
- 三个注解的定义
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface Before {
}@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface Test {
}@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface After {
}- 在自己的测试类中使用自定义好的三个注解
public class MyJunitTest {
@Before
public void prepare(){
System.out.println(" before :所有的测试方法之前都先执行这个方法");
}
@After
public void destroy(){
System.out.println(" destroy :所有的测试方法之后都要执行这个方法");
}
@Test
public void testAdd(){
System.out.println(" test :testadd() ");
}
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
System.out.println(" test :testUpdate() ");
}
}- 最重要的注解解析框架
public class ParseJunit {
public void parseMethod(Class clazz) throws InstantiationException,
IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
//Before 的注解只有一个,直接在外面定义一个Method类型的变量
Method methodsBefore=null;
Method[] methodsTest=null;
int index=0;
Method methodsAfter=null;
//循环所有的方法
for (Method m : methods) {
//得到方法上的所有注解,因为不确定是Before还是After、Test,不能直接根据class得到注解
Annotation[] myJunitTest =m.getAnnotations();
//循环所有的注解,根据名字匹配
for(int i=0;i<myJunitTest.length;i++){
//根据名字匹配注解的类型
if(myJunitTest[0].annotationType().getSimpleName().endsWith("Before")){
methodsBefore=m;
}else if(myJunitTest[0].annotationType().getSimpleName().endsWith("Test")){
//如果为 Test ,判断这个数组是否为空,否:存入定义好的 数组中 然后下标加一
if(methodsTest==null){
//是,新生成一个数组,然后将 m 存入
methodsTest=new Method[ methods.length ];
}
methodsTest[index]=m;
index++;
}else if(myJunitTest[0].annotationType().getSimpleName().endsWith("After")){
methodsAfter=m;
}
}
}
//1、先执行 Before注解的方法
if(methodsBefore!=null){
methodsBefore.invoke(obj);
}
//2、执行Test 注解的 数组中的方法
if(methodsTest!=null && methodsTest.length>0){
for(Method m: methodsTest){
if(m!=null){
m.invoke(obj);
}
}
}
//3、最后执行 After 注解的方法
if(methodsAfter!=null){
methodsAfter.invoke(obj);
}
}
}可能运行效率不是最好的,但是基本效果已经实现,小伙伴们有更好的解决办法,敬请指教啊
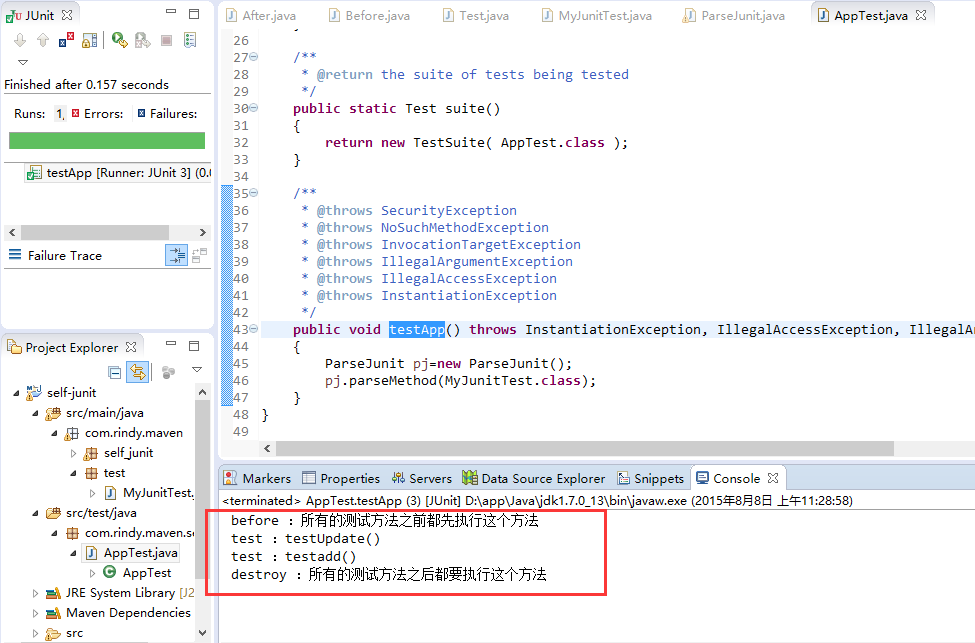
4. 下面我们测试一下自定义好的Junit
public void testApp() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException
{
ParseJunit pj=new ParseJunit();
pj.parseMethod(MyJunitTest.class);
}结果:
自定义注解,最核心的部分就是解析框架的实现,上面提到的三个案例都是基于方法的注解,有兴趣的小伙伴可以找找类注解、属性注解的解析。
























 2755
2755

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








