日常项目中经常有这样的需求,即需要几个紧密相关的内容存储起来,例如,xxx省xxx市xxx区等等。
例如下图:
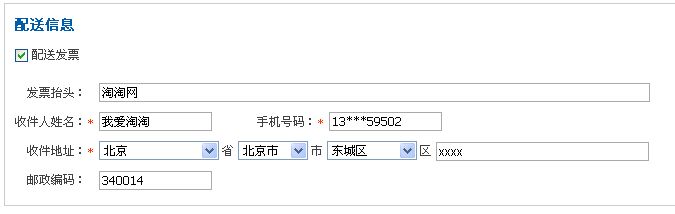
这些紧密相关的内容可能会经常增加或者减少某项内容,在数据库应用中,当然可以设计几个字段来存储或者设计一个专门的key-value表来存储这些可变内容,但是对于这类不会直接用条件进行检索的紧密关联的内容来讲,保存在一个字段traffic_description中似乎更为妥帖一点。既然要存储在一个字段中那么就涉及到如何分割和组装的问题。
一个比较直接的做法就是使用分号对每项值进行分割存储,这种方式属于一种平面的结构,还有一个更好的办法就是将这些字段组装成一个json 字符串,格式如{'key1':value1,'key2':['value2','value21']},这样就可以直接利用现成的对象存储方式来保存,当前就有很多第三方包对json提供了支持,如:java中提供了json-lib.jar,其他语言支持包见 www.json.org
下面提供一种简单的实现:
- import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
- import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
- import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
- import java.lang.annotation.Target;
- import java.lang.reflect.Field;
- import java.util.Collection;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Set;
- import net.sf.json.JSONArray;
- import net.sf.json.JSONObject;
- import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
- import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
- import org.apache.commons.lang.builder.ToStringBuilder;
- import com.alibaba.common.logging.Logger;
- import com.alibaba.common.logging.LoggerFactory;
- /**
- *
- * <p>
- * json 字符串生成和解析base类
- * </p>
- *
- * @author <a href="mailto:qingxu@taobao.com" mce_href="mailto:qingxu@taobao.com">清虚</a>
- * @since 2.0 2009-10-19上午10:42:57
- *
- */
- public class JsonDO {
- private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger("JsonDO");
- /**
- * json 属性标注 ,表示该属性需要放入json对象
- */
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
- public @interface JsonField {
- }
- private String value;// json字符串,一般存储在数据库中
- /**
- * 调用该方法会设置value属性,该方法一般在保存数据库时调用
- *
- * @return the value
- */
- public String getValue() {
- encode();
- return value;
- }
- /**
- * 调用该方法会解析value字符串,并设置相应的java 属性,该方法一般在从数据库中load时调用
- *
- * @param value
- * the value to set
- */
- public void setValue(String value) {
- this.value = value;
- decode();
- }
- /**
- *
- *
- * <p>
- * 将value json中的属性值设置到对应的java DO属性中去,java 属性必须有JsonField 标注才会被设置
- * </p>
- *
- * @author <a href="mailto:qingxu@taobao.com" mce_href="mailto:qingxu@taobao.com">清虚</a>
- * @since 2.0 2009-10-19下午02:39:56
- *
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- protected void decode() {
- if (this.value == null || this.value.trim().equals("")) {
- return;
- }
- Map<String, Class> classMap = new HashMap<String, Class>();
- Field[] fs = getClass().getDeclaredFields();
- for (Field f : fs) {
- if (f.isAnnotationPresent(JsonField.class)) {
- classMap.put(f.getName(), f.getClass());
- }
- }
- if (classMap.isEmpty()) {
- return;
- }
- JSONObject json = JSONObject.fromObject(this.value);
- JsonDO o = (JsonDO) JSONObject.toBean(json, getClass(), classMap);
- Set<String> set = classMap.keySet();
- Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();
- while (it.hasNext()) {
- String name = it.next();
- try {
- Object value = PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(o, name);
- BeanUtils.copyProperty(this, name, value);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- log.error("copy prorperty error src=" + this.value, e);
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- *
- *
- * <p>
- * 将JsonField 标注了的基本属性组装成json字符串保存在value中
- * </p>
- *
- * @author <a href="mailto:qingxu@taobao.com" mce_href="mailto:qingxu@taobao.com">清虚</a>
- * @since 2.0 2009-10-19下午02:41:27
- *
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- protected void encode() {
- JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
- Field[] fs = getClass().getDeclaredFields();
- for (Field f : fs) {
- if (f.isAnnotationPresent(JsonField.class)) {
- String name = f.getName();
- Object value = null;
- try {
- value=PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(this, name);
- //value = f.get(this);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- log.error("get field value failed! fieldName=" + name, e);
- }
- if (value == null) {
- continue;
- }
- Class type = f.getType();
- if (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) {
- Collection it = (Collection) value;
- for (Object v : it) {
- json.accumulate(name, v);
- }
- } else if (type.isArray()) {
- json.put(name, JSONArray.fromObject(value));
- } else {
- json.put(name, value);
- }
- }
- }
- this.value=json.toString();
- //setValue(json.toString());
- }
- /*
- * (non-Javadoc)
- *
- * @see java.lang.Object#toString()
- */
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(this);
- }
使用方式如下:
- public class TrafficDO extends JsonDO {
- /**
- *序列号
- */
- private static final long serialVersionUID = -5673233152393642499L;
- @JsonField
- private String invoiceTitle; //发票抬头
- @JsonField
- private String fullName; //配送人姓名
- @JsonField
- private String mobileTel; //配送手机号码
- @JsonField
- private String province; //省
- @JsonField
- private String city; //市
- @JsonField
- private String section; //区
- @JsonField
- private String address; //详细地址
- @JsonField
- private String post; //邮编
- private int shipmentType; //配送方式
- public static final int BY_MAIL_TYPE = 0; //挂号信邮寄方式
- public static final int BY_NOTNEED = -1; //不需要行程单
- /**
- * @return the shipmentType
- */
- public int getShipmentType() {
- return shipmentType;
- }
- /**
- * @param shipmentType the shipmentType to set
- */
- public void setShipmentType(int shipmentType) {
- this.shipmentType = shipmentType;
- }
- /**
- * @return the fullName
- */
- public String getFullName() {
- return fullName;
- }
- /**
- * @param fullName the fullName to set
- */
- public void setFullName(String fullName) {
- this.fullName = fullName;
- }
- /**
- * @return the mobile
- */
- public String getMobileTel() {
- return mobileTel;
- }
- /**
- * @param mobile the mobile to set
- */
- public void setMobileTel(String mobile) {
- this.mobileTel = mobile;
- }
- /**
- * @return the province
- */
- public String getProvince() {
- return province;
- }
- /**
- * @param province the province to set
- */
- public void setProvince(String province) {
- this.province = province;
- }
- /**
- * @return the city
- */
- public String getCity() {
- return city;
- }
- /**
- * @param city the city to set
- */
- public void setCity(String city) {
- this.city = city;
- }
- /**
- * @return the section
- */
- public String getSection() {
- return section;
- }
- /**
- * @param section the section to set
- */
- public void setSection(String section) {
- this.section = section;
- }
- /**
- * @return the address
- */
- public String getAddress() {
- return address;
- }
- /**
- * @param address the address to set
- */
- public void setAddress(String address) {
- this.address = address;
- }
- /**
- * @return the post
- */
- public String getPost() {
- return post;
- }
- /**
- * @param post the post to set
- */
- public void setPost(String post) {
- this.post = post;
- }
- /**
- * 邮寄
- *
- * @return
- */
- public boolean isMail() {
- return this.shipmentType == BY_MAIL_TYPE;
- }
- /**
- * 不需要
- *
- * @author qingxu
- * @since 2007-10-25下午04:48:12
- *
- * @return
- */
- public boolean isNotNeed() {
- return this.shipmentType == BY_NOTNEED;
- }
- public String getInvoiceTitle() {
- return invoiceTitle;
- }
- public void setInvoiceTitle(String invoiceTitle) {
- this.invoiceTitle = invoiceTitle;
- }
- }
@JsonField标注支持 基本类型和数组、collection类型域。
在从DB中load出traffic_description的值后
通过setValue()方法设置进去,那么所有的json域都会被填充好。同样的,如果填充了相应的json域,
在存储在数据库中时,可以调用getValue()得到字符串持久化到数据库中。
通过getValue()得到的字符串形式如下:
- {"section":"马龙县","fullName":"叮当","address":"vvvvvv","province":"云南省","invoiceTitle":"vvvvvv","mobileTel":"136**622627","post":"310014","city":"曲靖市"}
这种处理方式的好处是,可以方便的定义你自己要存储的内容,你所有做的仅仅是在新增一个field,然后在上面打上@JsonField标注即可。
而它的缺点也是明显的,1、这种方式明显增加了存储内容的长度 2、由于存储的key是属性的名称,如果名称不匹配也会找不到对应的值。3、如果要对其中的内容进行条件检索,只有进行文本匹配,如果有这种需求,这种方式不推荐。





















 280
280











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








