------<ahref="http://www.itheima.com" target="blank">Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训</a>、期待与您交流! -------
异常的基本概念
异常的分类
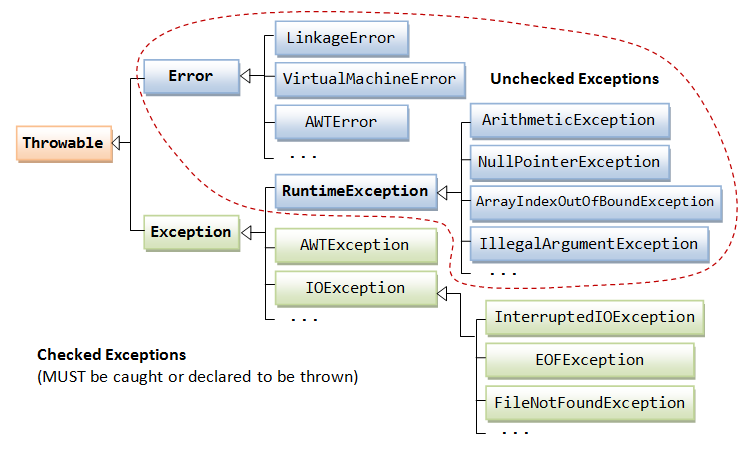
问题划分为两种:
Error类:严重的问题,一般不编写针对性的代码对其进行处理。Exception类:非严重的问题,可以使用针对性的处理方式进行处理。
Exception还可以进一步分成两类:
非RuntimeException:
1,编译时被检测的异常。
2,该异常在编译时,如果没有处理(没有抛也没有try),编译失败。
3,该异常被标识,代表这可以被处理。
RuntimeException:
1,编译时不被检测的异常,RuntimeException及其子类都是运行时的异常
2,在编译时,不需要处理,编译器不检查。
3,该异常的发生,建议不处理,让程序停止。需要对代码进行修正。
异常处理的基本格式
try
{
//需要被检测的代码:statements that can throw exceptions
}
catch (Exception e)
{
//处理异常的代码:statements executed when exception is thrown
}
finally {
//一定会执行的代码:statements are executed whether or not exceptions occour
}一个会产生异常的代码示例
class Division
{
int div(int a,int b)
{
return a/b;
}
}
class ExceptionDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Division d = new Division();
int x = d.div(4,1);
/*
* x=4
* over
*/
int y = d.div(4, 0);//在编译时期不会报错
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Division.div(ExceptionDemo.java:5)
at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:19)
该异常发生后,其下语句一概未执行
*/
System.out.println("x=" + x);
System.out.println("y=" + y);
System.out.println("over");
}
}异常的处理过程
try...catch:尝试、捕获与处理
class Division
{
int div(int a,int b)
{
return a/b;
}
}
class ExceptionDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Division d = new Division();
try
{
int x = d.div(4,0);//异常发生之处
System.out.println("x="+x);//此处的代码不再执行
}
catch (Exception e)//Exception e = new ArithmeticException();相当于多态
{
System.out.println("除零啦");
/*
除零啦
over
*/
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//String getMessage():获取异常信息。
/*
/ by zero
over
*/
System.out.println(e.toString());// 异常名称 : 异常信息。
/*
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
over
*/
e.printStackTrace();//异常名称,异常信息,异常出现的位置。打印异常的堆栈的跟踪信息。
/*
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Division.div(ExceptionDemo.java:5)
at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:17)
over
*/
//其实jvm默认的异常处理机制,就是在调用printStackTrace方法。
}
System.out.println("over");//因为有了catch语句,此处的over总是会执行到
}
}在方法上throws一个Exception:
这样的话,有可能出现问题的方法你不得不在使用它之前进行异常处理
class Division
{
int div(int a,int b) throws Exception//在功能上通过throws的关键字声明了该功能有可能会出现问题。
{
return a/b;
}
}
class ExceptionDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Division d = new Division();
int x = d.div(4,0);//异常发生之处
//此时不处理这个问题,编译就不会通过,把问题转换到编译时期
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Unhandled exception type Exception
at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:16)
*/
System.out.println("over");
}
}throws:我也不管了,抛出去让上面处理
针对上面不处理便会报错的情况,如果不用try..catch代码块进行处理,可以抛出问题。处理有问题的功能要么捕获处理、要么抛出去,两种方式。
与上一版本的区别是,上一版本不抛也不处理,连编译也不会通过,如果把问题抛出去了,编译可以通过,不过JVM还是会用默认处理方式打印错误信息。
class Division
{
int div(int a,int b) throws Exception//在功能上通过throws的关键字声明了该功能有可能会出现问题。
{
return a/b;
}
}
class ExceptionDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Division d = new Division();
int x = d.div(4,0);//异常发生之处
//此时不处理这个问题,编译就不会通过,把问题转换到编译时期
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Division.div(ExceptionDemo.java:5)
at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:16)
*/
System.out.println("over");//在抛的情况下,最后的这行代码不会执行到
}
}多异常处理
1,声明异常时,建议声明更为具体的异常。这样处理的可以更具体。
2,对方声明几个异常,就对应有几个catch块。不要定义多余的catch块。
3,如果多个catch块中的异常出现继承关系,父类异常catch块放在最下面。
4,建立在进行catch处理时,catch中一定要定义具体处理方式。不要简单定义一句 e.printStackTrace(),也不要简单的就书写一条输出语句。
2,对方声明几个异常,就对应有几个catch块。不要定义多余的catch块。
3,如果多个catch块中的异常出现继承关系,父类异常catch块放在最下面。
4,建立在进行catch处理时,catch中一定要定义具体处理方式。不要简单定义一句 e.printStackTrace(),也不要简单的就书写一条输出语句。
class Demo2
{
int div(int a,int b) throws ArithmeticException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException//在功能上通过throws的关键字声明了该功能有可能会出现问题。
{
int[] arr = new int[a];
System.out.println(arr[4]);
return a/b;
}
}
class ExceptionDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args) //throws Exception
{
Demo2 d = new Demo2();
try
{
int x = d.div(4,1);//脚标越界异常
int y = d.div(3, 0);//除零异常
System.out.println("x="+x);
}
catch (ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
System.out.println("被零除了!!");
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)//越界异常和除零异常不会同时执行到,一旦越界后面就不会执行
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
System.out.println("角标越界啦!!");
}
catch(Exception e)//父类异常一定要放在最下面,否则会报错,而且不建议这样写,会把问题给隐藏起来,真发生其他问题,就让程序停掉
{
System.out.println("hahah:"+e.toString());
}
/*如果把catch(Exception e)放到catch块最上面
*在它下面再catch ArithmeticException和ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,会发生如下错误:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problems:
Unreachable catch block for ArithmeticException. It is already handled by the catch block for Exception
Unreachable catch block for ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException. It is already handled by the catch block for Exception
at ExceptionDemo2.main(ExceptionDemo2.java:31)
*/
System.out.println("over");
}
}
自定义异常
为什么需要自定义异常?
因为项目中会出现特有的问题,而这些问题并未被java所描述并封装对象。所以对于这些特有的问题可以按照java的对问题封装的思想。将特有的问题。进行自定义的异常封装。
为什么自定义异常必须是自定义类继承Exception?
异常体系有一个特点:因为异常类和异常对象都被抛出。他们都具备可抛性。这个可抛性是Throwable这个体系中独有特点。只有这个体系中的类和对象才可以被throws和throw操作。
throws和throw的区别:
throws:使用在函数上,后面跟的异常类可以跟多个,用逗号隔开。throw:使用在函数内,throw后跟的是其抛出的异常对象。
/*
需求:在本程序中,对于除数是-1,也视为是错误的是无法进行运算的。
那么就需要对这个问题进行自定义的描述。
*/
class Demo3
{
int div(int a,int b)throws FuShuException//此处选择第二种处理方式,在函数上声明让调用者处理
/*当在函数内部出现了throw抛出异常对象,那么就必须要给对应的处理动作。
要么在内部try catch处理。
要么在函数上声明让调用者处理。
*/
{
if(b<0)
//在函数内部出现了throw抛出异常对象
throw new FuShuException("出现了除数是负数的情况------ / by Negative",b);//手动通过throw关键字抛出一个自定义异常的对象。
return a/b;
}
}
class FuShuException extends Exception //getMessage();
{
/*
如何定义异常信息?
因为父类中已经把异常信息的操作都完成了。
所以子类只要在构造时,将异常信息传递给父类通过super语句。
那么就可以直接通过getMessage方法获取自定义的异常信息。
*/
private int value;
/*对比:麻烦的方式-复写getMessage方法
private String msg;
FuShuException(String msg){//构造函数overload,获取传入的初始化msg
this.msg = msg
}
public String getMessage()//复写getMessage()的方法
{
return msg;
}
*/
FuShuException()//Throwable中已经有getMessage()方法了,不必再复写了
{
super();
}
//为了能够获取到输入错误的值所超载的构造函数
FuShuException(String msg,int value)//把分母的值传给了value
{
super(msg);//把msg传给父类Throwable的构造函数
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue()//封装,提供外界获取其值的方法
{
return value;
}
}
class ExceptionDemo3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Demo3 d = new Demo3();
try
{
int x = d.div(4,-9);
//int div(int a,int b)throws FuShuException,所以必须选择两种处理方式中的一种
System.out.println("x="+x);
}
catch (FuShuException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
/*
FuShuException: 出现了除数是负数的情况------ / by Negative
over
*/
System.out.println("除数出现负数了");
/*
除数出现负数了
over
*/
System.out.println("错误的负数是:"+e.getValue());
/*
错误的负数是:-9
over
*/
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
/*
出现了除数是负数的情况------ / by Negative
over
*/
}
System.out.println("over");
}
}
RuntimeException:运行时异常
不需要让调用者处理。当该异常发生,希望程序停止。因为在运行时,出现了无法继续运算的情况,希望停止程序后,对代码进行修正。
自定义异常时:如果该异常的发生,无法在继续进行运算,就让自定义异常继承RuntimeException。
class Demo4
{
//第一种情况:RuntimeException 运行时异常
/*在函数内容中通过throw关键字抛出该异常
*函数上可以不用抛出,编译一样通过
*
*如果不是RuntimeException,在函数内容中抛出该异常
*则要使用两种处理方式:
*1.在函数声明时throws:int div(int a,int b) throws Exception
*
*2.在函数声明的内部:try...catch:
int div(int a,int b)
{
if(b==0)
try
{
throw new Exception("被零除啦");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return a/b;
}
*/
int div(int a,int b)
{
if(b==0)
throw new ArithmeticException("被零除啦");//函数内部抛出错误了
//如果此处是throw new Exception();将会编译失败
return a / b;
}
//第二种情况:在函数上声明了该异常。调用者可以不用进行处理。编译一样通过;
/*如果不是RuntimeException,需要两种处理方式:
* 1. 调用者throws:
* public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
* 2. 调用者try..catch
Demo4 d = new Demo4();
int x = d.div(4,0);
try
{
int y = d.div2(3, 0);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
*/
int div2(int a,int b) throws ArithmeticException
{
return a / b;
}
}
class ExceptionDemo4
{
public static void main(String[] args)
//函数内部抛出错误了,在主函数调用时却没有try...catch,也没有throws,因为Arithmetic异常是运行时异常
{
Demo4 d = new Demo4();
int x = d.div(4,0);
int y = d.div2(3, 0);
System.out.println("x=" + x);
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: 被零除啦
at Demo4.div(ExceptionDemo4.java:6)
at ExceptionDemo4.main(ExceptionDemo4.java:17)
*/
System.out.println("y=" + y);//如果int x = d.div(4,0);已经发生异常,则此处不会被执行到
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Demo4.div2(ExceptionDemo4.java:53)
at ExceptionDemo4.main(ExceptionDemo4.java:66)
*/
System.out.println("over");
}
}
finally
finally代码块:定义一定执行的代码。通常用于关闭资源。
基本示例
try
{
//连接数据库;
//数据操作;;
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
//对数据库进行异常处理;
}
finally
{
//关闭数据库;
//该动作,无论数据操作是否成功,一定要关闭资源。
}
public class CrazyWithZeros {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
int answer = divideTheseNumbers(5, 0);
}
catch(Exception e)//5. 捕获到由divideTheseNumbers throws过来的Arithmetic异常,并给出相应的处理方法
{
System.out.println("Tried Twice, still didn't work");//6. 输出该异常处理的语句
}
}
public static int divideTheseNumbers(int a, int b) throws Exception
{
int c = 0;
try
{
c = a / b;
System.out.println("It worked!");
}
catch (Exception e) //1.发生异常后最先进入该catch块内
{
System.out.println("Didn't work the first time.");//2.输出异常处理语句
c = a / b;//3.再次运算a / b,再次发生异常,这一次发生异常,没有与之对应的catch块来处理该异常
System.out.println("It worked the second time!");//因为前面出现异常,这行代码永远不会执行到
}
finally
{
System.out.println("Better clean up my mess.");//4.执行finally语句中的内容,不管如何,该行代码总会运行
}
//finally执行完之后,由于在catch块中发生了异常,又没有嵌套的catch块来进行处理,通过
//public static int divideTheseNumbers(int a, int b) throws Exception,将系统自动捕获到的Arithmetic异常抛给上级调用者,此处是主函数
System.out.println("It worked after all");
return c;
}
}
/*
Didn't work the first time.
Better clean up my mess.
Tried Twice, still didn't work
*/
异常在子父类覆盖中的体现
1,子类在覆盖父类时,如果父类的方法抛出异常,那么子类的覆盖方法,只能抛出父类的异常或者该异常的子类。
2,如果父类方法抛出多个异常,那么子类在覆盖该方法时,只能抛出父类异常的子集。
3,如果父类或者接口的方法中没有异常抛出,那么子类在覆盖方法时,也不可以抛出异常。
4,如果子类方法发生了异常。就必须要进行try处理。绝对不能抛。
2,如果父类方法抛出多个异常,那么子类在覆盖该方法时,只能抛出父类异常的子集。
3,如果父类或者接口的方法中没有异常抛出,那么子类在覆盖方法时,也不可以抛出异常。
4,如果子类方法发生了异常。就必须要进行try处理。绝对不能抛。
class AException extends Exception
{
}
class BException extends AException
{
}
class CException extends Exception
{
}
/*
Exception
|--AException
|--BException
|--CException
*/
class Die
{
void show()throws AException
{
}
}
class Er extends Die
{
void show()throws BException//此处只能抛出A异常或者B异常,抛出C异常则出错,子类的覆盖方法,只能抛出父类的异常或者该异常的子类。
{
}
}




















 4313
4313











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








