随着JSON的广泛应用,解析JSON也成了程序员的一项基本技能。今天介绍JSON解析利器-Gson和fastjson
Gson是谷歌封装的JSON解析类库,使用方便,fastjson是阿里巴巴的产品,使用也非常方便,我问小满喜欢用哪个?他说Gson,why?因为Gson单词少,写着方便!小满,我觉得你说的很有道理。
- fromJson(String json, Class <T> classOfT)方法来实现从Json到java对象的转换。
- toJson(Object src)方法实现对象转化为JSON字符串。
首先看一下fromJson方法
通常我们都会从网络中获取数据,今天介绍一个获取百度天气的
http://api.map.baidu.com/telematics/v3/weather?location=CITY_NAME&output=json&ak=W69oaDTCfuGwzNwmtVvgWfGH
其中CITY_NAME就是城市名称,通过这个就可以获取到对应城市的天气了。下面就来解析它。
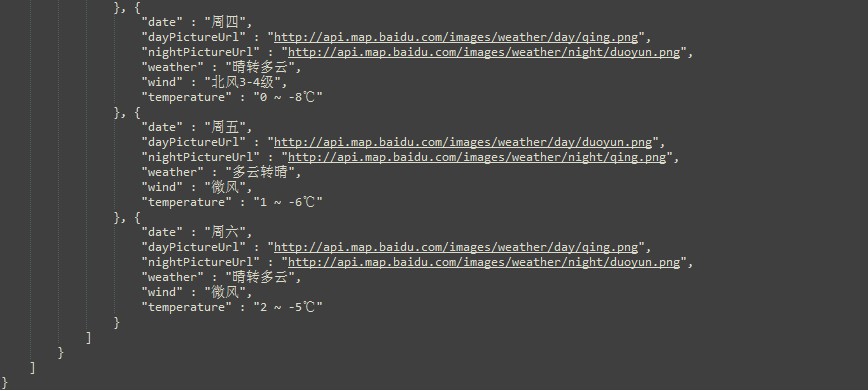
首先看一下天气的数据结构
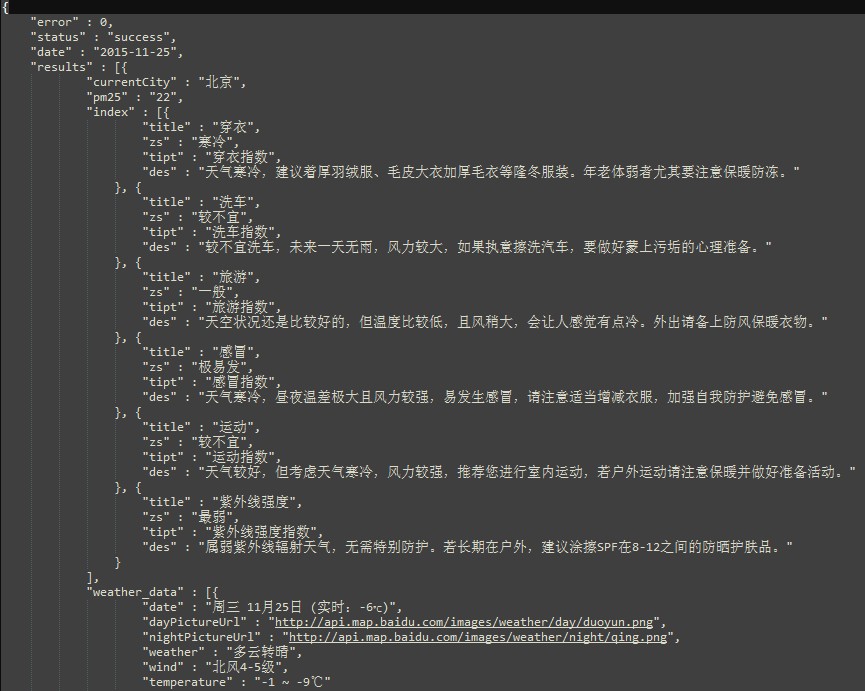
下面我们分析一下这个数据结构,再根据数据结构定义好对象就Ok啦
根元素
以下是我定义的根对象
public class WeatherInfo {
private int error;
private String status;
private String date;
private List<WeatherResults> results;
//省去setter和getter方法
}再定义
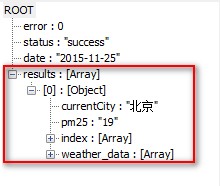
List型的results
public class WeatherResults {
private String currentCity;
private String pm25;
private List<WeatherSuggest> index;
private List<WeatherDay> weather_data;
//省去setter和getter方法
}在WeatherResults中再定义两个List型的index和weather_data
public class WeatherSuggest {
private String title;
private String zs;
private String tipt;
private String des;
//省去setter和getter方法
}
public class WeatherDay {
private String date;
private String dayPictureUrl;
private String nightPictureUrl;
private String weather;
private String wind;
private String temperature;
//省去setter和getter方法
}JSON数据太长,请访问
http://api.map.baidu.com/telematics/v3/weather?location=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC&output=json&ak=W69oaDTCfuGwzNwmtVvgWfGH
获取JSON数据,有了JSON数据下一步就是将JSON数据映射到对应的对象上
核心代码只需两行
String city = URLEncoder.encode("北京", "UTF-8");
String url = "http://api.map.baidu.com/telematics/v3/weather?location=CITY&output=json&ak=W69oaDTCfuGwzNwmtVvgWfGH".replace("CITY", city);
//调用一个发送http请求的方法,后面会有博客写如何发送http请求
//发送请求后就得到了json字符串
String jsonStr = sendGet(url);
//JSON的核心代码
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().create();
WeatherInfo weatherInfo = gson.fromJson(jsonStr, WeatherInfo.class);
//只需两行代码,就完成了json字符串到对象的映射
//如果除去Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().create();只有一行代码,是不是很方便使用fastjson的方法
WeatherInfo weatherInfo = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr, WeatherInfo.class);//只需一行有了对象,如果需要输出其中的数据,就很简单了。
假设要得到紫外线强度的des
weatherInfo.getResults().get(0).getIndex().get(5).getDes()得到数据
紫外线强度较弱,建议出门前涂擦SPF在12-15之间、PA+的防晒护肤品。
要得到天气情况
WeatherInfo weatherInfo = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr, WeatherInfo.class);
List<WeatherDay> weatherDatas = weatherInfo.getResults().get(0).getWeather_data();
System.out.println(weatherInfo.getResults().get(0).getCurrentCity());
for(WeatherDay weatherDay:weatherDatas){
System.out.print(weatherDay.getDate()+" ");
System.out.print(weatherDay.getWeather());
System.out.println(weatherDay.getTemperature());
}输出结果
北京
周三 11月25日 (实时:-7℃) 晴-1 ~ -9℃
周四 晴转多云0 ~ -8℃
周五 多云转晴1 ~ -6℃
周六 多云3 ~ -5℃
再看一下toJson方法
toJson方法更简单,有了对象,直接调用toJson即可得到JSON字符串
String json = gson.toJson(weatherInfo);使用fastjson的方法
String json = JSON.toJSONString(weatherInfo);使用fastjson会乱序,准确的说是fastjson对其进行了排序,而不是按照字段的顺序。
就可以得到同访问
http://api.map.baidu.com/telematics/v3/weather?location=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC&output=json&ak=W69oaDTCfuGwzNwmtVvgWfGH
一样的字符串

























 447
447

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








