1、仿函数Functor的结构
在C++的STL结构中,仿函数是为了算法服务的。也就是说设计某个算法时,如sort()。会使用相关的仿函数在实现排序,而且仿函数有特定的继承结构。
template<class T>
struct plus :public binary_function<T,T,T>
{
T operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const
{
return x + y;
}
};a、使用模板函数来设计function object,其中会继承binary_function或unary_function;
b、使用operator()操作符重载后,可以将plus类当做函数使用,这在之前篇章有介绍。使用如下:
plus<int> p;
int result = p(2, 3);
cout << result << endl; //5其中父类继承结构如下:
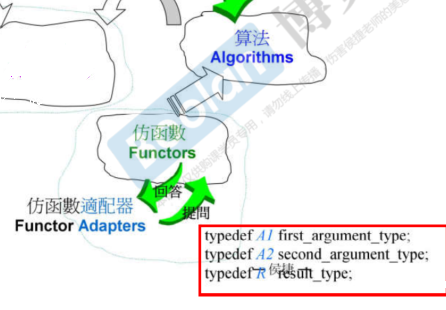
template <typename arg, typename result>
struct unary_function{
typedef arg argument_type;
typedef result result_type;
};
template <typename arg1, typename arg2, typename result>
struct binary_function{
typedef arg1 first_argument_type;
typedef arg2 second_argument_type;
typedef result result_type;
};a、父类结构binary_function或unary_function中都没有具体的数据定义,只有一些typedef;
b、binary_function是针对仿函数是有两个参数的,模板参数分别代表第一参数类型,第二参数类型和返回值类型;
c、unary_function是针对仿函数是有一个参数的,模板参数分别代表参数类型和返回值类型。
d、这个没有任何实际参数的定义作用其实是为了确定该仿函数是否可被适配的adaptable,也就是说能否被适配器使用。类似于迭代器中设计5个原则来回答算法的提问一样。
2、仿函数的使用
仿函数一般都是通过算法来使用的,如less仿函数被sort()排序算法使用:
template<class T>
struct less :public binary_function<T, T, bool>
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const
{
return x < y;
}
};算法sort()使用:
vector<int> v{ 15, 37, 94, 50, 73, 58, 28, 98 };
::sort(v.begin(), v.end(), less<int>());
for (auto i : v){
cout << i << " "; //15 28 37 50 58 73 94 98
}
cout << "\n";






















 311
311

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








