示例分析
在内核kernel/drivers/regulator/dummy.c文件中构造了一个虚拟的regulator,参考此文件编写一个虚拟的regulator driver。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/regulator/driver.h>
#include <linux/regulator/machine.h>
static struct regulator_dev *dummy_regulator_rdev;
static struct regulator_consumer_supply relate={
.dev_name = "reg-consumer",
.supply = "VCC",
};
static struct regulator_init_data dummy_initdata = {
.constraints = {
.name ="my_regulator_constrains",
.always_on = 1,
},
.num_consumer_supplies = 1,
.consumer_supplies = &relate,
};
static struct regulator_ops dummy_ops;
static struct regulator_desc dummy_desc = {
.name = "regulator-driver",
.id = -1,
.type = REGULATOR_VOLTAGE,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.ops = &dummy_ops,
};
static int regulator_driver_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct regulator_config config = { };
int ret;
config.dev = &pdev->dev;
config.init_data = &dummy_initdata;
dummy_regulator_rdev = regulator_register(&dummy_desc, &config);
if (IS_ERR(dummy_regulator_rdev)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(dummy_regulator_rdev);
pr_err("Failed to register regulator: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver regulator_driver = {
.probe = regulator_driver_probe,
.driver = {
.name = "reg-driver",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
static struct platform_device *regulator_pdev;
static int regulator_driver_init(void)
{
int ret;
regulator_pdev = platform_device_alloc("reg-driver", -1);
if (!regulator_pdev) {
pr_err("Failed to allocate dummy regulator device\n");
return -1;
}
ret = platform_device_add(regulator_pdev);
if (ret != 0) {
pr_err("Failed to register dummy regulator device: %d\n", ret);
platform_device_put(regulator_pdev);
return -1;
}
ret = platform_driver_register(®ulator_driver);
if (ret != 0) {
pr_err("Failed to register dummy regulator driver: %d\n", ret);
platform_device_unregister(regulator_pdev);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static void regulator_driver_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_EMERG "regulator: regulator_consumer_exit\n");
regulator_unregister(dummy_regulator_rdev);
platform_device_unregister(regulator_pdev);
platform_driver_unregister(®ulator_driver);
}
module_init(regulator_driver_init);
module_exit(regulator_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
regulator的作用就是管理consumer设备,给consumer设备提供voltage, current。所以必须实现一个consumer设备,代码如下:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/regulator/consumer.h>
static struct regulator* my_regulator;
static int regulator_consumer_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int ret;
printk(KERN_EMERG "regulator: regulator_consumer_probe\n");
my_regulator = regulator_get(&pdev->dev,"VCC");
ret = regulator_enable(my_regulator);
return 0;
}
static int regulator_consumer_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk(KERN_EMERG "regulator: regulator_consumer_remove\n");
regulator_put(my_regulator);
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver regulator_consumer_driver = {
.probe = regulator_consumer_probe,
.remove = regulator_consumer_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "reg-consumer",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
static struct platform_device *regulator_consumer;
static int regulator_consumer_init(void)
{
int ret;
printk(KERN_EMERG "regulator: regulator_consumer_init\n");
regulator_consumer = platform_device_alloc("reg-consumer", -1);
if (!regulator_consumer) {
pr_err("Failed to allocate dummy regulator consumer!\n");
return -1;
}
ret = platform_device_add(regulator_consumer);
if (ret != 0) {
pr_err("Failed to register dummy regulator consumer: %d\n", ret);
platform_device_put(regulator_consumer);
return -1;
}
ret = platform_driver_register(®ulator_consumer_driver);
if (ret != 0) {
pr_err("Failed to register dummy regulator consumer: %d\n", ret);
platform_device_unregister(regulator_consumer);
}
return ret;
}
static void regulator_consumer_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_EMERG "regulator: regulator_consumer_exit\n");
platform_device_unregister(regulator_consumer);
platform_driver_unregister(®ulator_consumer_driver);
}
module_init(regulator_consumer_init);
module_exit(regulator_consumer_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
测试结果
1. 先安装regulator.ko文件,安装此文件后会在/sys/devices/platform/下生成一个"reg-driver"的设备。
test:/sys/devices/platform/reg-driver # ls -l
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:13 driver -> ../../../bus/platform/drivers/reg-driver
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 2012-01-01 13:13 driver_override
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 2012-01-01 13:13 modalias
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:13 power
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:13 regulator
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:13 subsystem -> ../../../bus/platform
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 2012-01-01 13:13 ueventtest:/sys/class/regulator/regulator.27 # ls
device num_users subsystem suspend_mem_state type
name power suspend_disk_state suspend_standby_state uevent test:/sys/class/regulator/regulator.27 # cat name
my_regulator_constrains
test:/sys/devices/platform/reg-consumer # ls -l
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:29 driver -> ../../../bus/platform/drivers/reg-consumer
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 2012-01-01 13:29 driver_override
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 2012-01-01 13:29 modalias
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:29 power
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:29 subsystem -> ../../../bus/platform
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 2012-01-01 13:29 uevent
test:/sys/class/regulator/regulator.27 # ls
device power suspend_disk_state type
name reg-consumer-VCC suspend_mem_state uevent
num_users subsystem suspend_standby_statetest:/sys/kernel/debug/regulator # cat regulator_summary
regulator use open bypass voltage current min max
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
....
my_regulator_constrains 0 1 0 0mV 0mA 98mV 987mV
reg-consumer 0mV 0mV
test:/sys/kernel/debug/regulator/my_regulator_constrains # ls -l
total 0
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:13 bypass_count
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:13 open_count
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:28 reg-consumer-VCC
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 2012-01-01 13:13 use_count
代码分析
基于上述的测试结果,首先分析整个regulator的注册过程,已经regulator和consumer之间关系的匹配过程。regulator_register分析
struct regulator_dev *regulator_register(const struct regulator_desc *regulator_desc,const struct regulator_config *config)
{
const struct regulation_constraints *constraints = NULL;
const struct regulator_init_data *init_data;
static atomic_t regulator_no = ATOMIC_INIT(0);
struct regulator_dev *rdev;
struct device *dev;
int ret, i;
const char *supply = NULL;
if (regulator_desc == NULL || config == NULL)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
dev = config->dev;
WARN_ON(!dev);
if (regulator_desc->name == NULL || regulator_desc->ops == NULL)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
if (regulator_desc->type != REGULATOR_VOLTAGE &&
regulator_desc->type != REGULATOR_CURRENT)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
/* Only one of each should be implemented */
WARN_ON(regulator_desc->ops->get_voltage &&
regulator_desc->ops->get_voltage_sel);
WARN_ON(regulator_desc->ops->set_voltage &&
regulator_desc->ops->set_voltage_sel);
/* If we're using selectors we must implement list_voltage. */
if (regulator_desc->ops->get_voltage_sel &&
!regulator_desc->ops->list_voltage) {
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
if (regulator_desc->ops->set_voltage_sel &&
!regulator_desc->ops->list_voltage) {
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
rdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct regulator_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (rdev == NULL)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
init_data = regulator_of_get_init_data(dev, regulator_desc,
&rdev->dev.of_node);
if (!init_data) {
init_data = config->init_data;
rdev->dev.of_node = of_node_get(config->of_node);
}
mutex_lock(®ulator_list_mutex);
mutex_init(&rdev->mutex);
rdev->reg_data = config->driver_data;
rdev->owner = regulator_desc->owner;
rdev->desc = regulator_desc;
if (config->regmap)
rdev->regmap = config->regmap;
else if (dev_get_regmap(dev, NULL))
rdev->regmap = dev_get_regmap(dev, NULL);
else if (dev->parent)
rdev->regmap = dev_get_regmap(dev->parent, NULL);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rdev->consumer_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rdev->list);
BLOCKING_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(&rdev->notifier);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&rdev->disable_work, regulator_disable_work);
/* preform any regulator specific init */
if (init_data && init_data->regulator_init) {
ret = init_data->regulator_init(rdev->reg_data);
if (ret < 0)
goto clean;
}
/* register with sysfs */
rdev->dev.class = ®ulator_class;
rdev->dev.parent = dev;
dev_set_name(&rdev->dev, "regulator.%d",
atomic_inc_return(®ulator_no) - 1);
ret = device_register(&rdev->dev);
if (ret != 0) {
put_device(&rdev->dev);
goto clean;
}
dev_set_drvdata(&rdev->dev, rdev);
if (config->ena_gpio && gpio_is_valid(config->ena_gpio)) {
ret = regulator_ena_gpio_request(rdev, config);
if (ret != 0) {
rdev_err(rdev, "Failed to request enable GPIO%d: %d\n",
config->ena_gpio, ret);
goto wash;
}
}
/* set regulator constraints */
if (init_data)
constraints = &init_data->constraints;
ret = set_machine_constraints(rdev, constraints);
if (ret < 0)
goto scrub;
/* add attributes supported by this regulator */
ret = add_regulator_attributes(rdev);
if (ret < 0)
goto scrub;
if (init_data && init_data->supply_regulator)
supply = init_data->supply_regulator;
else if (regulator_desc->supply_name)
supply = regulator_desc->supply_name;
if (supply) {
struct regulator_dev *r;
r = regulator_dev_lookup(dev, supply, &ret);
if (ret == -ENODEV) {
/*
* No supply was specified for this regulator and
* there will never be one.
*/
ret = 0;
goto add_dev;
} else if (!r) {
dev_err(dev, "Failed to find supply %s\n", supply);
ret = -EPROBE_DEFER;
goto scrub;
}
ret = set_supply(rdev, r);
if (ret < 0)
goto scrub;
/* Enable supply if rail is enabled */
if (_regulator_is_enabled(rdev)) {
ret = regulator_enable(rdev->supply);
if (ret < 0)
goto scrub;
}
}
add_dev:
/* add consumers devices */
if (init_data) {
for (i = 0; i < init_data->num_consumer_supplies; i++) {
ret = set_consumer_device_supply(rdev,
init_data->consumer_supplies[i].dev_name,
init_data->consumer_supplies[i].supply);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "Failed to set supply %s\n",
init_data->consumer_supplies[i].supply);
goto unset_supplies;
}
}
}
list_add(&rdev->list, ®ulator_list);
rdev_init_debugfs(rdev);
out:
mutex_unlock(®ulator_list_mutex);
return rdev;
unset_supplies:
unset_regulator_supplies(rdev);
scrub:
if (rdev->supply)
_regulator_put(rdev->supply);
regulator_ena_gpio_free(rdev);
kfree(rdev->constraints);
wash:
device_unregister(&rdev->dev);
/* device core frees rdev */
rdev = ERR_PTR(ret);
goto out;
clean:
kfree(rdev);
rdev = ERR_PTR(ret);
goto out;
}
1. 对传入的静态参数regulator_desc和动态参数config做合法性判断。
2. 分配regulator_dev结构rdev,解析machine信息,也就是regulator的板级信息,如果解析不到,就使用config中的init_data。
3. 初始化reg_data, owner,desc,rehmap,以及consumer_list,list等变量。
4. 调用device_register函数将regulator注册到系统中。这样就会在devices/platform和class/regulator下存在相应的设备。
5. 设置regulator的约束信息,比如设置电压,电流等,最终会通过regulator中的regulator_ops函数设置。
6. 添加regulator的设备属性。
6. 判断regulator是否存在级联关系,处理级联关系。
7. 添加consumer设备,通过init_data中的num_consumer_supplies个数,添加consumer的信息。
static int set_consumer_device_supply(struct regulator_dev *rdev,
const char *consumer_dev_name,
const char *supply)
{
struct regulator_map *node;
int has_dev;
if (supply == NULL)
return -EINVAL;
if (consumer_dev_name != NULL)
has_dev = 1;
else
has_dev = 0;
list_for_each_entry(node, ®ulator_map_list, list) {
if (node->dev_name && consumer_dev_name) {
if (strcmp(node->dev_name, consumer_dev_name) != 0)
continue;
} else if (node->dev_name || consumer_dev_name) {
continue;
}
if (strcmp(node->supply, supply) != 0)
continue;
pr_debug("%s: %s/%s is '%s' supply; fail %s/%s\n",
consumer_dev_name,
dev_name(&node->regulator->dev),
node->regulator->desc->name,
supply,
dev_name(&rdev->dev), rdev_get_name(rdev));
return -EBUSY;
}
node = kzalloc(sizeof(struct regulator_map), GFP_KERNEL);
if (node == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
node->regulator = rdev;
node->supply = supply;
if (has_dev) {
node->dev_name = kstrdup(consumer_dev_name, GFP_KERNEL);
if (node->dev_name == NULL) {
kfree(node);
return -ENOMEM;
}
}
list_add(&node->list, ®ulator_map_list);
return 0;
}
8. 然后将此regulator_dev加入到regulator_list中。
9. 在debugfs下创建regulator的属性。
regulator_get分析
在consumer函数中,会通过regulator_get函数得到该consumer的regulator。接下来分析是如何得到consumer的regulator。
static struct regulator *_regulator_get(struct device *dev, const char *id,
bool exclusive, bool allow_dummy)
{
struct regulator_dev *rdev;
struct regulator *regulator = ERR_PTR(-EPROBE_DEFER);
const char *devname = NULL;
int ret;
if (id == NULL) {
pr_err("get() with no identifier\n");
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
if (dev)
devname = dev_name(dev);
if (have_full_constraints())
ret = -ENODEV;
else
ret = -EPROBE_DEFER;
mutex_lock(®ulator_list_mutex);
rdev = regulator_dev_lookup(dev, id, &ret);
if (rdev)
goto found;
regulator = ERR_PTR(ret);
/*
* If we have return value from dev_lookup fail, we do not expect to
* succeed, so, quit with appropriate error value
*/
if (ret && ret != -ENODEV)
goto out;
if (!devname)
devname = "deviceless";
/*
* Assume that a regulator is physically present and enabled
* even if it isn't hooked up and just provide a dummy.
*/
if (have_full_constraints() && allow_dummy) {
pr_warn("%s supply %s not found, using dummy regulator\n",
devname, id);
rdev = dummy_regulator_rdev;
goto found;
/* Don't log an error when called from regulator_get_optional() */
} else if (!have_full_constraints() || exclusive) {
dev_warn(dev, "dummy supplies not allowed\n");
}
mutex_unlock(®ulator_list_mutex);
return regulator;
found:
if (rdev->exclusive) {
regulator = ERR_PTR(-EPERM);
goto out;
}
if (exclusive && rdev->open_count) {
regulator = ERR_PTR(-EBUSY);
goto out;
}
if (!try_module_get(rdev->owner))
goto out;
regulator = create_regulator(rdev, dev, id);
if (regulator == NULL) {
regulator = ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
module_put(rdev->owner);
goto out;
}
rdev->open_count++;
if (exclusive) {
rdev->exclusive = 1;
ret = _regulator_is_enabled(rdev);
if (ret > 0)
rdev->use_count = 1;
else
rdev->use_count = 0;
}
out:
mutex_unlock(®ulator_list_mutex);
return regulator;
}
2. 找到之后跳到found标号处,创建regulator结构。设置统计参数。
此函数的重点就是查找regulator_dev的过程。
static struct regulator_dev *regulator_dev_lookup(struct device *dev,
const char *supply,
int *ret)
{
struct regulator_dev *r;
struct device_node *node;
struct regulator_map *map;
const char *devname = NULL;
regulator_supply_alias(&dev, &supply);
/* first do a dt based lookup */
if (dev && dev->of_node) {
node = of_get_regulator(dev, supply);
if (node) {
list_for_each_entry(r, ®ulator_list, list)
if (r->dev.parent &&
node == r->dev.of_node)
return r;
*ret = -EPROBE_DEFER;
return NULL;
} else {
/*
* If we couldn't even get the node then it's
* not just that the device didn't register
* yet, there's no node and we'll never
* succeed.
*/
*ret = -ENODEV;
}
}
/* if not found, try doing it non-dt way */
if (dev)
devname = dev_name(dev);
list_for_each_entry(r, ®ulator_list, list)
if (strcmp(rdev_get_name(r), supply) == 0)
return r;
list_for_each_entry(map, ®ulator_map_list, list) {
/* If the mapping has a device set up it must match */
if (map->dev_name &&
(!devname || strcmp(map->dev_name, devname)))
continue;
if (strcmp(map->supply, supply) == 0)
return map->regulator;
}
return NULL;
}
2. 在regulator_list中通过比较"supply"和rdev->constraints->name或者rdev->desc->name的名字比较。其中supply等于"VCC",而rdev->constraints->name的名字是"my_regulator_constrains",显然是不匹配的。
3. 最后会在regulator_map_list中通过在regulator_register中注册的dev_name和supply匹配,最终会找到注册的regulator_dev。
最终的注册查找可以用如下图概述:
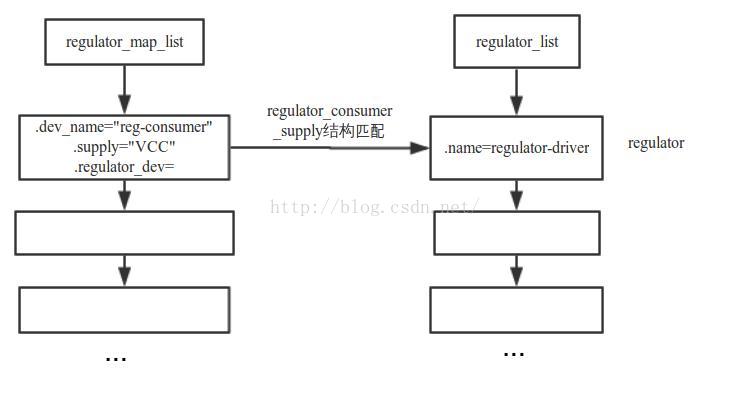
当然了一个regulator可以存在多个consumer设备的,具体情况具体分析。详细信息可以查看文档Documentation/power/regulator/machine.txt





















 652
652











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








