测试代码
public class TestGuavCallback {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//步骤1:使用线程池调用服务
ListeningExecutorService service = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10));
ListenableFuture<Future<Integer>> listenerFuture = service.submit(new Callable<Future<Integer>>() {
public Future<Integer> call() {
System.out.println("call");
return null;
}
});
//步骤2:返回结果,主要在静态的Futures中进行的操作
Futures.addCallback(listenerFuture, new FutureCallback<Future<Integer>>() {
public void onSuccess(Future<Integer> future) {
try {
Integer retInt = (Integer) future.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
System.out.println("onSuccess");
}
public void onFailure(Throwable thrown) {
System.out.println("onFailure");
}
});
}
}步骤1:使用线程池调用服务
1、 初始化一个ThreadPoolExecutor
//A1:最终ListeningDecorator 执行任务是使用的这个方法
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
delegate.execute(command);
}2、 初始化一个ListeningDecorator extends AbstractListeningExecutorService
public abstract class AbstractListeningExecutorService
extends AbstractExecutorService implements ListeningExecutorService {
@Override protected final <T> ListenableFutureTask<T> newTaskFor(Runnable runnable, T value) {
return ListenableFutureTask.create(runnable, value);
}
//覆盖掉的父类的方法newTaskFor,提供submit中调用,返回ListenableFutureTask
@Override protected final <T> ListenableFutureTask<T> newTaskFor(Callable<T> callable) {
return ListenableFutureTask.create(callable);
}
@Override public ListenableFuture<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return (ListenableFuture<?>) super.submit(task);
}
@Override public <T> ListenableFuture<T> submit(Runnable task, @Nullable T result) {
return (ListenableFuture<T>) super.submit(task, result);
}
//调用这个方法进行任务submit,回调当前覆盖掉的父类的方法newTaskFor
@Override public <T> ListenableFuture<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
return (ListenableFuture<T>) super.submit(task);
}
}对应的AbstractExecutorService类对应subm方法如下
/**
* @throws RejectedExecutionException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task);
execute(ftask);//A1:使用ThreadPoolExecutor的方法执行
return ftask;
}步骤2:绑定回调
1、 Futures的方法,将ListenableFuture和CallBack绑定
Futures的方法:
public static <V> void addCallback(ListenableFuture<V> future,
FutureCallback<? super V> callback) {
addCallback(future, callback, directExecutor());
}
public static <V> void addCallback(final ListenableFuture<V> future,
final FutureCallback<? super V> callback, Executor executor) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(callback);
Runnable callbackListener = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
final V value;
try {
// TODO(user): (Before Guava release), validate that this
// is the thing for IE.
value = getUninterruptibly(future);//循环调用获得结果
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
callback.onFailure(e.getCause());
return;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
callback.onFailure(e);
return;
} catch (Error e) {
callback.onFailure(e);
return;
}
callback.onSuccess(value);
}
};
future.addListener(callbackListener, executor);//在executor执行getUninterruptibly
}
public static <V> V getUninterruptibly(Future<V> future)
throws ExecutionException {
boolean interrupted = false;
try {
while (true) {
try {
return future.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
2、绑定的代码
public static <V> ListenableFutureTask<V> create(
Runnable runnable, @Nullable V result) {
return new ListenableFutureTask<V>(runnable, result);
}
ListenableFutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
super(callable);
}
ListenableFutureTask(Runnable runnable, @Nullable V result) {
super(runnable, result);
}
@Override
public void addListener(Runnable listener, Executor exec) {
executionList.add(listener, exec);//对用的listener方法处理
}
最终ExecutionList方法中执行对应的方法如下:
public void add(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) {
// Fail fast on a null. We throw NPE here because the contract of
// Executor states that it throws NPE on null listener, so we propagate
// that contract up into the add method as well.
Preconditions.checkNotNull(runnable, "Runnable was null.");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(executor, "Executor was null.");
// Lock while we check state. We must maintain the lock while adding the
// new pair so that another thread can't run the list out from under us.
// We only add to the list if we have not yet started execution.
synchronized (this) {
if (!executed) {
runnables = new RunnableExecutorPair(runnable, executor, runnables);
return;
}
}
// Execute the runnable immediately. Because of scheduling this may end up
// getting called before some of the previously added runnables, but we're
// OK with that. If we want to change the contract to guarantee ordering
// among runnables we'd have to modify the logic here to allow it.
executeListener(runnable, executor);//最终执行的方法
}
//实际执行方法的的DirectExecutor
/** See {@link #directExecutor} for behavioral notes. */
private enum DirectExecutor implements Executor {
INSTANCE;
@Override public void execute(Runnable command) {
command.run();
}
}
3、回调核心流程
ListenableFutureTask的done方法
主要属性:
// The execution list to hold our listeners.
private final ExecutionList executionList = new ExecutionList();
处理逻辑:
回调方法链,当在exector执行完成的时候,进行future结果设置的时候,触发done函数,从而执行executionList上的execture方法,执行对应的回调。
/**
* Internal implementation detail used to invoke the listeners.
*/
@Override
protected void done() {
executionList.execute();
}
ExecutionList类执中对应的回调的设置,核心逻辑在此。
public void execute() {
// Lock while we update our state so the add method above will finish adding
// any listeners before we start to run them.
RunnableExecutorPair list;
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) {
return;
}
executed = true;
list = runnables;
runnables = null; // allow GC to free listeners even if this stays around for a while.
}
// If we succeeded then list holds all the runnables we to execute. The pairs in the stack are
// in the opposite order from how they were added so we need to reverse the list to fulfill our
// contract.
// This is somewhat annoying, but turns out to be very fast in practice. Alternatively, we
// could drop the contract on the method that enforces this queue like behavior since depending
// on it is likely to be a bug anyway.
// N.B. All writes to the list and the next pointers must have happened before the above
// synchronized block, so we can iterate the list without the lock held here.
RunnableExecutorPair reversedList = null;
while (list != null) {
RunnableExecutorPair tmp = list;
list = list.next;
tmp.next = reversedList;
reversedList = tmp;
}
while (reversedList != null) {
executeListener(reversedList.runnable, reversedList.executor);
reversedList = reversedList.next;
}
}
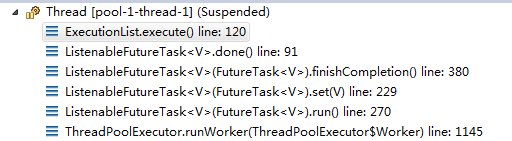
这里写代码片回调堆栈如下:
回调对象ExecutionList解析
@GuardedBy("this")
runnables是一个事件链表,其中每个对象中有引用一个执行体,详见下面RunnableExecutorPair对象。
private RunnableExecutorPair runnables;
@GuardedBy("this")
private boolean executed;
//事件绑定消息处理队列
private static final class RunnableExecutorPair {
final Runnable runnable;
final Executor executor;
@Nullable RunnableExecutorPair next;
RunnableExecutorPair(Runnable runnable, Executor executor, RunnableExecutorPair next) {
this.runnable = runnable;
this.executor = executor;
this.next = next;
}
}总结
实现的思路总结:
1、newTaskFor时候建立自己定制的ListenableFuture
2、针对定制的ListenableFuture,通过Futures将回调shijian和ListenableFuture进行关联
3、覆盖地址future的done方法,在done的时候执行对应的回调
4、guava还提供了ListeningExecutorService和ScheduledListeningDecorator的支持,后续可以继续分析
























 9481
9481











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










