一、依赖注入(DI)
依赖注入听起来很高深的样子,其实白话就是:给属性赋值。一共有两种方法,第一是以构造器参数的形式,另外一种就是以setting方法的形式。
1 构造器注入
1 使用构造器注入
使用xml的注入方式
A. 通过参数的顺序
<constructor-arg index="0"><value>张三</value></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1"><value>56</value></constructor-arg> B. 通过参数的类型
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.Integer"><value>56</value></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String"><value>张三</value></constructor-arg>具体实例
假如现在要对一个Person类注入参数,Student是一个另外一个类。
public class Person {
private String pid;
private String name;
private Student student;
public Person(String pid, Student student){
this.pid= pid;
this.student = student;
}
public Person(String pid, String name){
this.pid = pid;
this.name = name;
}
}配置applicationContext.xml,假如不进行参数配置,则报错,找不到相应的构造器。配置了相应的参数,则应在类中声明相应的构造函数。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.itheima10.spring.di.xml.constructor.Person">
<!--
不配参数,将会采取默认的构造器
constructor-arg person类中某一个构造器的某一个参数
index 为参数的角标
type 参数的类型
value 如果为基础属性,则用这个赋值
ref 引用类型赋值
-->
<constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="aaa"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="student"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="person1" class="com.itheima10.spring.di.xml.constructor.Person">
<property name="pid" value="1"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.itheima10.spring.di.xml.constructor.Student"></bean>
</beans>编写测试类DIXMLConstructorTest ,进行断点调试,将会发现根据配置的参数,进入的构造函数是Person(String pid, Student student)
public class DIXMLConstructorTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) context.getBean("person");
}
}2 使用属性setter方法进行注入
使用xml的注入方式:
A. 简单Bean的注入
简单Bean包括两种类型:包装类型和String
<bean id="personService" class="com.itcast.bean.impl.PersonServiceImpl">
<!-- 基本类型,string类型 -->
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
<property name="name" value="张无忌"></property>
</bean>B. 引用其他Bean
<bean id="person" class="com.itcast.bean.Person" />
<bean id="personService" class="com.itcast.bean.impl.PersonServiceImpl">
<property name="person" ref="person" />
</bean>1.1 装配list集合
<property name="lists">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
<ref bean="person" />
</list>
</property>1.2 装配set集合
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
<ref bean="person" />
</set>
</property>1.3 装配map
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="01">
<value>map01</value>
</entry>
<entry key="02">
<value>map02</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>map中的<entry>的数值和<list>以及<set>的一样,可以使任何有效的属性元素,需要注意的是key值必须是String的。
1.4 装配Properties
<property name="props">
<props>
<prop key="01">prop1</prop>
<prop key="02">prop2</prop>
</props>
</property> 具体实例
1.创建两个对象Person和Student
package xgp.spring.demo;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class Person {
private String pid;
private String name;
private Student student;
private List lists;
private Set sets;
private Map map;
private Properties properties;
private Object[] objects;
public Person(){
System.out.println("new person");
}
//省略getter和setter方法
}
package xgp.spring.demo;
public class Student {
public Student(){
System.out.println("new student");
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("student");
}
}配置applicationContext.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<!--
把person和student放入到spring容器中
property 用来描述Person类的属性
value 如果是一般属性,则用value赋值
ref 如果该属性是引用类型,用ref赋值
-->
<bean id="person" class="com.itheima10.spring.di.xml.setter.Person"
init-method="init"
lazy-init="true">
<property name="pid" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="王二麻子"></property>
<property name="student" ref="student"></property>
<property name="lists">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
<ref bean="student"/>
</list>
</property>
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>set1</value>
<value>set2</value>
<ref bean="student"/>
</set>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="entry1">
<value>map1</value>
</entry>
<entry key="entry2">
<ref bean="student"/>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<!--
不需要引用类型
-->
<prop key="prop1">prop1</prop>
<prop key="prop2">prop2</prop>
</props>
</property>
<property name="objects">
<list>
<value>aa</value>
<value>bb</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.itheima10.spring.di.xml.setter.Student"></bean>
</beans>编写测试类DIXMLSetterTest
package xgp.spring.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import xgp.spring.demo.Person;
public class DIXMLSetterTest {
/**
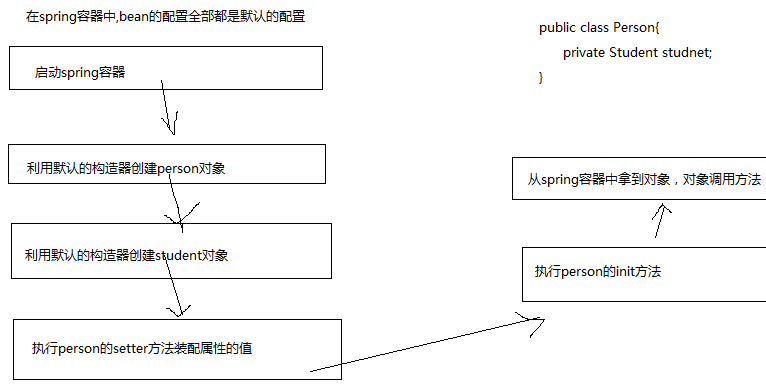
* spring 容器做的事情:
* 1、spring容器做了什么?(1)启动spring容器
* (2)为person和student两个bean创建对象
* (3)解析property的name属性,拼接setter方法,解析property的
* value或者ref属性,给setter方法传递参数,利用反射技术给对象赋值。
* (4)从spring容器中,把对象提取出来,对象调用方法。
* 2、spring容器执行顺序是什么?
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) context.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person.getPid());
System.out.println(person.getName());
System.out.println(person.getLists());
System.out.println(person.getSets());
System.out.println(person.getMap());
System.out.println(person.getObjects().length);
}
}
/*1
王五
[list1, list2, xgp.spring.demo.Student@76a9b9c]
[set1, set2, xgp.spring.demo.Student@76a9b9c]
{entry1=map1, entry2=map2}
2*/spring容器的执行顺序
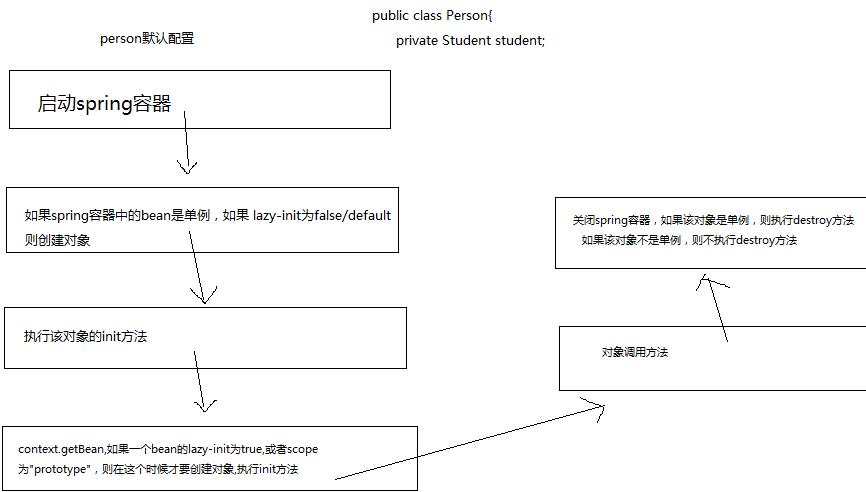
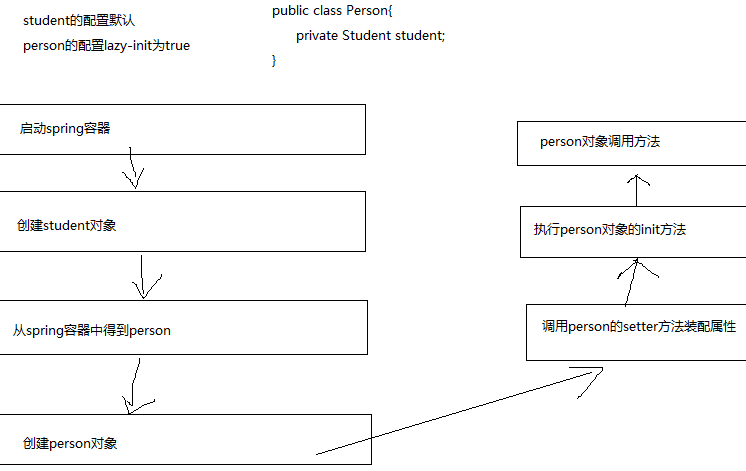
- 都是默认设置
2.设置student(lazy-init=true)
3.设置person(lazy-init=true)
总结
可以采用两种方法注入参数,构造器要写对应的构造函数,setter要生成相应的setter方法,并编写默认的构造器。
2.5 IOC与DI的意义
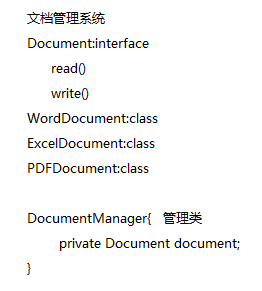
学了这些,发现有什么意义?下面写个文档管理系统例子来说明,需求见下图
1.编写Document 接口
public interface Document {
public void read();
public void write();
}2、编写实现类WordDocument ,ExcelDocument ,PDFDocument
public class WordDocument implements Document{
public void read() {
System.out.println("word read");
}
public void write() {
System.out.println("word write");
}
}3、编写文档管理 系统 DocumentManager
public class DocumentManager {
private Document document;
public void setDocument(Document document) {
this.document = document;
}
public DocumentManager(){
}
public DocumentManager(Document document) {
super();
this.document = document;
}
public void read(){
this.document.read();
}
public void write(){
this.document.write();
}
}
4、编写测试类DocumentTest
/**
* 利用ioc和di能做到完全的面向接口编程
*
*/
public class DocumentTest {
/**
* Document document = new WordDocument();
* 这行代码是不完全的面向接口编程,因为等号的右边出现了具体的类
*/
@Test
public void testDocument_NOSPRING(){
Document document = new WordDocument();
DocumentManager documentManager = new DocumentManager(document);
documentManager.read();
documentManager.write();
}
/**
* 在代码端不知道Document是由谁来实现的,这个是由spring的配置文件决定的
* <bean id="documentManager"
class="com.itheima10.spring.iocdi.document.DocumentManager">
<!--
document为一个接口
-->
<property name="document">
<!--
wordDocument是一个实现类,赋值给了document接口
-->
<ref bean="pdfDocument"/>
</property>
</bean>
*/
@Test
public void testDocument_Spring(){
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
DocumentManager documentManager =(DocumentManager)context.getBean("documentManager");
documentManager.read();
documentManager.write();
}
}
从上面可以看出不适用spring和适用spring的区别
<!--
documentManager,wordDocument,excelDocument,pdfDocument放入到spring容器中
-->
<bean id="wordDocument" class="com.itheima10.spring.iocdi.document.WordDocument"></bean>
<bean id="excelDocument" class="com.itheima10.spring.iocdi.document.ExcelDocument"></bean>
<bean id="pdfDocument" class="com.itheima10.spring.iocdi.document.PDFDocument"></bean>
<bean id="documentManager"
class="com.itheima10.spring.iocdi.document.DocumentManager">
<!--
document为一个接口
-->
<property name="document">
<!--
wordDocument是一个实现类,赋值给了document接口
-->
<ref bean="pdfDocument"/>
</property>
</bean>使用spring只需要在applicationContext中配置相应的<ref bean="">对象,而不需要关注具体的实现类,实现完全的面向接口编程,这也是为什么spring能够和这么多工具集成的原因。
2.6 mvc实例–模拟structs2
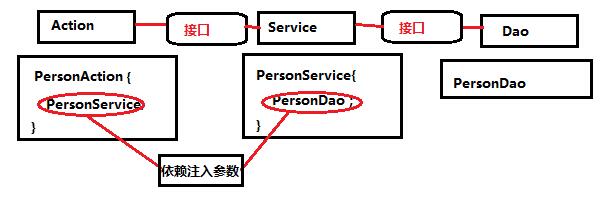
需求描述
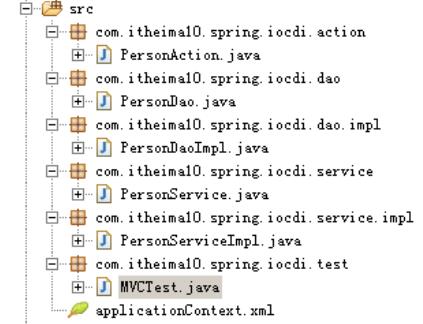
建立工程目录
编码:
1、创建Dao层
建立PersonDao接口和实现类PersonDaoImpl
public interface PersonDao {
public void savePerson();
}public class PersonDaoImpl implements PersonDao {
@Override
public void savePerson() {
System.out.println(" save person");
}
}2、建立service层,PersonService接口与PersonServiceImpl实现类
public interface PersonService {
public void savePerson();
}public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService{
private PersonDao personDao;
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
@Override
public void savePerson() {
this.personDao.savePerson();
}
}3、建立Action,PersonAction类
public class PersonAction {
private PersonService personService;
public void setPersonService(PersonService personService) {
this.personService = personService;
}
public void savePerson(){
this.personService.savePerson();
}
}4、配置applicationContext.xml
<!--
把service,dao,action层的类放入到spring容器中
-->
<bean id="personDao" class="xgp.spring.demo.PersonDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="xgp.spring.demo.PersonServiceImpl">
<property name="personDao">
<ref bean="personDao"/>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="personAction" class="xgp.spring.demo.PersonAction">
<property name="personService">
<ref bean="personService"/>
</property>
</bean>5、编写测试类testMVC
public class MVCTest {
@Test
public void testMVC(){
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
PersonAction personAction = (PersonAction)context.getBean("personAction");
personAction.savePerson();//save person
}
}上述实例很清楚的展现出了spring的面向接口编程,service层只需调用dao层的接口,而不需要关注于dao层的实现类,action也只需调用service的接口,而不需要关注service的实现类。























 191
191











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








