解题报告 之 HDU5323 Solve this interesting problem
Description
Have you learned something about segment tree? If not, don’t worry, I will explain it for you.
Segment Tree is a kind of binary tree, it can be defined as this:
- For each node u in Segment Tree, u has two values:
 and
and 
 .
.
- If



 ,
u is a leaf node.
,
u is a leaf node.
- If

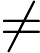

 ,
u has two children x and y,with
,
u has two children x and y,with 



 ,
,








 ,
,









 ,
,



 .
.
Here is an example of segment tree to do range query of sum.

Given two integers L and R, Your task is to find the minimum non-negative n satisfy that: A Segment Tree with root node's value





 and
and 





 contains
a node u with
contains
a node u with 


 and
and 


 .
.
Segment Tree is a kind of binary tree, it can be defined as this:
- For each node u in Segment Tree, u has two values:

 and
and 
 .
. - If




 ,
u is a leaf node.
,
u is a leaf node. - If


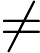

 ,
u has two children x and y,with
,
u has two children x and y,with 



 ,
,








 ,
,










 ,
,



 .
. Here is an example of segment tree to do range query of sum.
Given two integers L and R, Your task is to find the minimum non-negative n satisfy that: A Segment Tree with root node's value






 and
and 





 contains
a node u with
contains
a node u with 


 and
and 


 .
. Input
The input consists of several test cases.
Each test case contains two integers L and R, as described above.













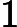

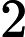


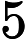
Each test case contains two integers L and R, as described above.








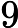





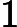

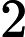


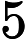
Output
For each test, output one line contains one integer. If there is no such n, just output -1.
Sample Input
6 7 10 13 10 11
Sample Output
7 -1 12
分析:红果果的搜索,线段树区间的分配方法决定了向上反推的时候可能有四种情况,这样就要向四个方向搜索分别是
[l,r+len]
[l,r+len-1]
[l-len,r]
[l-len-1,r]
是因为区间长度的奇偶性造成的。
重要的剪枝是如果L已经小于0,或者已经小于length,那么则不可能是通过任何一个区间分出来的。那么停止搜索,其他的每次搜索到l==0的时候表示找到了一个新的满足要求的区间,则进行一次更新。第二个剪枝是如果r已经大于了现有的n。那么则再怎么搜索下去也不可能得到更小的答案了。
上代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll n;
bool inline Check( ll l, ll r,ll mid)
{
if(l < 0) return false;
return true;
}
void dfs( ll l, ll r )
{
if(l == 0 && (n == -1 || n > r))
{
n = r;
return;
}
if(n != -1 && r >= n) return;
ll length = r - l + 1;
if(l < length) return;
ll nl = l - length;
if(Check( nl, r, l-1 ))
dfs( nl, r );
nl--;
if(Check( nl, r, l-1 ))
dfs( nl, r );
ll nr = r + length;
if(Check( l, nr, r ))
dfs( l, nr );
nr--;
if(Check( l, nr, r ));
dfs( l, nr );
}
int main()
{
ll l, r;
while(scanf( "%lld%lld", &l, &r ) == 2)
{
n = -1;
dfs( l, r );
printf( "%lld\n", n );
}
return 0;
}



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








