| 对话框大合集
今天我用自己写的一个Demo和大家详细介绍一个Android中的对话框的使用技巧。 |
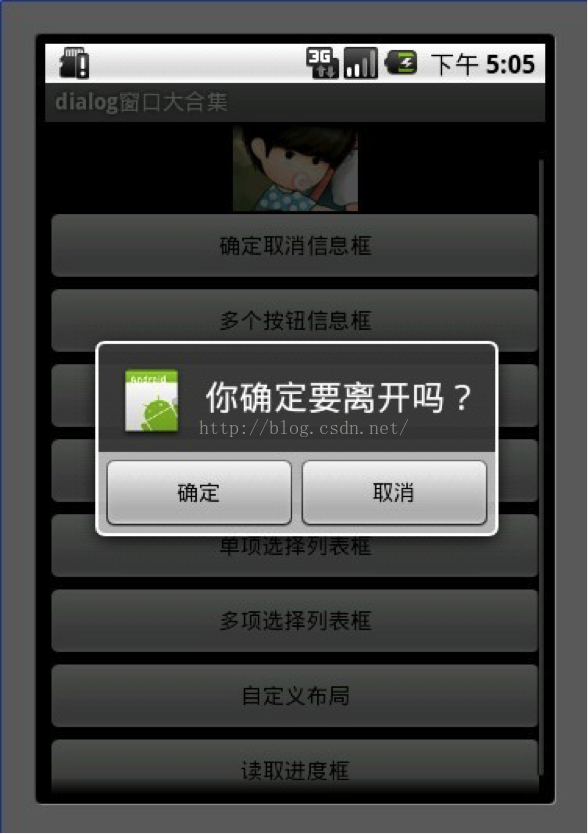
1.确定取消对话框
对话框中有2个按钮 通过调用setPositiveButton方法和 setNegativeButton方法可以设置按钮的显示内容以及按钮的监听事件。
我们使用AlerDialog创建对话框
1 AlertDialog.Builder builder = newAlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
复制代码
使用builder设置对话框的title button icon等等
1 builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
2 builder.setTitle("你确定要离开吗?");
3 builder.setPositiveButton("确定",new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
4 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
5 //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑
6 showDialog("你选择了确定");
7 }
8 });
9 builder.setNegativeButton("取消",new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
10 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
11 //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑
12 showDialog("你选择了取消");
13 }
14 });
15 builder.create().show();
16
复制代码
这个dialog用于现实onClick后监听的内容信息
1 private void showDialog(String str) {
2 newAlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this)
3 .setMessage(str)
4
5 .show();
6 }
复制代码
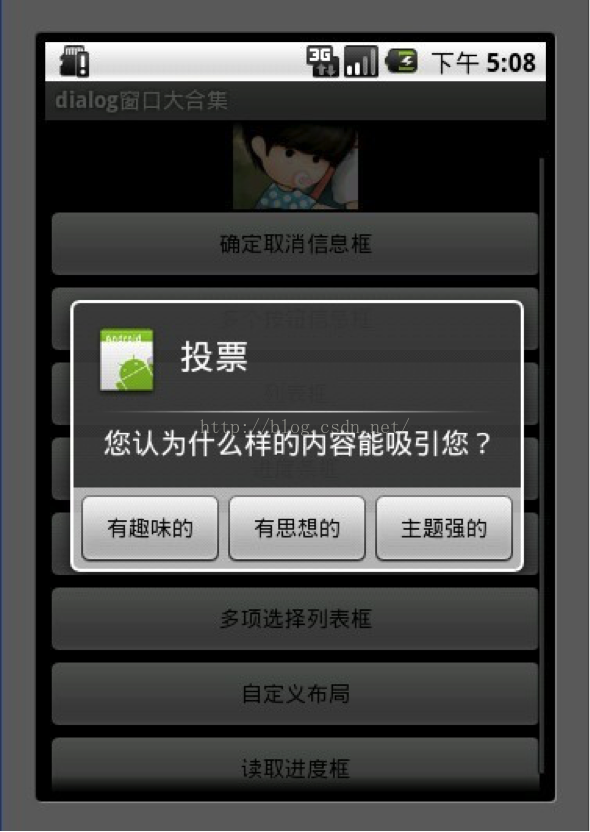
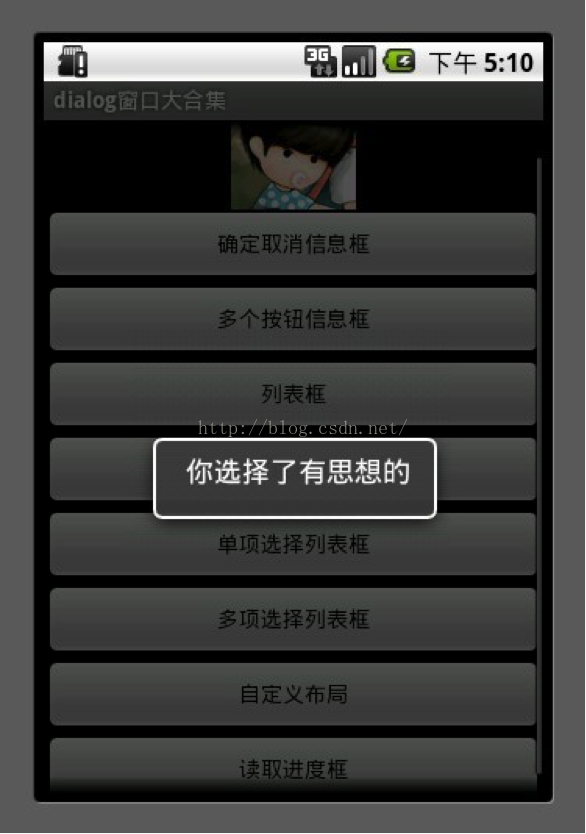
2.多个按钮信息框
1 AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
2 builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
3 builder.setTitle("投票");
4 builder.setMessage("您认为什么样的内容能吸引您?");
5 builder.setPositiveButton("有趣味的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
6 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
7 showDialog("你选择了有趣味的");
8 }
9 });
10 builder.setNeutralButton("有思想的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
11 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
12 showDialog("你选择了有思想的");
13 }
14 });
15 builder.setNegativeButton("主题强的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
16 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
17 showDialog("你选择了主题强的");
18 }
19 });
20 builder.create().show();
复制代码
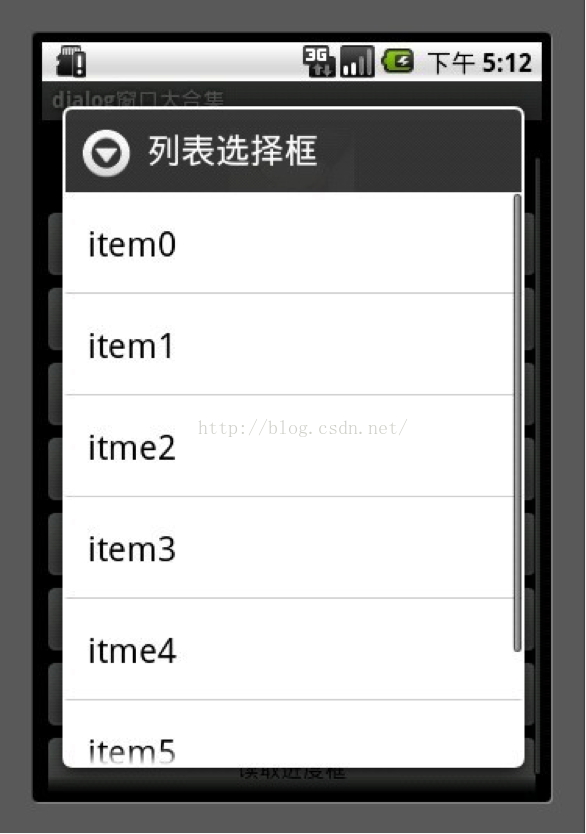
3.列表框
这个数组用于列表选择
1 final String[] mItems ={"item0","item1","itme2","item3","itme4","item5","item6"};
复制代码
1 AlertDialog.Builder builder = newAlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
2 builder.setTitle("列表选择框");
3 builder.setItems(mItems, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
4 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
5 //点击后弹出窗口选择了第几项
6 showDialog("你选择的id为" + which+ " , " + mItems[which]);
7 }
8 });
9 builder.create().show();
10
复制代码
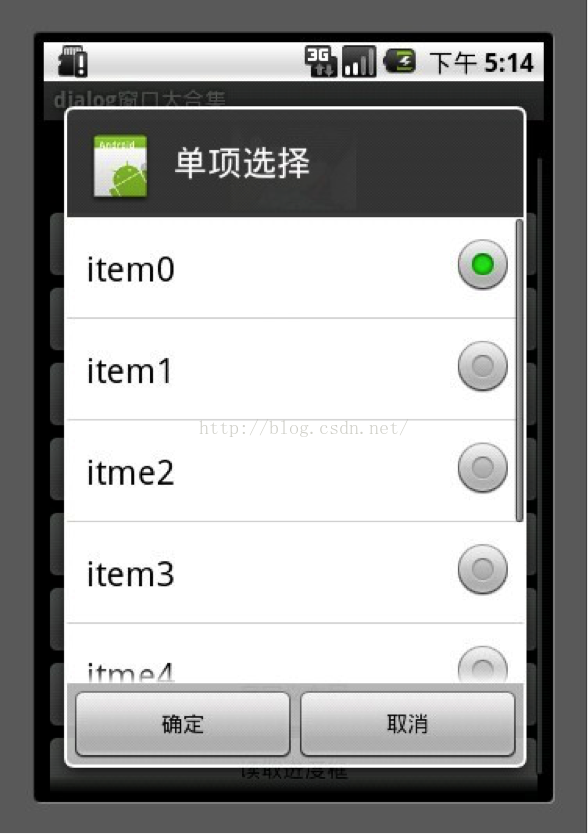
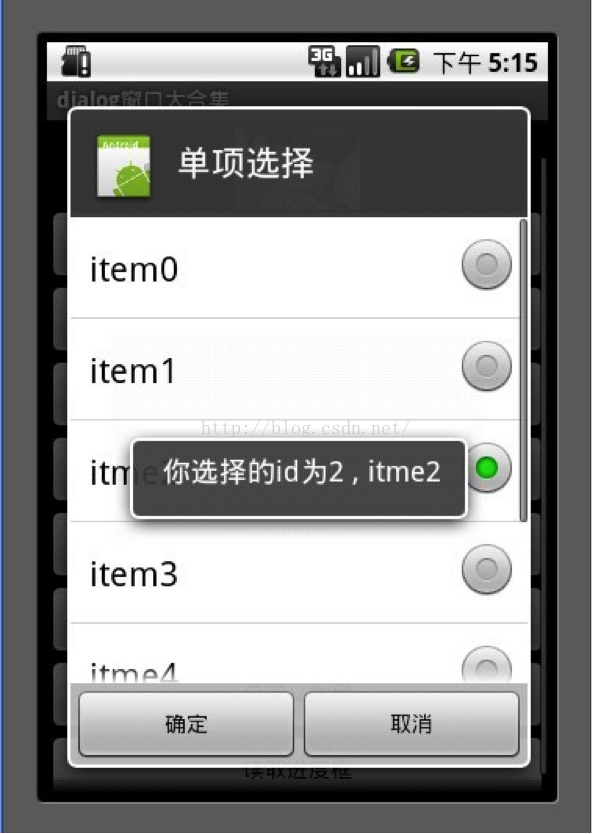
4.单项选择列表框
mSingleChoice用于记录单选中的ID
1 int mSingleChoiceID = -1;
复制代码
1 AlertDialog.Builder builder = newAlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
2
3 mSingleChoiceID =-1;
4 builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
5 builder.setTitle("单项选择");
6 builder.setSingleChoiceItems(mItems, 0, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
7 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
8 mSingleChoiceID =whichButton;
9 showDialog("你选择的id为" +whichButton + " , " + mItems[whichButton]);
10 }
11 });
12 builder.setPositiveButton("确定", newDialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
13 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
14 if(mSingleChoiceID > 0) {
15 showDialog("你选择的是" + mSingleChoiceID);
16 }
17 }
18 });
19 builder.setNegativeButton("取消", newDialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
20 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
21
22 }
23 });
24 builder.create().show();
复制代码
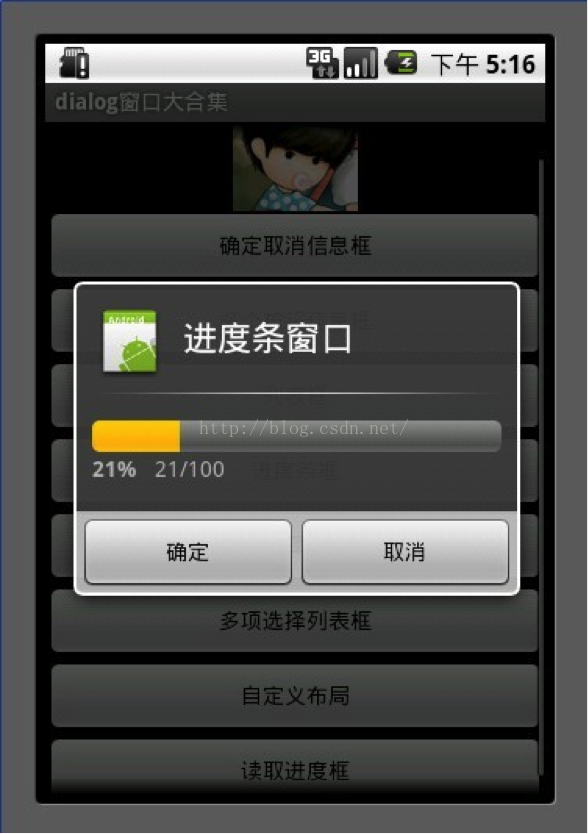
5.进度条框
点击进度条框按钮后开启一个线程计算读取的进度假设读取结束为 100
Progress在小于100的时候一直在线程中做循环++只到读取结束后,停止线程。
1 mProgressDialog = newProgressDialog(MainDialog.this);
2 mProgressDialog.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
3 mProgressDialog.setTitle("进度条窗口");
4 mProgressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
5 mProgressDialog.setMax(MAX_PROGRESS);
6 mProgressDialog.setButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
7 public voidonClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
8 //这里添加点击后的逻辑
9 }
10 });
11 mProgressDialog.setButton2("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
12 public voidonClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
13 //这里添加点击后的逻辑
14 }
15 });
16 mProgressDialog.show();
17 new Thread(this).start();
18
19 public void run() {
20 int Progress = 0;
21 while(Progress <MAX_PROGRESS) {
22 try {
23 Thread.sleep(100);
24 Progress++;
25 mProgressDialog.incrementProgressBy(1);
26 } catch(InterruptedException e) {
27 //TODO Auto-generated catch block
28 e.printStackTrace();
29 }
30
31 }
32
33 }
复制代码
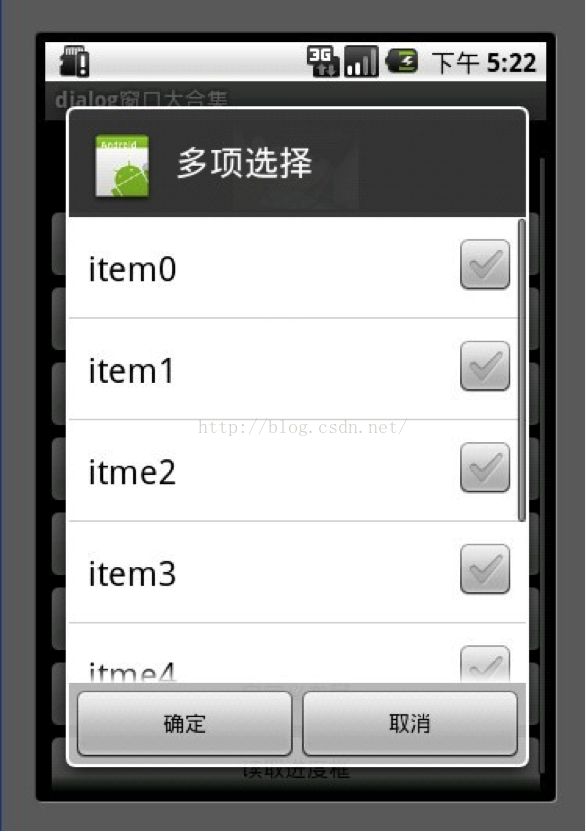
6.多项选择列表框
MultiChoiceID用于记录多选选中的id号存在ArrayList中
选中后add进ArrayList
取消选中后remove出ArrayList。
1 ArrayList <Integer>MultiChoiceID = new ArrayList<Integer>();
复制代码
1 AlertDialog.Builderbuilder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
2
3 MultiChoiceID.clear();
4 builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
5 builder.setTitle("多项选择");
6 builder.setMultiChoiceItems(mItems,
7 new boolean[]{false, false, false,false, false, false, false},
8 newDialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
9 public voidonClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton,
10 boolean isChecked) {
11 if(isChecked) {
12 MultiChoiceID.add(whichButton);
13 showDialog("你选择的id为" + whichButton + " , " +mItems[whichButton]);
14 }else {
15 MultiChoiceID.remove(whichButton);
16 }
17
18 }
19 });
20 builder.setPositiveButton("确定",new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
21 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
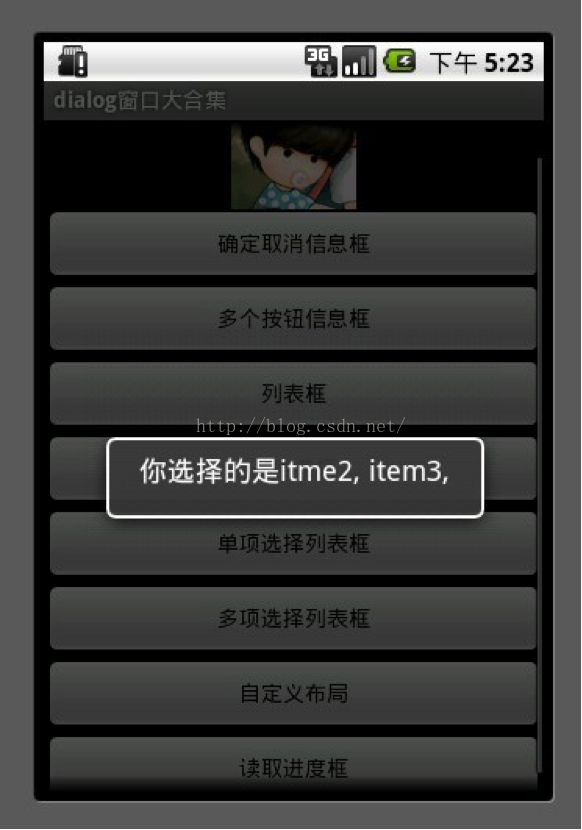
22 String str = "";
23 int size = MultiChoiceID.size();
24 for (int i = 0 ;i < size; i++) {
25 str+= mItems[MultiChoiceID.get(i)]+ ", ";
26 }
27 showDialog("你选择的是" + str);
28 }
29 });
30 builder.setNegativeButton("取消",new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
31 public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, intwhichButton) {
32
33 }
34 });
35 builder.create().show();
复制代码
7.自定义布局
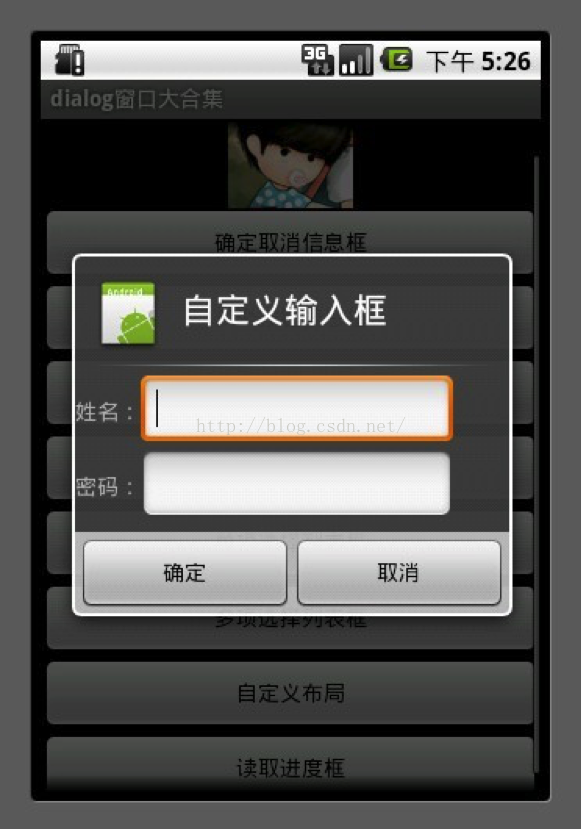
讲到自定义布局我就得多说一说了,为什么要多说一说呢? 其实自定义布局在Android的开发中非常重要因为它能让开发者做出自己五彩缤纷的Activity而不用去使用系统枯燥的界面。自定义dialog有什么好处?比如我们在开发过长当中要通过介绍系统发送的一个广播弹出一个dialog . 但是dialog必需是基于activity才能呈现出来如果没有activity的话程序就会崩溃。所以我们可以写一个自定义的 dialog 把它定义成一个activity 这样我们收到一条打开dialog的广播后直接启动这个activity 程序正常运行~~ 这就是自定义dialog的好处。注明:下面这个例子只是写了自定义dialog没有把它单独的写在一个activity中如果须要的话可以自己改一下。
1 AlertDialog.Builder builder = newAlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
2 LayoutInflaterfactory = LayoutInflater.from(this);
3 finalView textEntryView = factory.inflate(R.layout.test, null);
4 builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
5 builder.setTitle("自定义输入框");
6 builder.setView(textEntryView);
7 builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
8 public void onClick(DialogInterfacedialog, int whichButton) {
9
10 EditText userName = (EditText)textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.etUserName);
11 EditText password = (EditText)textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.etPassWord);
12 showDialog("姓名:" +userName.getText().toString() + "密码:" + password.getText().toString() );
13 }
14 });
15 builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
16 public void onClick(DialogInterfacedialog, int whichButton) {
17
18 }
19 });
20 builder.create().show();
复制代码
1 <span style="color:#000000;"><?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <RelativeLayoutxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
4 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
5 android:orientation="horizontal"
6 android:id="@+id/dialog">
7 <LinearLayout
8 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
9 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
10 android:orientation="horizontal"
11 android:id="@+id/dialogname">
12
13 <TextViewandroid:layout_height="wrap_content"
14 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
15 android:id="@+id/tvUserName"
16 android:text="姓名:" />
17 <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content"
18 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
19 android:id="@+id/etUserName"
20 android:minWidth="200dip"/>
21 </LinearLayout>
22 <LinearLayout
23 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
24 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
25 android:orientation="horizontal"
26 android:id="@+id/dialognum"
27 android:layout_below="@+id/dialogname"
28 >
29 <TextViewandroid:layout_height="wrap_content"
30 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
31 android:id="@+id/tvPassWord"
32 android:text="密码:" />
33 <EditTextandroid:layout_height="wrap_content"
34 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
35 android:id="@+id/etPassWord"
36 android:minWidth="200dip"/>
37 </LinearLayout>
38 </RelativeLayout></span>
复制代码
8.读取进度框显示一个正在转圈的进度条loading
1 mProgressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this);
2 mProgressDialog.setTitle("读取ing");
3 mProgressDialog.setMessage("正在读取中请稍候");
4 mProgressDialog.setIndeterminate(true);
5 mProgressDialog.setCancelable(true);
6 mProgressDialog.show();
复制代码
最后如果你还是觉得我写的不够详细不要紧我把源代码的下载地址贴出来欢迎大家一起讨论学习雨松MOMO希望可以和大家一起进步。




















 243
243











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








