参考http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6a4fccc90101a31r.html
y=filtfilt(a,b,x);的a,b系数由MATLAB实现
例如 在MATLAB中
[b,a]=butter(5,0.1,'low');%低通滤波
disp('b=')
disp(b)
disp('a=')
disp(a)
C语言实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define EPS 0.000001
//filter函数
void filter(const double* x, double* y, int xlen, double* a, double* b, int nfilt, double* zi)//nfilt为系数数组长度
{
double tmp;
int i,j;
//normalization
if( (*a-1.0>EPS) || (*a-1.0<-EPS) )
{
tmp=*a;
for(i=0;i<nfilt;i++)
{
b[i]/=tmp;
a[i]/=tmp;
}
}
memset(y,0,xlen*sizeof(double));//将y清零,以双浮点为单位
a[0]=0.0;
for(i=0;i<xlen;i++)
{
for(j=0;i>=j&&j<nfilt;j++)
{
y[i] += (b[j]*x[i-j]-a[j]*y[i-j]);
}
if(zi&&i<nfilt-1) y[i] += zi[i];
}
a[0]=1.0;
}
//矩阵乘法
void trmul(double *a,double *b,double *c,int m,int n,int k)//矩阵乘法 m为a的行数,n为a的列数数,k为b的行数,第一个矩阵列数必须要和第二个矩阵的行数相同
{
int i,j,l,u;
for (i=0; i<=m-1; i++)
for (j=0; j<=k-1; j++)
{
u=i*k+j; c[u]=0.0;
for (l=0; l<=n-1; l++)
c[u]=c[u]+a[i*n+l]*b[l*k+j];
}
return;
}
//求逆矩阵,当返回值为0时成功,a变为逆矩阵
int rinv(double *a,int n)//逆矩阵
{
int *is,*js,i,j,k,l,u,v;
double d,p;
is=(int *)malloc(n*sizeof(int));
js=(int *)malloc(n*sizeof(int));
for (k=0; k<=n-1; k++)
{ d=0.0;
for (i=k; i<=n-1; i++)
for (j=k; j<=n-1; j++)
{ l=i*n+j; p=fabs(a[l]);
if (p>d) { d=p; is[k]=i; js[k]=j;}
}
if (d+1.0==1.0)
{ free(is); free(js); printf("err**not invn");
return(0);
}
if (is[k]!=k)
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
{ u=k*n+j; v=is[k]*n+j;
p=a[u]; a[u]=a[v]; a[v]=p;
}
if (js[k]!=k)
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
{ u=i*n+k; v=i*n+js[k];
p=a[u]; a[u]=a[v]; a[v]=p;
}
l=k*n+k;
a[l]=1.0/a[l];
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
if (j!=k)
{ u=k*n+j; a[u]=a[u]*a[l];}
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
if (i!=k)
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
if (j!=k)
{ u=i*n+j;
a[u]=a[u]-a[i*n+k]*a[k*n+j];
}
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
if (i!=k)
{ u=i*n+k; a[u]=-a[u]*a[l];}
}
for (k=n-1; k>=0; k--)
{
if (js[k]!=k)
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
{ u=k*n+j; v=js[k]*n+j;
p=a[u]; a[u]=a[v]; a[v]=p;
}
if (is[k]!=k)
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
{ u=i*n+k; v=i*n+is[k];
p=a[u]; a[u]=a[v]; a[v]=p;
}
}
free(is);
free(js);
return(0);
}
//filtfilt函数
int filtfilt(double* x, double* y, int xlen, double* a, double* b, int nfilt)
{
int nfact;
int tlen; //length of tx
int i;
double *tx,*tx1,*p,*t,*end;
double *sp,*tvec,*zi;
double tmp,tmp1;
nfact=nfilt-1; //3*nfact: length of edge transients
if(xlen<=3*nfact || nfilt<2) return -1;
//too short input x or a,b
//Extrapolate beginning and end of data sequence using a "reflection
//method". Slopes of original and extrapolated sequences match at
//the end points.
//This reduces end effects.
tlen=6*nfact+xlen;
tx=(double *)malloc(tlen*sizeof(double));
tx1=(double *)malloc(tlen*sizeof(double));
sp=(double *)malloc( sizeof(double) * nfact * nfact );
tvec=(double *)malloc( sizeof(double) * nfact );
zi=(double *)malloc( sizeof(double) * nfact );
if( !tx || !tx1 || !sp || !tvec || !zi ){
free(tx);
free(tx1);
free(sp);
free(tvec);
free(zi);
return 1;
}
tmp=x[0];
for(p=x+3*nfact,t=tx;p>x;--p,++t)
*t=2.0*tmp-*p;
for(end=x+xlen;p<end;++p,++t)
*t=*p;
tmp=x[xlen-1];
for(end=tx+tlen,p-=2;t<end;--p,++t)
*t=2.0*tmp-*p;
//now tx is ok.
end = sp + nfact*nfact;
p=sp;
while(p<end) *p++ = 0.0L; //clear sp
sp[0]=1.0+a[1];
for(i=1;i<nfact;i++)
{
sp[i*nfact]=a[i+1];
sp[i*nfact+i]=1.0L;
sp[(i-1)*nfact+i]=-1.0L;
}
for(i=0;i<nfact;i++)
{
tvec[i]=b[i+1]-a[i+1]*b[0];
}
if(rinv(sp,nfact)){
free(zi);
zi=NULL;
}
else{
trmul(sp,tvec,zi,nfact,nfact,1);
}//zi is ok
free(sp);free(tvec);
//filtering tx, save it in tx1
tmp1=tx[0];
if(zi)
for( p=zi,end=zi+nfact; p<end;) *(p++) *= tmp1;
filter(tx,tx1,tlen,a,b,nfilt,zi);
//reverse tx1
for( p=tx1,end=tx1+tlen-1; p<end; p++,end--){
tmp = *p;
*p = *end;
*end = tmp;
}
//filter again
tmp1 = (*tx1)/tmp1;
if(zi)
for( p=zi,end=zi+nfact; p<end;) *(p++) *= tmp1;
filter(tx1,tx,tlen,a,b,nfilt,zi);//
//reverse to y
end = y+xlen;
p = tx+3*nfact+xlen-1;
while(y<end){
*y++ = *p--;
}
free(zi);
free(tx);
free(tx1);
return 0;
}
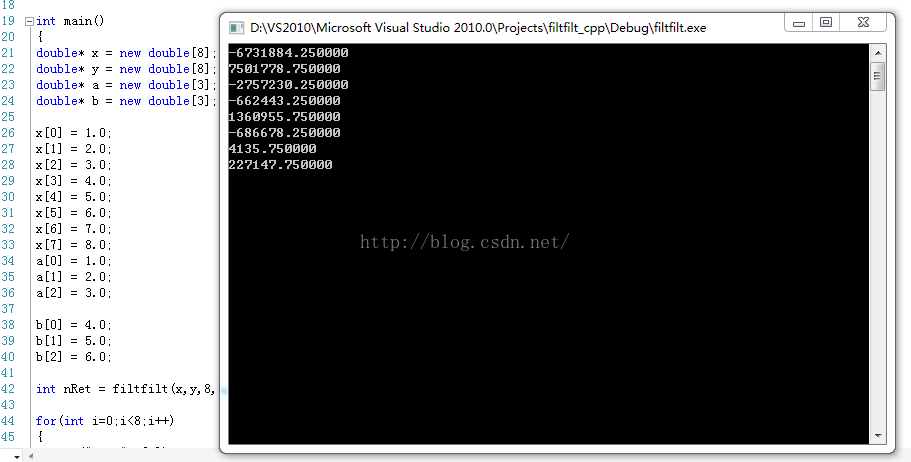
int main()
{
double* x = new double[8];
double* y = new double[8];
double* a = new double[3];
double* b = new double[3];
x[0] = 1.0;
x[1] = 2.0;
x[2] = 3.0;
x[3] = 4.0;
x[4] = 5.0;
x[5] = 6.0;
x[6] = 7.0;
x[7] = 8.0;
a[0] = 1.0;
a[1] = 2.0;
a[2] = 3.0;
b[0] = 4.0;
b[1] = 5.0;
b[2] = 6.0;
int nRet = filtfilt(x,y,8,a,b,3);
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
printf("%f\n",y[i]);
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
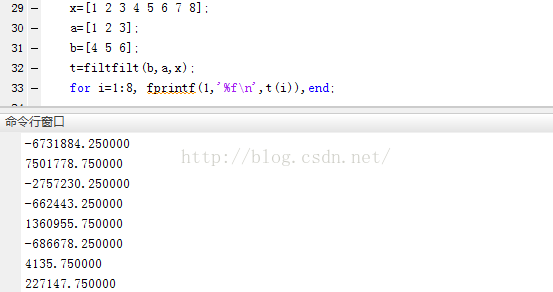
在MATLAB中:
x=[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8];
a=[1 2 3];
b=[4 5 6];
t=filtfilt(b,a,x);
for i=1:8, fprintf(1,'%f\n',t(i)), end;
结果:
例子在VS和MATLAB下运行的filtflit计算结果一致





















 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








