在Android系统的预装apk病毒和elf病毒的清除时,经常需要先获取root权限,再执行 “mount -o remount,rw /system” 命令修改系统分区属性为可写,然后才能将system/xbin、system/bin以及system/app下的病毒清除干净。在清除Android系统病毒的这个过程中,必须涉及到 mount修改Android系统的分区属性为可写的行为,这里就学习和研究一下Android系统的mount命令。mount命令在Android安全学习的过程中经常会遇到,这里就学习这个命令。
一、mount 命令代码实现
在Android4.4.2的源码路径android4.4.2/system/core/init/builtins.c路径下有Android系统mount命令的代码实现,do_mount()函数的具体实现的功能就是Android系统的mount命令对应的实现。do_mount()函数最终调用Linux系统mount()函数来实现修改系统分区属性的功能。
- /*
- * Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
- *
- * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
- * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
- * You may obtain a copy of the License at
- *
- * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- *
- * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
- * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
- * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
- * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
- * limitations under the License.
- */
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <linux/kd.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <linux/if.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <sys/mount.h>
- #include <sys/resource.h>
- #include <sys/wait.h>
- #include <linux/loop.h>
- #include <cutils/partition_utils.h>
- #include <cutils/android_reboot.h>
- #include <sys/system_properties.h>
- #include <fs_mgr.h>
- #include <selinux/selinux.h>
- #include <selinux/label.h>
- #include "init.h"
- #include "keywords.h"
- #include "property_service.h"
- #include "devices.h"
- #include "init_parser.h"
- #include "util.h"
- #include "log.h"
- #include <private/android_filesystem_config.h>
- void add_environment(const char *name, const char *value);
- extern int init_module(void *, unsigned long, const char *);
- static int write_file(const char *path, const char *value)
- {
- int fd, ret, len;
- fd = open(path, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_NOFOLLOW, 0600);
- if (fd < 0)
- return -errno;
- len = strlen(value);
- do {
- ret = write(fd, value, len);
- } while (ret < 0 && errno == EINTR);
- close(fd);
- if (ret < 0) {
- return -errno;
- } else {
- return 0;
- }
- }
- static int _open(const char *path)
- {
- int fd;
- fd = open(path, O_RDONLY | O_NOFOLLOW);
- if (fd < 0)
- fd = open(path, O_WRONLY | O_NOFOLLOW);
- return fd;
- }
- static int _chown(const char *path, unsigned int uid, unsigned int gid)
- {
- int fd;
- int ret;
- fd = _open(path);
- if (fd < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- ret = fchown(fd, uid, gid);
- if (ret < 0) {
- int errno_copy = errno;
- close(fd);
- errno = errno_copy;
- return -1;
- }
- close(fd);
- return 0;
- }
- static int _chmod(const char *path, mode_t mode)
- {
- int fd;
- int ret;
- fd = _open(path);
- if (fd < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- ret = fchmod(fd, mode);
- if (ret < 0) {
- int errno_copy = errno;
- close(fd);
- errno = errno_copy;
- return -1;
- }
- close(fd);
- return 0;
- }
- static int insmod(const char *filename, char *options)
- {
- void *module;
- unsigned size;
- int ret;
- module = read_file(filename, &size);
- if (!module)
- return -1;
- ret = init_module(module, size, options);
- free(module);
- return ret;
- }
- static int setkey(struct kbentry *kbe)
- {
- int fd, ret;
- fd = open("/dev/tty0", O_RDWR | O_SYNC);
- if (fd < 0)
- return -1;
- ret = ioctl(fd, KDSKBENT, kbe);
- close(fd);
- return ret;
- }
- static int __ifupdown(const char *interface, int up)
- {
- struct ifreq ifr;
- int s, ret;
- strlcpy(ifr.ifr_name, interface, IFNAMSIZ);
- s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
- if (s < 0)
- return -1;
- ret = ioctl(s, SIOCGIFFLAGS, &ifr);
- if (ret < 0) {
- goto done;
- }
- if (up)
- ifr.ifr_flags |= IFF_UP;
- else
- ifr.ifr_flags &= ~IFF_UP;
- ret = ioctl(s, SIOCSIFFLAGS, &ifr);
- done:
- close(s);
- return ret;
- }
- static void service_start_if_not_disabled(struct service *svc)
- {
- if (!(svc->flags & SVC_DISABLED)) {
- service_start(svc, NULL);
- }
- }
- int do_chdir(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- chdir(args[1]);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_chroot(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- chroot(args[1]);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_class_start(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- /* Starting a class does not start services
- * which are explicitly disabled. They must
- * be started individually.
- */
- service_for_each_class(args[1], service_start_if_not_disabled);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_class_stop(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- service_for_each_class(args[1], service_stop);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_class_reset(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- service_for_each_class(args[1], service_reset);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_domainname(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- return write_file("/proc/sys/kernel/domainname", args[1]);
- }
- int do_exec(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- return -1;
- }
- int do_export(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- add_environment(args[1], args[2]);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_hostname(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- return write_file("/proc/sys/kernel/hostname", args[1]);
- }
- int do_ifup(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- return __ifupdown(args[1], 1);
- }
- static int do_insmod_inner(int nargs, char **args, int opt_len)
- {
- char options[opt_len + 1];
- int i;
- options[0] = '\0';
- if (nargs > 2) {
- strcpy(options, args[2]);
- for (i = 3; i < nargs; ++i) {
- strcat(options, " ");
- strcat(options, args[i]);
- }
- }
- return insmod(args[1], options);
- }
- int do_insmod(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- int i;
- int size = 0;
- if (nargs > 2) {
- for (i = 2; i < nargs; ++i)
- size += strlen(args[i]) + 1;
- }
- return do_insmod_inner(nargs, args, size);
- }
- int do_mkdir(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- mode_t mode = 0755;
- int ret;
- /* mkdir <path> [mode] [owner] [group] */
- if (nargs >= 3) {
- mode = strtoul(args[2], 0, 8);
- }
- ret = make_dir(args[1], mode);
- /* chmod in case the directory already exists */
- if (ret == -1 && errno == EEXIST) {
- ret = _chmod(args[1], mode);
- }
- if (ret == -1) {
- return -errno;
- }
- if (nargs >= 4) {
- uid_t uid = decode_uid(args[3]);
- gid_t gid = -1;
- if (nargs == 5) {
- gid = decode_uid(args[4]);
- }
- if (_chown(args[1], uid, gid) < 0) {
- return -errno;
- }
- /* chown may have cleared S_ISUID and S_ISGID, chmod again */
- if (mode & (S_ISUID | S_ISGID)) {
- ret = _chmod(args[1], mode);
- if (ret == -1) {
- return -errno;
- }
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
- static struct {
- const char *name;
- unsigned flag;
- } mount_flags[] = {
- { "noatime", MS_NOATIME },
- { "noexec", MS_NOEXEC },
- { "nosuid", MS_NOSUID },
- { "nodev", MS_NODEV },
- { "nodiratime", MS_NODIRATIME },
- { "ro", MS_RDONLY },
- { "rw", 0 },
- { "remount", MS_REMOUNT },
- { "bind", MS_BIND },
- { "rec", MS_REC },
- { "unbindable", MS_UNBINDABLE },
- { "private", MS_PRIVATE },
- { "slave", MS_SLAVE },
- { "shared", MS_SHARED },
- { "defaults", 0 },
- { 0, 0 },
- };
- #define DATA_MNT_POINT "/data"
- /* mount <type> <device> <path> <flags ...> <options> */
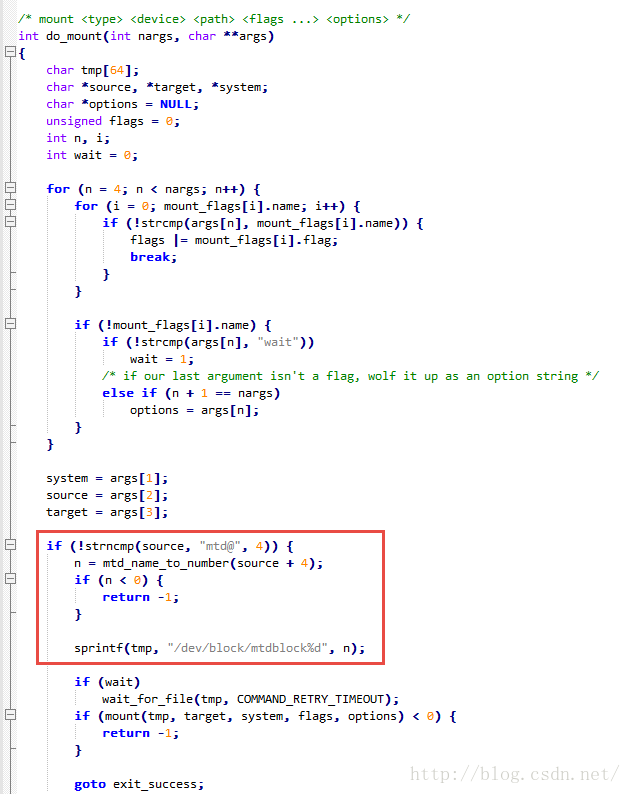
- int do_mount(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- char tmp[64];
- char *source, *target, *system;
- char *options = NULL;
- unsigned flags = 0;
- int n, i;
- int wait = 0;
- for (n = 4; n < nargs; n++) {
- for (i = 0; mount_flags[i].name; i++) {
- if (!strcmp(args[n], mount_flags[i].name)) {
- flags |= mount_flags[i].flag;
- break;
- }
- }
- if (!mount_flags[i].name) {
- if (!strcmp(args[n], "wait"))
- wait = 1;
- /* if our last argument isn't a flag, wolf it up as an option string */
- else if (n + 1 == nargs)
- options = args[n];
- }
- }
- system = args[1];
- source = args[2];
- target = args[3];
- if (!strncmp(source, "mtd@", 4)) {
- n = mtd_name_to_number(source + 4);
- if (n < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- sprintf(tmp, "/dev/block/mtdblock%d", n);
- if (wait)
- wait_for_file(tmp, COMMAND_RETRY_TIMEOUT);
- if (mount(tmp, target, system, flags, options) < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- goto exit_success;
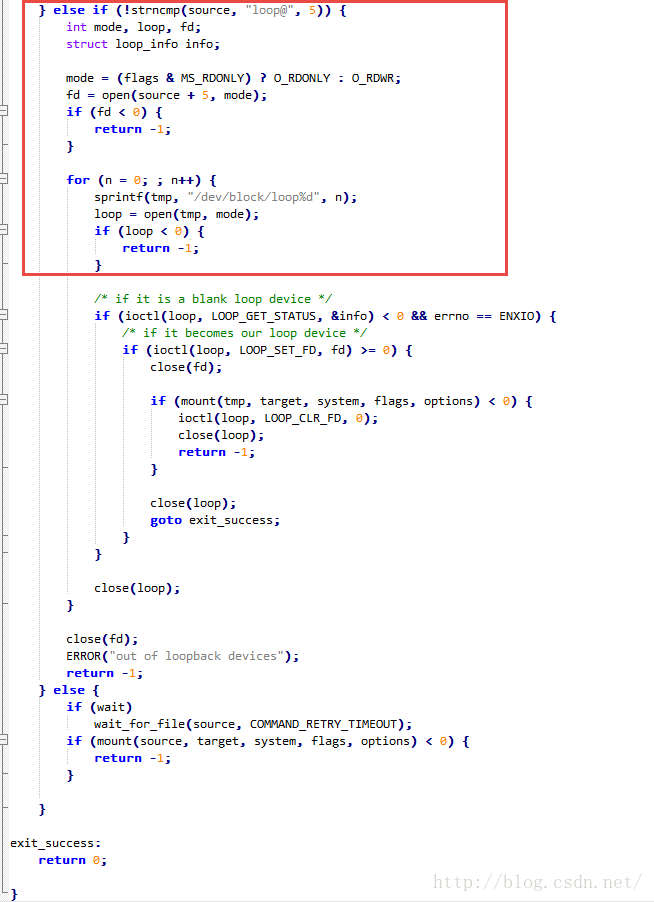
- } else if (!strncmp(source, "loop@", 5)) {
- int mode, loop, fd;
- struct loop_info info;
- mode = (flags & MS_RDONLY) ? O_RDONLY : O_RDWR;
- fd = open(source + 5, mode);
- if (fd < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- for (n = 0; ; n++) {
- sprintf(tmp, "/dev/block/loop%d", n);
- loop = open(tmp, mode);
- if (loop < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- /* if it is a blank loop device */
- if (ioctl(loop, LOOP_GET_STATUS, &info) < 0 && errno == ENXIO) {
- /* if it becomes our loop device */
- if (ioctl(loop, LOOP_SET_FD, fd) >= 0) {
- close(fd);
- if (mount(tmp, target, system, flags, options) < 0) {
- ioctl(loop, LOOP_CLR_FD, 0);
- close(loop);
- return -1;
- }
- close(loop);
- goto exit_success;
- }
- }
- close(loop);
- }
- close(fd);
- ERROR("out of loopback devices");
- return -1;
- } else {
- if (wait)
- wait_for_file(source, COMMAND_RETRY_TIMEOUT);
- if (mount(source, target, system, flags, options) < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- }
- exit_success:
- return 0;
- }
- int do_mount_all(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- pid_t pid;
- int ret = -1;
- int child_ret = -1;
- int status;
- const char *prop;
- struct fstab *fstab;
- if (nargs != 2) {
- return -1;
- }
- /*
- * Call fs_mgr_mount_all() to mount all filesystems. We fork(2) and
- * do the call in the child to provide protection to the main init
- * process if anything goes wrong (crash or memory leak), and wait for
- * the child to finish in the parent.
- */
- pid = fork();
- if (pid > 0) {
- /* Parent. Wait for the child to return */
- waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
- if (WIFEXITED(status)) {
- ret = WEXITSTATUS(status);
- } else {
- ret = -1;
- }
- } else if (pid == 0) {
- /* child, call fs_mgr_mount_all() */
- klog_set_level(6); /* So we can see what fs_mgr_mount_all() does */
- fstab = fs_mgr_read_fstab(args[1]);
- child_ret = fs_mgr_mount_all(fstab);
- fs_mgr_free_fstab(fstab);
- if (child_ret == -1) {
- ERROR("fs_mgr_mount_all returned an error\n");
- }
- exit(child_ret);
- } else {
- /* fork failed, return an error */
- return -1;
- }
- /* ret is 1 if the device is encrypted, 0 if not, and -1 on error */
- if (ret == 1) {
- property_set("ro.crypto.state", "encrypted");
- property_set("vold.decrypt", "1");
- } else if (ret == 0) {
- property_set("ro.crypto.state", "unencrypted");
- /* If fs_mgr determined this is an unencrypted device, then trigger
- * that action.
- */
- action_for_each_trigger("nonencrypted", action_add_queue_tail);
- }
- return ret;
- }
- int do_swapon_all(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- struct fstab *fstab;
- int ret;
- fstab = fs_mgr_read_fstab(args[1]);
- ret = fs_mgr_swapon_all(fstab);
- fs_mgr_free_fstab(fstab);
- return ret;
- }
- int do_setcon(int nargs, char **args) {
- if (is_selinux_enabled() <= 0)
- return 0;
- if (setcon(args[1]) < 0) {
- return -errno;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_setenforce(int nargs, char **args) {
- if (is_selinux_enabled() <= 0)
- return 0;
- if (security_setenforce(atoi(args[1])) < 0) {
- return -errno;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_setkey(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- struct kbentry kbe;
- kbe.kb_table = strtoul(args[1], 0, 0);
- kbe.kb_index = strtoul(args[2], 0, 0);
- kbe.kb_value = strtoul(args[3], 0, 0);
- return setkey(&kbe);
- }
- int do_setprop(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- const char *name = args[1];
- const char *value = args[2];
- char prop_val[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
- int ret;
- ret = expand_props(prop_val, value, sizeof(prop_val));
- if (ret) {
- ERROR("cannot expand '%s' while assigning to '%s'\n", value, name);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- property_set(name, prop_val);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_setrlimit(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- struct rlimit limit;
- int resource;
- resource = atoi(args[1]);
- limit.rlim_cur = atoi(args[2]);
- limit.rlim_max = atoi(args[3]);
- return setrlimit(resource, &limit);
- }
- int do_start(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- struct service *svc;
- svc = service_find_by_name(args[1]);
- if (svc) {
- service_start(svc, NULL);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_stop(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- struct service *svc;
- svc = service_find_by_name(args[1]);
- if (svc) {
- service_stop(svc);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_restart(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- struct service *svc;
- svc = service_find_by_name(args[1]);
- if (svc) {
- service_restart(svc);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_powerctl(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- char command[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
- int res;
- int len = 0;
- int cmd = 0;
- char *reboot_target;
- res = expand_props(command, args[1], sizeof(command));
- if (res) {
- ERROR("powerctl: cannot expand '%s'\n", args[1]);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- if (strncmp(command, "shutdown", 8) == 0) {
- cmd = ANDROID_RB_POWEROFF;
- len = 8;
- } else if (strncmp(command, "reboot", 6) == 0) {
- cmd = ANDROID_RB_RESTART2;
- len = 6;
- } else {
- ERROR("powerctl: unrecognized command '%s'\n", command);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- if (command[len] == ',') {
- reboot_target = &command[len + 1];
- } else if (command[len] == '\0') {
- reboot_target = "";
- } else {
- ERROR("powerctl: unrecognized reboot target '%s'\n", &command[len]);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- return android_reboot(cmd, 0, reboot_target);
- }
- int do_trigger(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- action_for_each_trigger(args[1], action_add_queue_tail);
- return 0;
- }
- int do_symlink(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- return symlink(args[1], args[2]);
- }
- int do_rm(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- return unlink(args[1]);
- }
- int do_rmdir(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- return rmdir(args[1]);
- }
- int do_sysclktz(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- struct timezone tz;
- if (nargs != 2)
- return -1;
- memset(&tz, 0, sizeof(tz));
- tz.tz_minuteswest = atoi(args[1]);
- if (settimeofday(NULL, &tz))
- return -1;
- return 0;
- }
- int do_write(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- const char *path = args[1];
- const char *value = args[2];
- char prop_val[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
- int ret;
- ret = expand_props(prop_val, value, sizeof(prop_val));
- if (ret) {
- ERROR("cannot expand '%s' while writing to '%s'\n", value, path);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- return write_file(path, prop_val);
- }
- int do_copy(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- char *buffer = NULL;
- int rc = 0;
- int fd1 = -1, fd2 = -1;
- struct stat info;
- int brtw, brtr;
- char *p;
- if (nargs != 3)
- return -1;
- if (stat(args[1], &info) < 0)
- return -1;
- if ((fd1 = open(args[1], O_RDONLY)) < 0)
- goto out_err;
- if ((fd2 = open(args[2], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0660)) < 0)
- goto out_err;
- if (!(buffer = malloc(info.st_size)))
- goto out_err;
- p = buffer;
- brtr = info.st_size;
- while(brtr) {
- rc = read(fd1, p, brtr);
- if (rc < 0)
- goto out_err;
- if (rc == 0)
- break;
- p += rc;
- brtr -= rc;
- }
- p = buffer;
- brtw = info.st_size;
- while(brtw) {
- rc = write(fd2, p, brtw);
- if (rc < 0)
- goto out_err;
- if (rc == 0)
- break;
- p += rc;
- brtw -= rc;
- }
- rc = 0;
- goto out;
- out_err:
- rc = -1;
- out:
- if (buffer)
- free(buffer);
- if (fd1 >= 0)
- close(fd1);
- if (fd2 >= 0)
- close(fd2);
- return rc;
- }
- int do_chown(int nargs, char **args) {
- /* GID is optional. */
- if (nargs == 3) {
- if (_chown(args[2], decode_uid(args[1]), -1) < 0)
- return -errno;
- } else if (nargs == 4) {
- if (_chown(args[3], decode_uid(args[1]), decode_uid(args[2])) < 0)
- return -errno;
- } else {
- return -1;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- static mode_t get_mode(const char *s) {
- mode_t mode = 0;
- while (*s) {
- if (*s >= '0' && *s <= '7') {
- mode = (mode<<3) | (*s-'0');
- } else {
- return -1;
- }
- s++;
- }
- return mode;
- }
- int do_chmod(int nargs, char **args) {
- mode_t mode = get_mode(args[1]);
- if (_chmod(args[2], mode) < 0) {
- return -errno;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_restorecon(int nargs, char **args) {
- int i;
- for (i = 1; i < nargs; i++) {
- if (restorecon(args[i]) < 0)
- return -errno;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_setsebool(int nargs, char **args) {
- const char *name = args[1];
- const char *value = args[2];
- SELboolean b;
- int ret;
- if (is_selinux_enabled() <= 0)
- return 0;
- b.name = name;
- if (!strcmp(value, "1") || !strcasecmp(value, "true") || !strcasecmp(value, "on"))
- b.value = 1;
- else if (!strcmp(value, "0") || !strcasecmp(value, "false") || !strcasecmp(value, "off"))
- b.value = 0;
- else {
- ERROR("setsebool: invalid value %s\n", value);
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- if (security_set_boolean_list(1, &b, 0) < 0) {
- ret = -errno;
- ERROR("setsebool: could not set %s to %s\n", name, value);
- return ret;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- int do_loglevel(int nargs, char **args) {
- if (nargs == 2) {
- klog_set_level(atoi(args[1]));
- return 0;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- int do_load_persist_props(int nargs, char **args) {
- if (nargs == 1) {
- load_persist_props();
- return 0;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- int do_wait(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- if (nargs == 2) {
- return wait_for_file(args[1], COMMAND_RETRY_TIMEOUT);
- } else if (nargs == 3) {
- return wait_for_file(args[1], atoi(args[2]));
- } else
- return -1;
- }
Linux系统调用--mount/umount函数的使用说明
- 【 mount/umount系统调用】
- 功能描述:
- mount挂上文件系统,umount执行相反的操作。
- 用法:
- #include <sys/mount.h>
- int mount(const char *source, const char *target,
- const char *filesystemtype, unsigned long mountflags, const void *data);
- int umount(const char *target);
- int umount2(const char *target, int flags);
- 参数:
- source:将要挂上的文件系统,通常是一个设备名。
- target:文件系统所要挂在的目标目录。
- filesystemtype:文件系统的类型,可以是"ext2","ext3","msdos","proc","nfs","iso9660" 。。。
- mountflags:指定文件系统的读写访问标志,可能值有以下
- MS_BIND:执行bind挂载,使文件或者子目录树在文件系统内的另一个点上可视。
- MS_DIRSYNC:同步目录的更新。
- MS_MANDLOCK:允许在文件上执行强制锁。
- MS_MOVE:移动子目录树。
- MS_NOATIME:不要更新文件上的访问时间。
- MS_NODEV:不允许访问设备文件。
- MS_NODIRATIME:不允许更新目录上的访问时间。
- MS_NOEXEC:不允许在挂上的文件系统上执行程序。
- MS_NOSUID:执行程序时,不遵照set-user-ID 和 set-group-ID位。
- MS_RDONLY:指定文件系统为只读。
- MS_REMOUNT:重新加载文件系统。这允许你改变现存文件系统的mountflag和数据,而无需使用先卸载,再挂上文件系统的方式。
- MS_SYNCHRONOUS:同步文件的更新。
- MNT_FORCE:强制卸载,即使文件系统处于忙状态。
- MNT_EXPIRE:将挂载点标志为过时。
- data:文件系统特有的参数。
- 返回说明:
- 成功执行时,返回0。失败返回-1,errno被设为以下的某个值
- EACCES:权能不足,可能原因是,路径的一部分不可搜索,或者挂载只读的文件系统时,没有指定 MS_RDONLY 标志。
- EAGAIN:成功地将不处于忙状态的文件系统标志为过时。
- EBUSY:一. 源文件系统已被挂上。或者不可以以只读的方式重新挂载,因为它还拥有以写方式打开的文件。二. 目标处于忙状态。
- EFAULT: 内存空间访问出错。
- EINVAL:操作无效,可能是源文件系统超级块无效。
- ELOOP :路径解析的过程中存在太多的符号连接。
- EMFILE:无需块设备要求的情况下,无用设备表已满。
- ENAMETOOLONG:路径名超出可允许的长度。
- ENODEV:内核不支持某中文件系统。
- ENOENT:路径名部分内容表示的目录不存在。
- ENOMEM: 核心内存不足。
- ENOTBLK:source不是块设备。
- ENOTDIR:路径名的部分内容不是目录。
- EPERM : 调用者权能不足。
- ENXIO:块主设备号超出所允许的范围。
二、Android手机上mount命令的使用
已经获取到手机root权限的情况下,在电脑上手动执行错误的 mount 命令的时候,adb shell终端会提示 “mount [-r] [-w] [-o options] [-t type] device directory”,可能就是说我们在adb shell终端环境下执行的mount命令不正确。下面就网上一些博客分享的Android手机上执行mount命令的方法,总结整理一下。
A、方法一
如果是愣头青,搞不清清楚Android手机系统的修改分区属性的命令,那就老老实实的使用简化的命令:
- <pre name="code" class="cpp">
- #修改系统分区属性为可写
- mount -o remount,rw /system
- #修改系统分区属性为只读
- mount -o remount,ro /system
因为linux系统自己会去维护一个已经mount的表,因此只需要输入现有的挂载点,系统会根据现有的挂载点去寻找对应的需要挂载的设备文件。
B、方法二
自己手动为mount命令寻找需要挂载的设备文件,并写到mount命令中去(使用Nexus 5设备Android4.4.4的系统为测试环境),说明下-不同的手机设备/system文件对应的系统设备文件是不同的,不能一概而论。
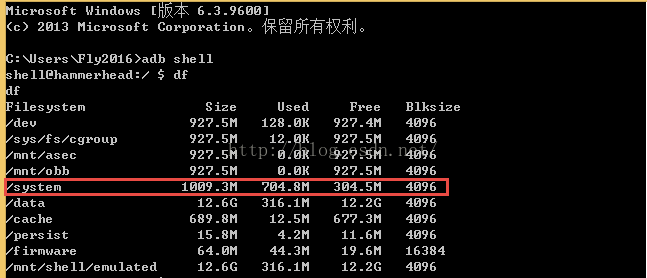
1.使用 df 命令查看档案系统的状况或是看所有档案系统的状况(预设值),发现/system分区有1009.3MB的大小。
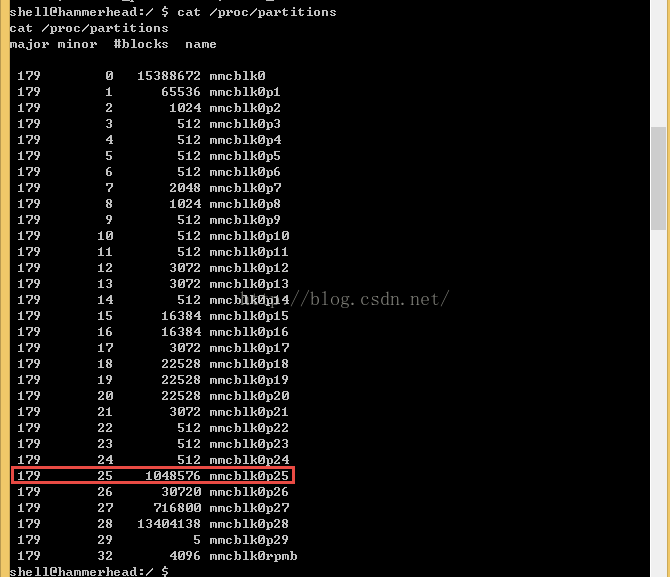
接着执行命令cat /proc/partitions 查看/proc下的partitions分区的大小。
看的出来,分区mmcblk0p25的大小最接近1009.3MB,判断挂载点/system就对应该设备文件了。但是这种方法明显操作起来不是很方便而且比较繁琐,需要计算和比较。
- #修改系统分区属性为可写
- mount -o remount,rw /dev/block/mmcblk0p25 /system
- #修改系统分区属性为只读
- mount -o remount,ro /dev/block/mmcblk0p25 /system
- #修改系统分区属性为可写
- mount -o remount,rw /dev/block/platform/msm_sdcc.1/by-name/system /system
- #修改系统分区属性为只读
- mount -o remount,ro /dev/block/platform/msm_sdcc.1/by-name/system /system
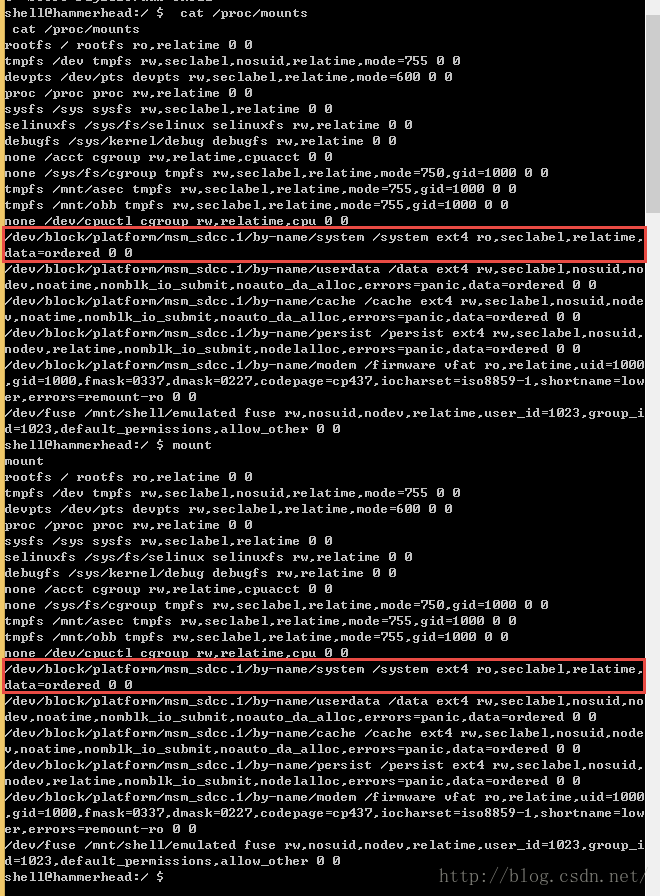
在这里需要注意下,可能由于手机的CPU的类型不同,执行cat /proc/mounts 或者 mount 命令显示的结果还是有所区别的,上面的结果是高通的CPU显示的结果。其中也有博客的作者提到在adb shell的环境下执行cat /proc/mtd 命令来看手机设备的分区的信息,但是呢,经过在Nexus 5的手机上测试发现 cat /proc/mtd 是执行不成功的,会提示“/system/bin/sh: cat: /proc/mtd: No such file or directory”错误。
特地mark一下,还有博主提到 尝试用其他信息代替”/dev/block/mmcblk0p25“,试了一下居然也是可行的;甚至用任何分块号mtdblock3、mtdblock4、mtdblock11等等都替换 /dev/block/mmcblk0p25 也能正常运行!那么这种错误命令为什么能成功呢?其实我们的命令 参数“-o remount”其实自动 忽略了/dev/block/mtdblock? 这一段参数,只是简单的把/system重新挂载了一下而已。
C、方法三
- </pre><pre code_snippet_id="1875306" snippet_file_name="blog_20160910_8_46145" name="code" class="cpp">#修改系统分区属性为可写
- mount -o remount,rw mtd@system /system
- #修改系统分区属性为只读
- mount -o remount,ro mtd@system /system
这种方法虽然也是可以的。之所以这么写是参考init.rc里面的mount写法。不清楚这个是怎么回事,要是原生的linux mount命令应该不会这样的。具体的原因,我猜应该看看,联想一下mount命令的实现源码,也许执行下面的命令也能修改系统分区的属性:
- #修改系统分区属性为可写
- mount -o remount,rw loop@system /system
- #修改系统分区属性为只读
- mount -o remount,ro loop@system /system
不墨迹了,该整理的也整理了。很多的内容是参阅大神的博客,本人Linux菜鸟一枚,再此不一一致谢了。本文的有些地方(知识点)还是需要验证和再思考的。如果有问题,希望大神们能指出来,拿砖拍我。关于Android系统上mount命令的使用就此做个比较,方便自己也方便他人。
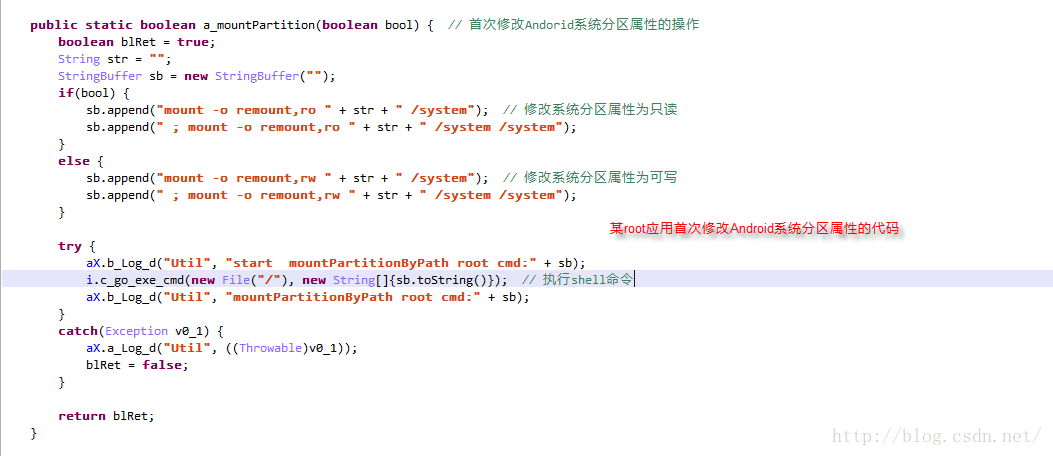
三、某安全应用修改Android系统分区属性所采用的方法
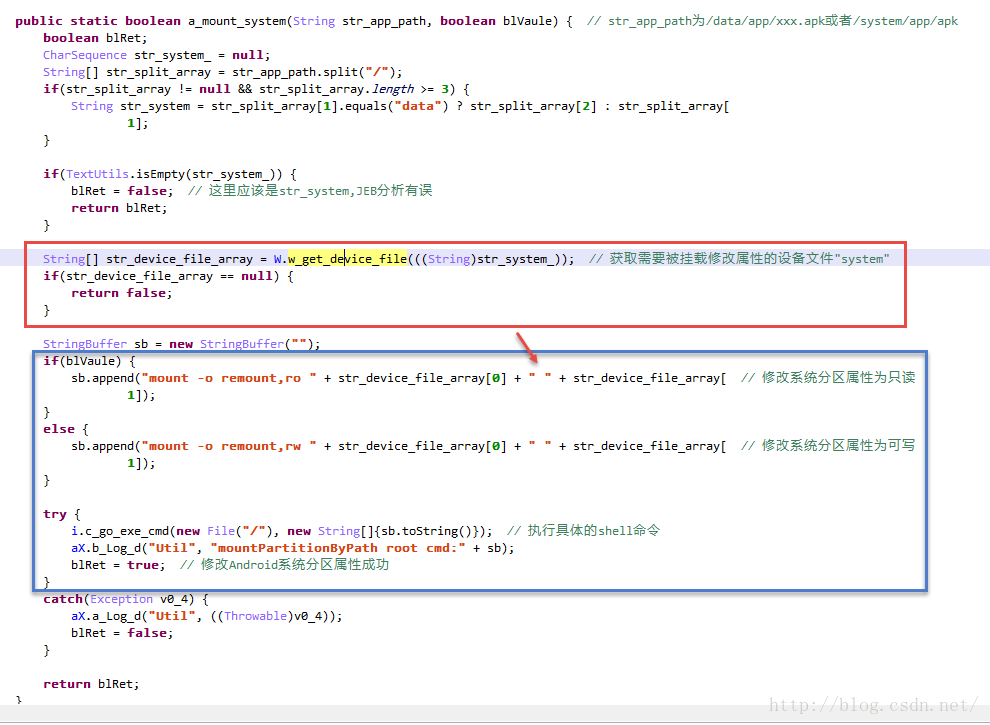
很多Rom喜欢内置恶意的app软件,清除掉这些预转的恶意apk应用就需要在root授权的情况下,修改Android系统分区的属性为可写,将/system/app下的预装apk删除掉。某安全应用就提供了卸载预装系统apk的功能,比较好奇就稍微逆向分析了一下,该应用修改Android系统分区的方法如下:
第1次修改Android系统分区,执行的命令操作:
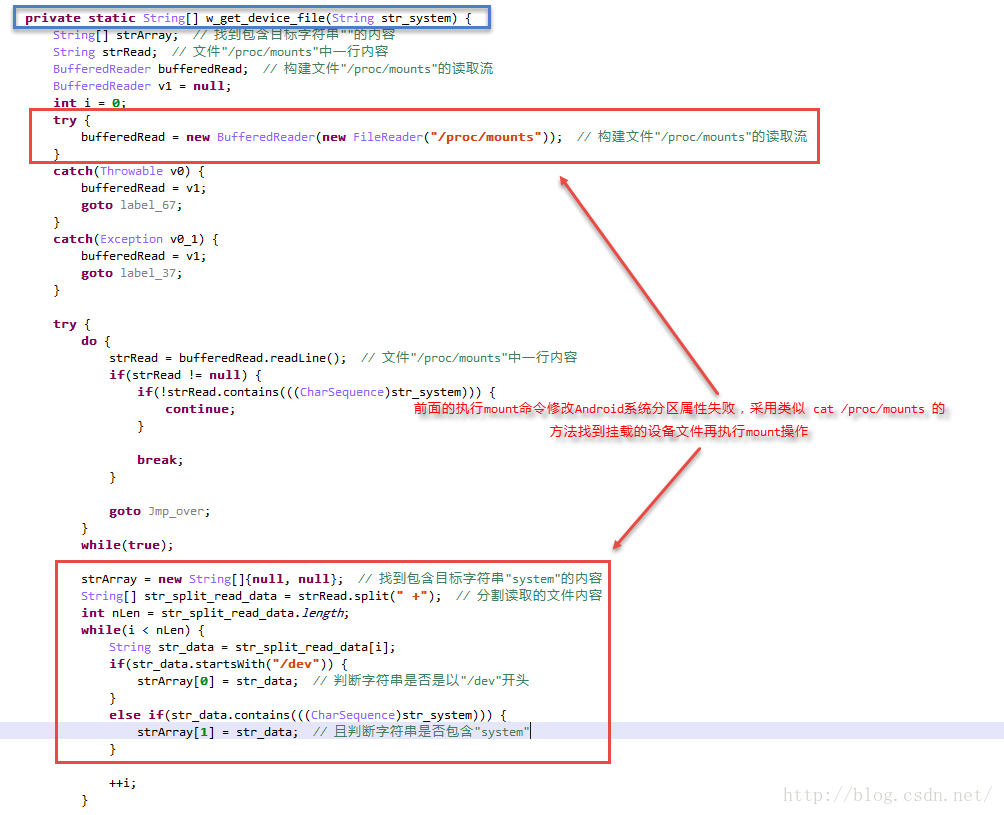
当前面第1次修改Android系统分区属性的方法失败,采用类似 执行cat /proc/mounts 或者 mount 找挂载设备文件的方法,再次执行mount命令。
补充一点:
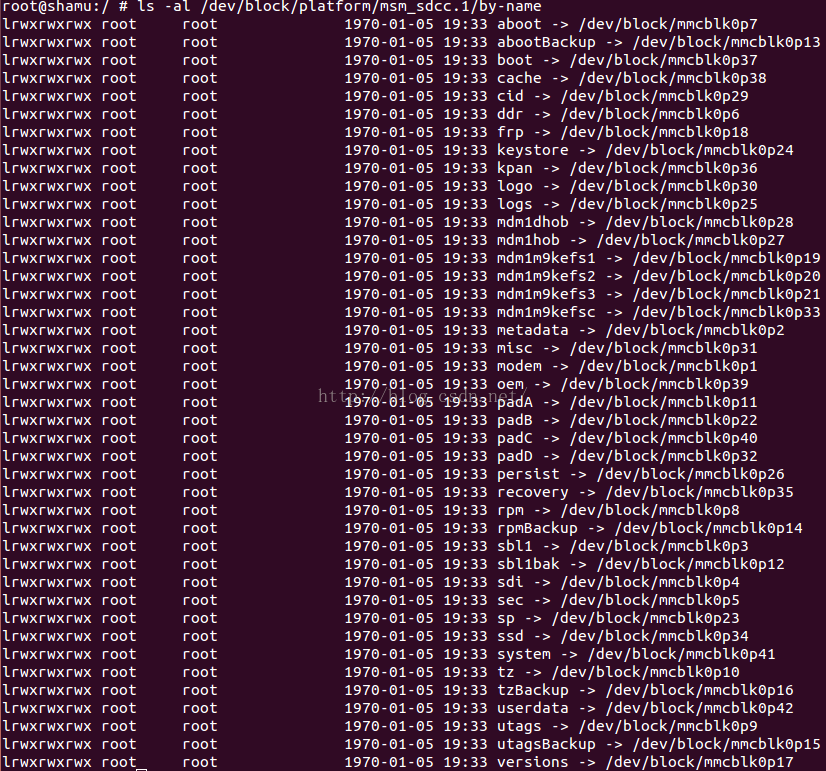
如果想看某些分区的别名信息,对于高通平台上来说,可以通过下面的命令:
- ls -al /dev/block/platform/msm_sdcc.1/by-name
在Google Nexus 6设备上,命令的显示结果如下:
这些信息可以帮助发现每个分区到底是用来干什么的,比如/dev/block/mmcblk0p41这个分区就是用来存放/system的。
有了这些信息,就可以使用dd命令,将感兴趣的分区全部倒出来进行分析。比如,如果想将TrustZone相关的tz分区倒出到sdcard上,可以使用下面的命令:
- dd if=/dev/block/platform/msm_sdcc.1/by-name of=/sdcard/tz.img
感谢链接:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-22731254-id-3222708.html
http://blog.csdn.net/cainiao413/article/details/6156812
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/330050292
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4a4aca6501008ath.html
http://blog.csdn.net/candyguy242/article/details/8054973
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20564848-id-73964.html





















 1027
1027











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








