puppet资源file资源介绍
资源的介绍
资源是puppet最基本的元素,每个资源的定义都具有标题、类型以及一系列的属性。puppet的特性就是处理资源与资源之间的依赖关系。
任何相同类型的资源都会具有一些相同的属性。
资源定义有如下的特性:
1.puppet使用title在编译时期区分每个资源,使用命名变量(namevar)在执行时区分资源。
2.在同一类资源中title和namevar都是唯一的。
3.每个类型都有部分属性有默认值
4,如果不指定namevar,则默认赋予其title的值。
file资源
Description
Manages files, including their content, ownership, and permissions.The file type can manage normal files, directories, and symlinks; the type should be specified in the ensure attribute. Note that symlinks cannot be managed on Windows systems.
File contents can be managed directly with the content attribute, or downloaded from a remote source using the source attribute; the latter can also be used to recursively serve directories (when the recurse attribute is set to true or local). On Windows, note that file contents are managed in binary mode; Puppet never automatically translates line
endings.
Autorequires: If Puppet is managing the user or group that owns a file, the file resource will autorequire them. If Puppet is managing any parent directories of a file, the file resource will autorequire them.
这个是官方对于puppet file资源的介绍,下面我们从使用的角度出发,如何去配置file资源。
file资源的作用
1.管理文件、目录、软链接
2.管理文件内容、属性、权限
3.通过属性开指定文件来源,也可以通过source属性从远程服务器中下载。
设置recurse属性为true或者local传输整个目录
file资源可使用的参数
ensure 默认为文件或目录
backup 通过filebucket备份文件
checksum 检查文件是否被修改的方法
ctime 只读属性,文件的更新时间
mtime 只读属性,文件的修改时间
content 文件的内容,与source和target互斥
force 强制执行删除文件、软链接机目录的操作
owner 用户名或用户ID
group 指定文加年的用户组或组id
link 软链接
mode 文件权限配置,通常采用数字符号
path 文件路径
注意:以上是我们的常见参数,基本满足日常的需求,如果需要更多的参数可以参考官方文档予以查看。
资源示例
环境如下所示:
服务端:
1. 192.168.3.248 (master.example.com)
客户端:
2. 192.168.3.249 (agent1.example.com)
3. 192.168.3.239 (agent2.example.com)
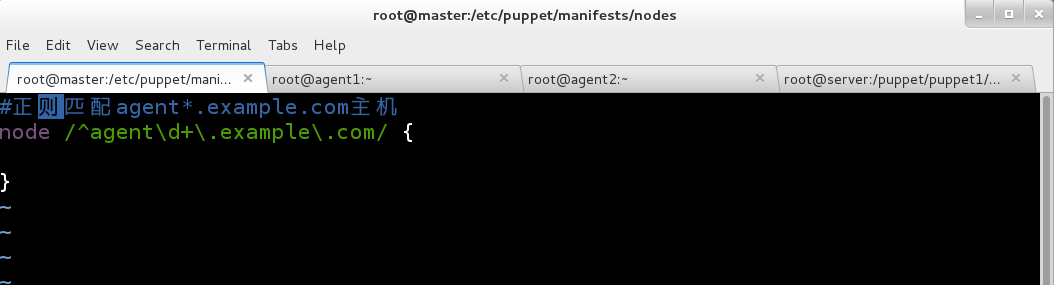
在puppet的服务段为agent1.example.com和agent2.example.com创建对应的配置文件,因为两者的主机名只有号码的差别,所以这里采用正则表达式的方式对两者进行创建。
(1)首先在/etc/puppet/manifests/目录下创建节点目录nodes:
[root@master manifests]# mkdir /etc/puppet/manifests/nodes
然后在nodes目录下创建配置文件:
[root@master nodes]# touch agent.example.com.pp
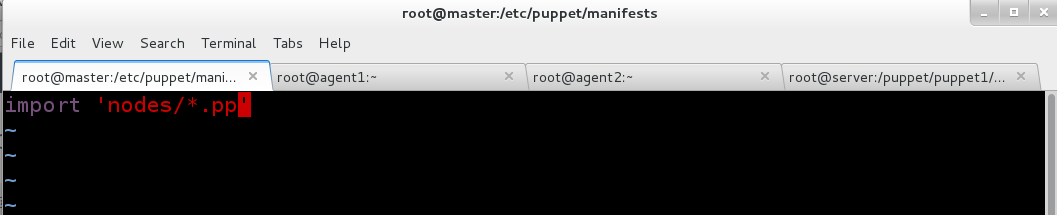
最后记得在/etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp文件中包含nodes目录里的配置文件:
案例1
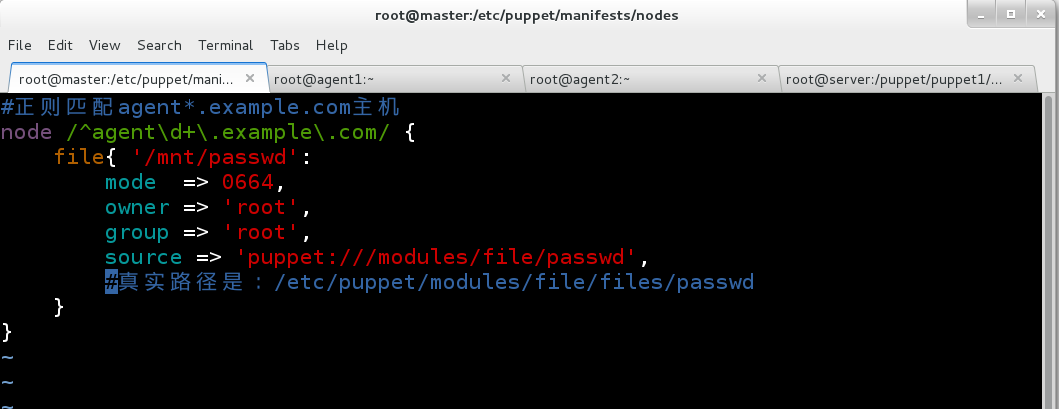
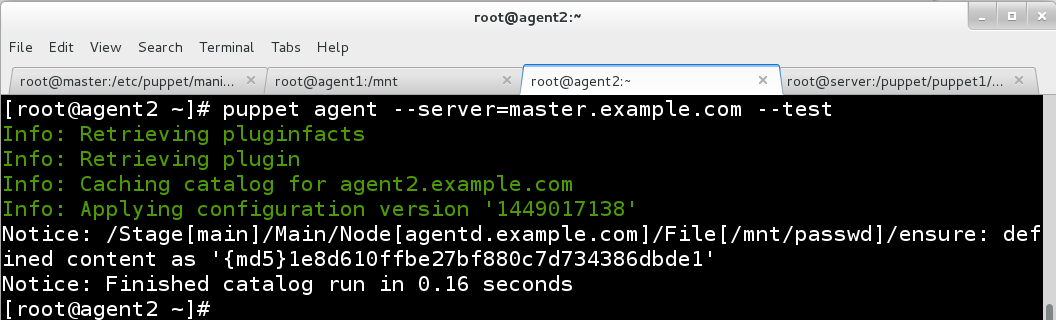
1.要求从服务器指定路径下载passwd文件到本地的/mnt/passwd,要求文件的权限是664,属于的用户和组都是root。
修改/etc/puppet/manifests/nodes/agent.example.com.pp文件:
使用agent1.exmaple.com和agent2.example.com节点进行同步:
agent1.example.com:
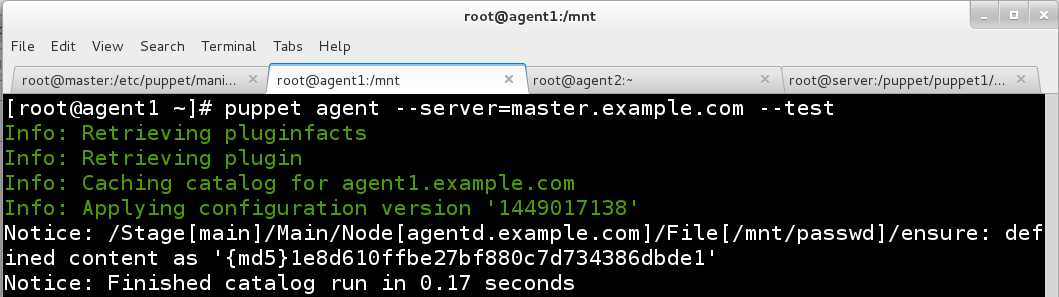
agent2.example.com:
案例2
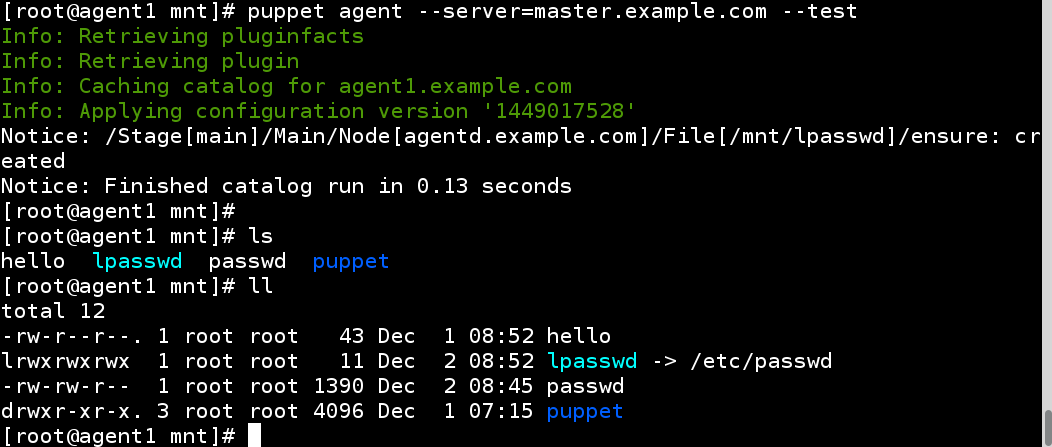
在节点上创建/etc/passwd的软链接为/mnt/lpasswd
修改配置文件:
agent同步后可以看到链接文件已经创建成功:
案例3
在节点上创建目录/mnt/haha,要求目录下除了dir外的所欧目录及文件的权限是0755,所有者为puppet
配置如下:
小结:
上述示例列举出了puppet对file资源的处理,它可以使对应的agent创建或者下载相应的文件,关于其使用细节我们在后续的章节继续进行讲解,敬请期待。





 本文详细介绍了Puppet中的file资源,包括其作用、可使用的参数和多个实战案例,展示了如何管理文件、目录、软链接,设置权限、来源等。通过示例展示如何在agent节点上创建、下载和配置文件及其属性。
本文详细介绍了Puppet中的file资源,包括其作用、可使用的参数和多个实战案例,展示了如何管理文件、目录、软链接,设置权限、来源等。通过示例展示如何在agent节点上创建、下载和配置文件及其属性。


















 22
22

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








