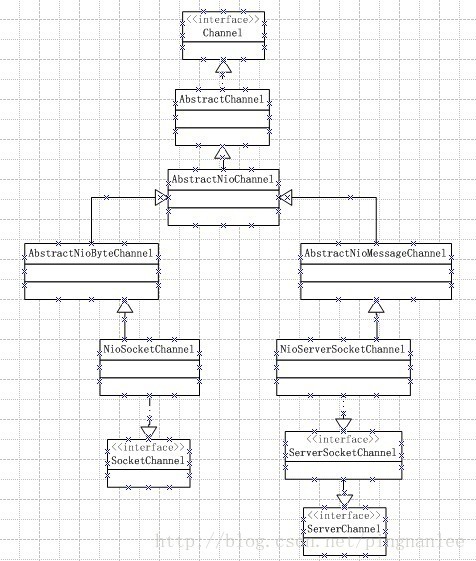
1、channel总体机构图
nio channel的总体结构图如下:
2、关键类和接口分析
2.1 基于NioServerSocketChannel进行分析
1)Channel
Channel是顶层接口,继承了AttributeMap, ChannelOutboundInvoker, ChannelPropertyAccess, Comparable<Channel>,它作为一个具体IO能力的组件提供给开发者,包括read, write, connect, and bind等操作。另外还提供了Channel配置的功能,以及获取Channel所在的eventloop的功能。
2)AbstractChannel
AbstractChannel实现Channel接口,关键代码如下:
- private final Channel parent;
- private final long hashCode = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong();
- private final Unsafe unsafe;
- private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline;
- private final ChannelFuture succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(this, null);
- private final VoidChannelPromise voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(this, true);
- private final VoidChannelPromise unsafeVoidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(this, false);
- private final CloseFuture closeFuture = new CloseFuture(this);
- private volatile SocketAddress localAddress;
- private volatile SocketAddress remoteAddress;
- private volatile EventLoop eventLoop;
- private volatile boolean registered;
- /** Cache for the string representation of this channel */
- private boolean strValActive;
- private String strVal;<pre name="code" class="java"> /**
- * Creates a new instance.
- *
- * @param parent
- * the parent of this channel. {@code null} if there's no parent.
- */
- protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
- this.parent = parent;
- unsafe = newUnsafe();
- pipeline = new DefaultChannelPipeline(this);
- }
3)AbstractNioChannel
AbstractNioChannel继承AbstractChannel,从这个类开始涉及到JDK的socket,参考如下关键代码:
- private final SelectableChannel ch;
- protected final int readInterestOp;
- private volatile SelectionKey selectionKey;
- private volatile boolean inputShutdown;
- <pre name="code" class="java"> @Override
- protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
- boolean selected = false;
- for (;;) {
- try {
- selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
- return;
- } catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
- if (!selected) {
- // Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
- // cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
- eventLoop().selectNow();
- selected = true;
- } else {
- // We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
- // for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
- throw e;
- }
- }
- }
- }
/** * Create a new instance * * @param parent the parent {@link Channel} by which this instance was created. May be {@code null} * @param ch the underlying {@link SelectableChannel} on which it operates * @param readInterestOp the ops to set to receive data from the {@link SelectableChannel} */ protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) { super(parent); this.ch = ch; this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp; try { ch.configureBlocking(false); } catch (IOException e) { try { ch.close(); } catch (IOException e2) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn( "Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2); } } throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e); } } 从上面的代码可以看出,这里定义真正的Socket Channel(SelectableChannel),关心的事件,注册后的key。将Socket设置为非阻塞,这是所有异步IO的关键,也就是说不管多么好的框架,底层基础还是不会变,可见学好基础的重要性啊,^_^。这里重点要关注一下register函数,这个函数是将Channel和事件循环进行关联的关键。每个事件循环都有一个自己的selector,channel实际上是注册到了相应eventloop的selector中,这也是Nio Socket编程的基础。
从这个类中已经可以看到netty的channel是如何和socket 的nio channel关联的了,以及channel是如何和eventloop关联的了。
4)AbstractNioMessageChannel
这个类继承AbstractNioChannel,主要是提供了一个newUnsafe方法返回NioMessageUnsafe对象的实例(实现read方法)。另外还定义doReadMessages和doWriteMessage两个抽象方法。
5)ServerSocketChannel和ServerChannel
这两个接口主要是定义了一个config方法,以及获取网络地址的方法。
6)NioServerSocketChannel
NioServerSocketChannel继承AbstractNioMessageChannel,实现ServerSocketChannel,它是一个具体类,提供给开发者使用。
- /**
- * A {@link io.netty.channel.socket.ServerSocketChannel} implementation which uses
- * NIO selector based implementation to accept new connections.
- */
- public class NioServerSocketChannel extends AbstractNioMessageChannel
- implements io.netty.channel.socket.ServerSocketChannel {
- private static final ChannelMetadata METADATA = new ChannelMetadata(false);
- private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
- private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket() {
- try {
- return ServerSocketChannel.open();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new ChannelException(
- "Failed to open a server socket.", e);
- }
- }
- private final ServerSocketChannelConfig config;
- /**
- * Create a new instance
- */
- public NioServerSocketChannel() {
- super(null, newSocket(), SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
- config = new DefaultServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
- }
- @Override
- protected ServerSocketChannel javaChannel() {
- return (ServerSocketChannel) super.javaChannel();
- }
- @Override
- protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
- javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
- }
- @Override
- protected void doClose() throws Exception {
- javaChannel().close();
- }
- @Override
- protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
- SocketChannel ch = javaChannel().accept();
- try {
- if (ch != null) {
- buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
- return 1;
- }
- } catch (Throwable t) {
- logger.warn("Failed to create a new channel from an accepted socket.", t);
- try {
- ch.close();
- } catch (Throwable t2) {
- logger.warn("Failed to close a socket.", t2);
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
- // Unnecessary stuff
- @Override
- protected boolean doConnect(
- SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
- throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
- }
- @Override
- protected void doFinishConnect() throws Exception {
- throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
- }
- @Override
- protected SocketAddress remoteAddress0() {
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- protected void doDisconnect() throws Exception {
- throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
- }
- @Override
- protected boolean doWriteMessage(Object msg, ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
- throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
- }
- }
2.2 基于NioSocketChannel进行分析
在NioServerSocketChannel中介绍过的类和接口,这里不再介绍。其实和NioServerSocketChannel差不多,只是它是基于Byte的。
1)AbstractNioByteChannel
这个类继承AbstractNioChannel,主要也是提供了一个newUnsafe方法返回NioByteUnsafe对象的实例(实现read方法)。另外还定义doReadBytes和doWriteBytes两个抽象方法。
2)SocketChannel
这个接口继承了Channel接口,定义了多个shutdown方法,以及一个parent方法,返回该SocketChannel相应的ServerSocketChannel。
3)NioSocketChannel
这个类继承AbstractNioByteChannel,并且实现SocketChannel接口,是一个具体类,提供给开发者使用。
- /**
- * {@link io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel} which uses NIO selector based implementation.
- */
- public class NioSocketChannel extends AbstractNioByteChannel implements io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel {
- private static final ChannelMetadata METADATA = new ChannelMetadata(false);
- private static SocketChannel newSocket() {
- try {
- return SocketChannel.open();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a socket.", e);
- }
- }
- private final SocketChannelConfig config;
- /**
- * Create a new instance
- */
- public NioSocketChannel() {
- this(newSocket());
- }
- /**
- * Create a new instance using the given {@link SocketChannel}.
- */
- public NioSocketChannel(SocketChannel socket) {
- this(null, socket);
- }
- /**
- * Create a new instance
- *
- * @param parent the {@link Channel} which created this instance or {@code null} if it was created by the user
- * @param socket the {@link SocketChannel} which will be used
- */
- public NioSocketChannel(Channel parent, SocketChannel socket) {
- super(parent, socket);
- config = new DefaultSocketChannelConfig(this, socket.socket());
- }
- @Override
- protected SocketChannel javaChannel() {
- return (SocketChannel) super.javaChannel();
- }
- @Override
- public boolean isActive() {
- SocketChannel ch = javaChannel();
- return ch.isOpen() && ch.isConnected();
- }
- @Override
- public boolean isInputShutdown() {
- return super.isInputShutdown();
- }
- @Override
- public InetSocketAddress localAddress() {
- return (InetSocketAddress) super.localAddress();
- }
- @Override
- public InetSocketAddress remoteAddress() {
- return (InetSocketAddress) super.remoteAddress();
- }
- @Override
- public boolean isOutputShutdown() {
- return javaChannel().socket().isOutputShutdown() || !isActive();
- }
- @Override
- public ChannelFuture shutdownOutput() {
- return shutdownOutput(newPromise());
- }
- @Override
- public ChannelFuture shutdownOutput(final ChannelPromise promise) {
- EventLoop loop = eventLoop();
- if (loop.inEventLoop()) {
- try {
- javaChannel().socket().shutdownOutput();
- promise.setSuccess();
- } catch (Throwable t) {
- promise.setFailure(t);
- }
- } else {
- loop.execute(new Runnable() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- shutdownOutput(promise);
- }
- });
- }
- return promise;
- }
- @Override
- protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
- if (localAddress != null) {
- javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress);
- }
- boolean success = false;
- try {
- boolean connected = javaChannel().connect(remoteAddress);
- if (!connected) {
- selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
- }
- success = true;
- return connected;
- } finally {
- if (!success) {
- doClose();
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- protected void doFinishConnect() throws Exception {
- if (!javaChannel().finishConnect()) {
- throw new Error();
- }
- }
- @Override
- protected void doDisconnect() throws Exception {
- doClose();
- }
- @Override
- protected void doClose() throws Exception {
- javaChannel().close();
- }
- @Override
- protected int doReadBytes(ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
- return byteBuf.writeBytes(javaChannel(), byteBuf.writableBytes());
- }
- @Override
- protected int doWriteBytes(ByteBuf buf) throws Exception {
- final int expectedWrittenBytes = buf.readableBytes();
- final int writtenBytes = buf.readBytes(javaChannel(), expectedWrittenBytes);
- return writtenBytes;
- }
- @Override
- protected long doWriteFileRegion(FileRegion region) throws Exception {
- final long position = region.transfered();
- final long writtenBytes = region.transferTo(javaChannel(), position);
- return writtenBytes;
- }
- @Override
- protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
- for (;;) {
- // Do non-gathering write for a single buffer case.
- final int msgCount = in.size();
- if (msgCount <= 1) {
- super.doWrite(in);
- return;
- }
- // Ensure the pending writes are made of ByteBufs only.
- ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = in.nioBuffers();
- if (nioBuffers == null) {
- super.doWrite(in);
- return;
- }
- int nioBufferCnt = in.nioBufferCount();
- long expectedWrittenBytes = in.nioBufferSize();
- final SocketChannel ch = javaChannel();
- long writtenBytes = 0;
- boolean done = false;
- for (int i = config().getWriteSpinCount() - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
- final long localWrittenBytes = ch.write(nioBuffers, 0, nioBufferCnt);
- if (localWrittenBytes == 0) {
- break;
- }
- expectedWrittenBytes -= localWrittenBytes;
- writtenBytes += localWrittenBytes;
- if (expectedWrittenBytes == 0) {
- done = true;
- break;
- }
- }
- if (done) {
- // Release all buffers
- for (int i = msgCount; i > 0; i --) {
- in.remove();
- }
- // Finish the write loop if no new messages were flushed by in.remove().
- if (in.isEmpty()) {
- clearOpWrite();
- break;
- }
- } else {
- // Did not write all buffers completely.
- // Release the fully written buffers and update the indexes of the partially written buffer.
- for (int i = msgCount; i > 0; i --) {
- final ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) in.current();
- final int readerIndex = buf.readerIndex();
- final int readableBytes = buf.writerIndex() - readerIndex;
- if (readableBytes < writtenBytes) {
- in.progress(readableBytes);
- in.remove();
- writtenBytes -= readableBytes;
- } else if (readableBytes > writtenBytes) {
- buf.readerIndex(readerIndex + (int) writtenBytes);
- in.progress(writtenBytes);
- break;
- } else { // readableBytes == writtenBytes
- in.progress(readableBytes);
- in.remove();
- break;
- }
- }
- setOpWrite();
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
3、总结
NioSocketChannel和NioServerSocketChannel这两个具体类是提供给开发者使用的。从上面的分析可以看出,实际上他们底层关联的还是JDK的SocketChannel和ServerSocketChannel。netty的Socket Channel是对JDK的Socket Channel的封装,它将Channel和loop关联,在loop中处理Channel的事件通知。
备注:Channel是netty的核心数据结构,这篇文章只是对Channel的Socket部分进行简单分析,不过通过它基本上已经能够了解netty是如何将它的Channel和上一篇的event关联的,以及它是如何将channel和JDK的channel关联的。





















 5481
5481











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








