1.前言
从今天起开始写几篇关于Spring的文章,来总结一下,近来的学习情况,也想与大家分享一下学习Spring的心得和体会。希望大家能够多多指正。
2.Spring简单介绍
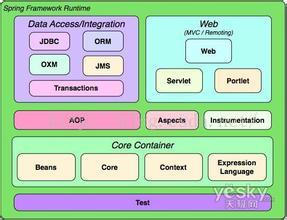
上图是有关Spring的整个架构图,从图中我们可以看出,Spring主要包括AOP、数据访问,WEB访问等几大块内容。
Spring是一个基于JAVA的轻量级J2EE的应用框架。 那么Spring能干什么呢?目前我们看到市面上有很多的框架,比如Struts2+Spring、Spring+Servlet、Spring+ibatis、因此可以说Spring是一个超级的“黏合平台”,能够将很多的技术黏合在一起,形成一个整体,使每个组件发挥其最大的功效。
3.jar包整理
有关Spring需要的jar包整理如下
开发所使用的jar包(核心jar包)
• spring-beans-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar
• spring-context-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar
• spring-core-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar
• spring-expression-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar
日志相关jar包(从依赖资源中获取)
• commons-logging-1.1.1.jar
• commons-logging日志整合,与slf4j类似,由apache提供
• log4j-1.2.15.jar
4.上下文获取方式
1.使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象获取
<span style="font-family:SimSun;font-size:18px;"> //获取Spring需要Spring的工厂,需要把applicationContext.xml文件放置到src下 ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService user=ctx.getBean("userService", UserService.class); user.printTest();</span>2.使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext对象获取
<span style="font-family:SimSun;font-size:18px;">/*文件系统获取上下文,需要把applicationContext.xml文件放置到工程路径下面*/ ApplicationContext ctx2=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService user2=ctx2.getBean("userService", UserService.class); System.out.println(user2.getId()); System.out.println(user2.getName()); user2.printTest();</span>
3.使用BeanFactory工厂进行获取
<span style="font-family:SimSun;font-size:18px;">// 通过BeanFactory创建bean,具有延迟加载的作用,当用到的时候,再去创建 Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"); BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource); UserService user3 = beanFactory.getBean("userService", UserService.class); System.out.println(user3.getId()); System.out.println(user3.getName()); user3.printTest();</span>
4.三者的比较
使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象获取,必须把applicationContext.xml放置到类的加载路径中,也就是Src下面
使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext对象获取,必须把applicationContext.xml放置到工程目录下面,也就是项目路径的下面
BeanFactory与ApplicationContext的区别
加载方式
• BeanFactory:延迟加载,使用bean时才进行初始化
• ApplicationContext:加载配置文件时,初始化bean对象
功能
• ApplicationContext提供更多的功能
l 国际化处理
l 事件传递
l Bean自动装配
l 各种不同应用层的Context实现























 4万+
4万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








