17.Web MVC framework
17.1 Spring Web MVC 简介
Spring Web MVC framework围绕一个可以分派请求到相应处理者的DispatcherServlet设计,它支持可配置的处理映射、视图解析、区域和主题解析并且同时支持文件上传。默认的处理者是基于@Controller和@RequestMapping注解,提供十分灵活的处理方法。根据Spring3.0的介绍,@Controller机制也允许你创建RESTful Web站点和应用程序,通过利用@PathVariable注解以及其他功能。使用Spring Web MVC 你可以把任何一个对象用来做命令对象或者表单回填对象;而不用必须实现一个特定的框架接口或者基类。Spring 的数据绑定也是很灵活的:比如,Spring框架把类型不匹配错误作为可以被应用程序解决的验证错误处理,而不是当作系统错误。因此你不必复制业务对象属性为简单的,无类型的字符串到表单对象中去,仅仅是为了验证提交或者适当的转化字符串。取而代之的是直接绑定到业务对象。
Spring 的视图解析也是相当的灵活。通常一个Controller主要负责准备一个包含有数据的模型Map并且选择一个视图名称,但是它也可以直接向响应流中写入内容并完成请求。视图名称解析也是高度可配置的。可以通过文件扩展名或者接收头内容类型协议,实体名称,属性文件,甚至是一个定制的ViewResolver的实现来配置。Model(MVC 中的 M)是一个Map接口,完全与视图技术剥离,也就是说跟使用何种视图技术没有关系。你可以将Model直接与那些基于JSP、Velocity和Freemarker这些呈现技术的模板集成,或者直接生成XML,JSON,以及许多其他类型的内容。模型Map只需要转换为合适的格式,比如JSP请求属性,Velocity模板模型。
Spring Web MVC的特色
Spring的web模块包含有很多独一无二的web支持功能:
- 分工明确。每一个角色-控制器、验证器、命令对象、表单对象、域模型、DispatcherServlet、处理器映射表、视图解析器、等角色可以分别被一个特定的对象履行。
- 强大并且直观的配置框架和应用像配置javaBeans一样。配置能力包括在不同的上下文环境中交叉引用,比如从控制器到业务模型和验证器。
- 可变、无侵入、灵活。定义你需要的控制器方法签名,尽可能的使用参数注解(如:@RequestParam,@RequestHeader,@PathVariable等等)针对给定的应用场景。
- 可重用的业务代码,无需重复。利用存在的业务对象作为命令对象或者表单对象而不需要反射他们去扩展一个特定的框架基类。
- 可定制的绑定和验证。类型不匹配作为应用级的验证错误,保存有违规的数据、本地化的日期和数字绑定等等而不是作为一个只包含有字符串属性的表单对象,需要人工解析并转换为业务对象。
- 可定制的处理器映射和视图解析。Spring提供从最简单的基于URL的配置到复杂的,特定用途的处理器映射和视图解析策略。Spring比起那些强制使用一种特定的技术进行请求映射的框架要更具有灵活性。
- 灵活的模型传递。模型传递有了一个键值对Map的支持很容易的跟任何类型的视图技术结合。
- 可定制的语言环境和主题解析,支持JSPs不论有没有Spring标签库,支持JSTL,支持Velocity不需要其他的纽带。
- 一个简单却有力的JSP标签库,也就是所说的Spring标签库,他提供对数据绑定和主题定制功能的支持。定制标签考虑到尽可能大的灵活性就标记代码来讲。想要知道关于标签库描述的信息,请看题名为: Appendix G.spring.tld的附录。
- 拥有一个JSP表单标签库,在Spring2.0版本时引入的,使得编写JSP页面的表单变得更容易。关于JSP表单标签库的描述见附录:Appendix H, spring-form.tld。
- 所有beans的生命周期被局限到当前的HTTP请求或者HTTP Session。这不是Sprign MVC自身特有的功能,而是Spring MVC所使用的WebApplicationContext 容器所具有的。Bean的范围描述在Request, session, andglobalsession scopes部分。
其他类型MVC框架可插入性
在有些项目中Non-Spring MVC的实现是更受人喜欢的。许多团队希望利用他们在技术和工具上的既有的投资。大量的Struts框架的知识和经验。如果你能够忍受Struts设计上的瑕疵,Struts也是web层一个不错的选择;也同样适用于WebWork以及其他的web MVC框架。
如果你不想使用Spring的Web MVC,但是又想要利用Spring提供的其他方面的解决方案,你可以轻松的将你选择的MVC框架跟Spring集成在一起。只需要利用ContextLoaderListener启动一个Spring跟应用上下文,通过来自Struts或者WebWork action内部的ServletContext属性(或者利用Spring的帮助方法)来访问它。不涉及任何插件,因此没有专用的集成是必须的。站在web层的观点来看,你只是使用把Spring当做一个库来使用,把根应用上下文实体作为一个入口。
尽管没有用Spring 的 Web MVC是注册 的实体和Spring服务也是唾手可得的。在这方面Spring跟Struts或者WebWork不是竞争关系。Spring致力于很多方面然而那些纯粹的web MVC框架做不到这些,从实体配置到数据访问以及事务管理。因此你可以充实你的应用程序利用Spring的中间层和/或数据访问层,甚至你可以只使用抽象于JDBC或者Hibernate的事务。
17.2 TheDispatcherServlet
Spring Web MVC 跟许多其他的Web MVC框架类似,请求驱动,围绕一个中心Servlet设计,这个中央Servlet分配请求到对应的Controller并且提供其他的功能以促进web应用的开发。但是Spring Web MVC 的DispatcherServlet能做的远远不止这些。它完全跟Spring IoC 容器集成在一起正因为如此你可以使用Spring 具有的任何其他功能。
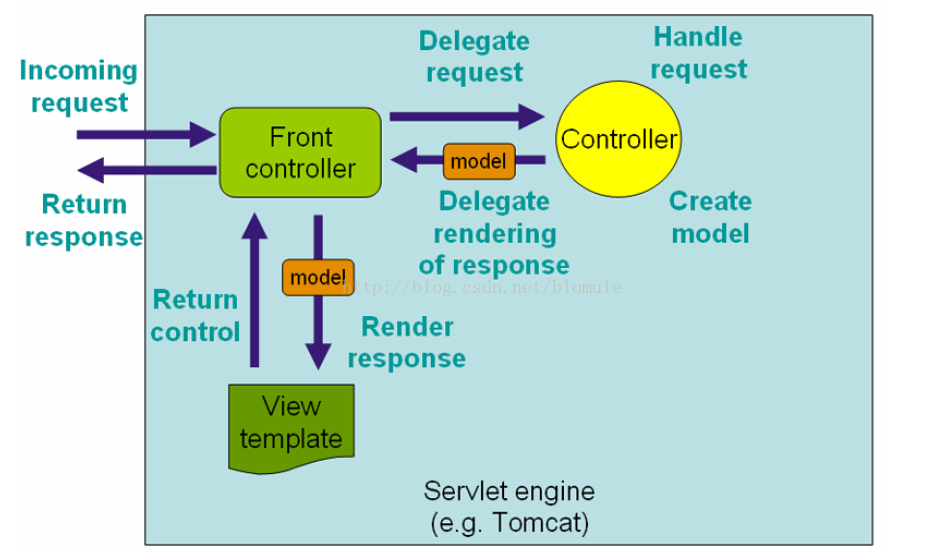
Spring Web MVC 的DispatcherServlet处理请求的工作流在下图中阐述.深谙设计模式的读者会意识到DispatcherServlet是“前端控制器”(一种设计模式 Spring Web MVC与其他主流的web框架所公用的)设计模式的一种表现形式。
Spring Web MVC 处理请求流程图(顶级)
DiapatcherServlet其实就是一个Servlet(它继承自HttpServlet这个基类),因此需要在你的web项目的web.xml中被声明。你需要映射那些你想要DispatcherServlet处理的请求,通过使用URL映射在同一个web.xml文件中。这是一个标准的Java EE Servlet 配置;下面的例子向你展示了一个DispatcherServlet的声明以及映射:
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/example/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
在前面的例子中,所有的以/example 开头的请求将会被命名为example的DispatcherServlet实体处理。在一个Servlet3.0以上的环境中,你也可以选择以编程的方式配置Servlet容器。下面是的代码基本等效于上面的web.xml例子:
public classMyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer{
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container){
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration=container.addServlet("dispatcher",newDispatcherServlet());
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/example/*");
}
}WebApplicationInitializer是一个Spring MVC提供的接口用来确保你的基于代码的配置能够被检测到并自动被用来初始化任何类型的Servlet 3容器。一个实现了该接口的抽象基类AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer使注册DisapatcherServlet变得更加容易,只需要简单的制定的servlet 的映射。在Code-based Servlet containerinitialization了解更多信息。
以上只是设置Spring Web MVC 框架的第一步。接下来你需要配置多种多样的Spring Web MVC框架需要使用的实体(除了DispatcherServlet以外的)。
正如在5.14节详细说明的一样“ApplicationContext的附加功能”,Spring中的Application -Context实体是有范围的。在Web MVC框架中,每一个DispatcherServlet有它自己的Web Appli -cationContext,这个WebApplicationContext继承所有已经在根Web ApplicationContext中定义的实体。这些被继承的实体可以在特定的Servelt范围内被重写,你也可以为一个给定的Ser -vlet实体定义新的特定范围的实体。
在初始化一个DispatcherServlet 的时候,SpringMVC 会在你的web项目的WEB-INF目录下去寻找一个以[servlet-name]-servlet.xml命名规范命名的配置文件并会创建在这个配置文件中声明的实体,也会重写在全局范围内以相同名称被定义的实体。
思考下面的DispatcherServlet配置(在 web.xml中):
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>golfing</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>golfing</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/golfing/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
如果你的项目中用到了上面这中配置,那么在你项目中需要有这样一个配置文件:WEB-INF/golfi -ng -servlet.xml;这个文件中包含有跟你的Spring MVC框架相关的组件。你可以使用Servelt初始化参数来改变这个这个配置文件的确切位置(将在下文中做详细介绍)。
WebApplicationContext是对原始的ApplicationContext的扩展,增加了一些web应用需要的功能。WebApplicationContext跟一般的ApplicationContext的不同之处在于它具有解析主题的能力并且它知道自己跟哪个Servlet相关联(WebApplicationContext引用了ServletContext)。WebApplicationContext被绑定到ServletContext上,当你需要访问WebApplicationContext的时候你可以使用RequestContextUtils提供的静态方法来获取WebApplicationContext。
WebApplicationContext中的特殊实体
Spring 的DispatcherServlet利用特殊的实体来处理来之页面的请求并且渲染合适的视图。这些实体是Spring MVC的一部分。你可以根据自己的需要在配置这些实体。Spring MVC 维护有一组默认的实体,当你没做任何的配置的时候,那些默认的实体将会被使用,因此你不一定必须配置实体。更多信息将在下一节中讲述。先看看下面的表格,列出了DispatcherServlet所依赖的一些特殊的实体。
表 17.1. WebApplicationContext中的特殊类型的实体
| 实体类型 | 说明 |
| HandlerMapping | 将请求映射到对应的处理器以及以系列的前置或后置处理(处理者拦截器)根据一些标准,这些标准的细节可以被HandlerMapping 的实现多样化。最受欢迎的实现支持带有注解的控制器但是也有其他类型实现。 |
| HandlerAdapter | 帮助DispatcherServlet调用映射到请求的处理器,而不用管实际调用的是那个处理者。比如,调用一个有注解的控制器需要解析多个注解。因此HandlerAdapter 的作用就是对DispatcherServlet隐藏这些细节。 |
| HandlerExceptionResolver | 将异常映射到视图或者更复杂的一场处理代码 |
| ViewResolver | 解析字符串类型的逻辑视图名称到实际的视图类型 |
| LocaleResolver | 解析用户的使用的地域,为了提供国际化视图 |
| ThemeResolver | 解析你的web应用可以使用的主题,比如想要提供个性化的布局 |
| MultipartResolver | 解析多部请求例如支持来自HTML表单的文件上传 |
| FlashMapHandler | 存储、检索输入和输出的FlashMap用来在请求之间传递属性,通常用在重定向的时候。 |
默认的DispatcherServlet配置
前面提到的每一个特定的实体DispatcherServlet都默认维护有一系列他们的实现。关于这些实体的信息保存在org.springframework.web.servlet包下面的DispatcherServlet.properties文件中。
所有的特定实体都有自己合理的默认值。尽管迟早你会你会定制这些实体的属性。比如,你会经常配置一个InternalResourceViewResolver并设置它的prefix属性为视图文件的父文件夹。
不用关注细节,理解这个地方的重要理论是一旦你配置了一个特殊的实体比如一个InternalReso –urceViewResolver在你的WebApplicationContext中,你实际上重写了默认的,本该被使用的实现列表。例如如果你配置了一个InternalResourcesViewResolver,默认的ViewResolver实现列表将会被忽略。
在17.15部分“配置Spring MVC”你将了解配置Spring MVC的其他可选项,包括 用java文件配置MVC以及MVC XML的命名空间,那些知识仅仅向你提供了一个简单的切入点。假设你已经对Spring MVC如何工作有了一定的了解。不管你是以何种方式配置你的应用程序,在该部分讲解的基本概念都将对你有所帮助。
DispatcherServlet处理顺序
在你设置好一个DispatcherServlet以后,并且这个DispatcherServlet对应的请求到来,接着DispatcherServlet按照下面的步骤处理该请求:
1. 相应WebApplicationContext将会被寻找并且作为一个属性被绑定到请求上为了方便处理过程中用到的处理器和其他元素使用。默认情况下会被绑定到DispatcherServlet.WEB_APPLICATION_CO -NTEXT_ATTRIBUTE键下。
2. 地域解析器也会被绑定到请求上便于处理过程中的其他元素在处理请求(渲染视图、准备数据等)的时候可以确定使用区域。如果你不需要解析地域,那么你将不需要用它。
3. 主题解析器被绑定到请求上为了让视图这类处理元素知道使用哪种主题。如果你不适用主题,你可以忽略。
4. 如果你指定了多部件文件解析器,则会在请求中检查多部分;如果多部分被找到了,那么请求将会被封装为MultipartHttpServletRequest便于处理流程中接下来的元素来处理改请求。请看17.10,“Spring 的多部(文件上传)支持”获取跟多部处理有关的更多信息。
5. 一个合适的处理器被搜索。如果一个处理者被找到了,为了准备model或者渲染,跟该处理者(前置处理器,后置处理器,控制器)关联的执行链将会被执行。
6. 如果一个模型被返回,视图将会被渲染。如果没有模型返回,(可能是以为一个前置处理器或者后置处理器拦截了请求,也有可能因为安全原因),不会有视图被渲染,因为请求到此已经完成了。
声明在WebApplicationContext中的处理异常解析器收集处理请求过程中被抛出的异常。利用这些异常解析器你可以定制异常的处理行为。
Spring的DispatcherServlet也支持返回last-modification-date,像Servlet API规定的一样。决定某一请求的最后修改时间的处理流程是比较直观的:DispatcherServlet寻找一个合适的处理者映射并且检查这些处理者是否实现了LastModified接口。如果实现了,LastModified接口的Long getLastModified(request)方法的返回值将会被返回到客户端。
你可以在web.xml中声明Servlet的时候为DispatcherServlet设置初始化参数来定制个人的DispatcherServlet。下面的表中显示了支持的参数。
表17.2 DispatcherServlet初始化参数
| 参数 | 说明 |
| contextClass | 一个类实现了WebApplicationContext接口,实例化Servlet使用的上下文。默认情况下XmlWebapplicationContext被使用。 |
| contextConfigLocation | 一个被传递给上下文实例(contextClass指定的)的字符串用来指明上下文可以在哪里被找到。这个字符串可以包含多个子串(子串之间用逗号分隔)来初始化多个上下文。同一个实体的位置被定义两次的话靠后的位置将会起作用。 |
| namespace | WebApplicationContext的命名空间。默认的是[servlet-name]-servlet |
17.3控制器的实现
控制器可以访问应用程序行为通常你通过一个服务接口定义的。控制器翻译用户输入成为一个模型,对视图来说代表用户。Spring用很抽象的方法实现一个控制器,因此你可以创建多种多样的控制器。
Spring2.5为MVC控制器引入了基于注解的编程模型,可以使用@RequestMapping,@RequestPara -m,@ModelAttribute等。Servlet MVC 和Portlet都可以使用这些注解。以此种方式实现的控制器无需扩展特定的基类或者实现特定的接口。此外他们不会经常直接依赖Servlet或者Portle -t APIs,但是你可以轻松的配置对Servlet或Portlet的访问。
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping("/helloWorld")
public String helloWorld(Model model){
model.addAttribute("message","Hello World!");
return "helloWorld";
}
}正如你看到一样,@Controller和@RequestMapping注解允许灵活的方法名和签名。在这个特定例子中这个方法接收一个Model并且以字符串的形式返回一个视图的逻辑名称,但是其他类型的接收参数和返回参数也是可以被使用的,将在这一章节的后面讲述。@Controller和@RequestMa -ppding以及许多其他的注解构成了Spring MVC实现的基石。该部分记载那些在Servl -et环境中最常使用的注解。
用@Controller定义一个控制器
@Controller注解表明一个特定的类起着控制器的作用。Spring 不要求你扩展任何的控制器基类或者引用Servelet API。如果需要你也可以引用特定的Servlet的功能。
@Controller注解扮演着一个原型对被注解的类来说,声明了类的扮演的角色。分配器扫描带有@Controller注解的类寻找被影射的方法并且找出@RequestMapping注解(请看下节)。
你可以用标准的Spring实体定义方法,明确的定义注解的控制器在分配器上下文中。@Controller原型也支持自动检测,与Spring通常支持在类路径上检测组件类并自动注册为他们定义的实体一致。
为了能够使用自动检测被注解的控制器,你需要在你的配置文件添加组件扫描。利用spring-context模式像下面列出的XML片段一样:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.samples.petclinic.web"/>
</beans>





















 630
630











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








