APUE读书笔记—进程间通信(IPC)之管道和有名管道(FIFO)
1. 管道
pipe函数可以创建管道,提供一个单向数据流(半双工)。
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
//返回值:若成功,返回0,若出错,返回-1- 该函数返回两个文件描述符,fd[0],fd[1]。前者打开来读,后者打开来写。所以管道在用户程序看起来像是一个打开的文件,通过read(fd[0])或者write(fd[1])。向这个文件读写数据其实是在读写内核缓冲区。
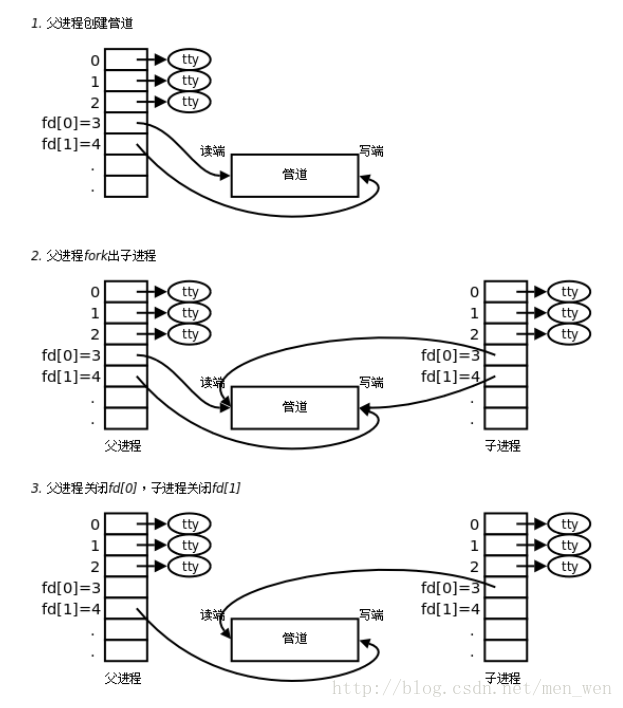
- 调用pipe函数时在内核中开辟一块缓冲区(称为管道)用于通信,它有一个读端一个写端,然后通过pipefd参数传出给用户程序两个文件描述符。
- 管道作用于有血缘关系的进程之间,先pipe,再通过fork来传递。
- 管道使用环形队列实现的,数据从写端流入从读端流出。
1.1 管道如何进行通信
- 父进程调用pipe函数在内核中开辟管道,得到两个文件描述符指向管道的两端。
- 父进程调用fork函数,子进程共享两个文件描述符指向同一管道。
- 父进程关闭管道读端,子进程关闭管道写端。父进程可以往管道里写,子进程可以从管道里读。
1.2 管道实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
int len;
int flag;
char str[1024] = "hello world\n";
char buf[1024];
if(pipe(fd) < 0){
perror("pipe err");
exit(1);
}
//父写子读
if((pid = fork()) < 0){
perror("fork err");
exit(1);
}else if(pid > 0){ //parent
close(fd[0]); //关闭父进程读端
sleep(5);
write(fd[1], str, strlen(str));
close(fd[1]); //写完关闭写端
wait(NULL);
}else{ //child
close(fd[1]); //关闭子进程写端
//设置子进程读端为非阻塞,如失败返回EAGAIN
flag = fcntl(fd[0], F_GETFL);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd[0], F_SETFL, flag);
tryagain:
len = read(fd[0], buf, sizeof(str));
if(len < 0){
if(errno == EAGAIN){ //非阻塞读若失败则返回EAGAIN
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "try again\n", 10);
sleep(1);
goto tryagain;
}else{
perror("read err");
exit(1);
}
}
close(fd[0]); //读完关闭读端
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, len);
}
return 0;
}父进程睡眠5秒后为子进程写数据,子进程每秒尝试读数据,读不到打印出try again,否则打印出读到的数据,运行如下:
try again
try again
try again
try again
try again
hello world1.3 管道的使用事项
- 两个进程通过一个管道只能实现单向通信,如果要实现双向通信必须使用两个管道。
- 写端关闭,当读端读完管道的内容,再次读,返回0,相当于读到EOF。
- 如果管道写端没关闭,写端暂时无数据,读端读完管道里的数据后再次读,读端会阻塞。
- 读端关闭,写端写管道,会产生SIGPIPE信号,写进程默认情况下会终止进程。
- 读端没读管道数据,当写端写满管道后,再次写,写端阻塞。
1.4 管道大小
利用fpathconf函数可以查看本机管道大小
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fd[2];
pipe(fd);
printf("pipe buf = %ld\n", fpathconf(fd[1], _PC_PIPE_BUF));
return 0;
}运行结果:
pipe buf = 40962. FIFO有名管道
FIFO是指先进先出(first in first out),它是一个单向数据流(半双工),每个FIFO有一个路径名与之关联,从而允许无亲缘关系的进程访问同一个FIFO。FIFO又称有名管道。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
//返回值:若成功,返回0,若出错,返回-1- pathname是一个普通的路径名,它是FIFO的名字。
- mode指定文件权限位。
- mkfifo函数隐含包含O_CREATE | O_EXCL。也就是说,要么创建一个新的FIFO,要么返回一个EEXIST错误。
2.1 例子:无亲缘关系的客户与服务器
服务器主函数代码 server_main,c
#include "unpipc.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int readfd, writefd;
//create two FIFO
if((mkfifo(FIFO1, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST))
sys_err("can't create FIFO1\n");
if((mkfifo(FIFO2, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST)) {
unlink(FIFO1);
sys_err("can't create FIFO2\n");
}
readfd = open(FIFO1, O_RDONLY, 0);
writefd = open(FIFO2, O_WRONLY, 0);
server(readfd, writefd);
exit(0);
}服务器函数代码 server.c
#include "unpipc.h"
void server(int readfd, int writefd)
{
int fd;
ssize_t n;
char buff[MAXLINE + 1];
//read pathname from ipc channel
if((n = read(readfd, buff, MAXLINE)) == 0)
sys_err("end-of-file while reading pathname");
buff[n] = '\0';
if((fd = open(buff, O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
snprintf(buff + n, sizeof(buff) - n, ": can't open, %s\n", strerror(errno)); //tell client error
n = strlen(buff);
write(writefd, buff, n);
} else {
while((n = read(fd, buff, MAXLINE)) > 0)
write(writefd, buff, n);
close(fd);
}
}客户端主函数代码 client_main.c
#include "unpipc.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int readfd, writefd;
writefd = open(FIFO1, O_WRONLY, 0);
readfd = open(FIFO2, O_RDONLY, 0);
client(readfd, writefd);
close(readfd);
close(writefd);
unlink(FIFO2);
unlink(FIFO1);
exit(0);
客户端函数代码 client.c
#include "unpipc.h"
void client(int readfd, int writefd)
{
size_t len;
ssize_t n;
char buff[MAXLINE];
//read pathname
fgets(buff, MAXLINE, stdin); //fgets 会读最后一个‘\n’字节
len = strlen(buff);
if(buff[len-1] == '\n')
len--; //del newline from fgets
//write pathname to ipc channel
write(writefd, buff, len);
//read from ipc. write to standard output
while((n = read(readfd, buff, MAXLINE)) > 0)
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buff, n);
}头文件 unpipc.h
#ifndef _UNPIPE_H_
#define _UNPIPE_H_
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define MAXLINE 4096
#define FILE_MODE (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH)
#define FIFO1 "/home/menwen/work/APUE/IPC/apue_code/fifo.1"
#define FIFO2 "/home/menwen/work/APUE/IPC/apue_code/fifo.2"
void client(int readfd, int writefd);
void server(int readfd, int writefd);
void sys_err(char *str);
#endif出错处理函数代码
//sys_err.c是我自己简单封装的一个出错处理函数
#include "unpipc.h"
void sys_err(char *str)
{
perror(str);
exit(1);
}- 编译:
gcc server.c server_main.c unpipc.h sys_err.c -o server
gcc client.c client_main.c unpipc.h -o client - 运行:
➜ apue_code ./server & //后台运行服务器端代码
[1] 21581
➜ apue_code ./client //在执行客户端代码
/home/menwen/work/APUE/IPC/apue_code/unpipc.h //输入一个文件的路径,就会通过FIFO得到文件内容如下:正是unpipc.h的内容
#ifndef _UNPIPE_H_
#define _UNPIPE_H_
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define MAXLINE 4096
#define FILE_MODE (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH)
#define FIFO1 "/home/menwen/work/APUE/IPC/apue_code/fifo.1"
#define FIFO2 "/home/menwen/work/APUE/IPC/apue_code/fifo.2"
void client(int readfd, int writefd);
void server(int readfd, int writefd);
void sys_err(char *str);
#endif
[1] + 21581 done ./server




 本文介绍《Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment》一书中关于进程间通信(IPC)中的管道和有名管道(FIFO)。内容包括pipe函数的使用、管道通信流程、管道的注意事项、有名管道的创建和应用实例等。
本文介绍《Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment》一书中关于进程间通信(IPC)中的管道和有名管道(FIFO)。内容包括pipe函数的使用、管道通信流程、管道的注意事项、有名管道的创建和应用实例等。
















 730
730

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








