上一篇文章大概总结注解的基本用途,参考慕课网的相关课程,实现一个简单的项目需求,就是新建一个实体类,这个实体类对应数据库中的一张表,我们可以通过类的实例构建一个过滤条件,并按照该条件去数据库查询相关数据。这次我们充分利用到自定义注解实现从过滤类的名字上注解过滤的表名,在类的属性上标注对应的字段名,这样我们可以通过对类的注解扫描去寻找对应字段名与对应字段的值与对应的表,构造sql语句,返回的sql语句并去查询数据库返回结果。大概需求就是这样。数据持久化我用的jdbc连接。
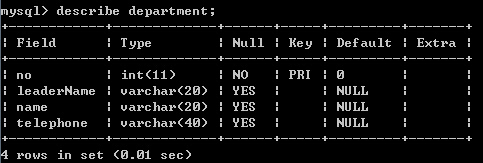
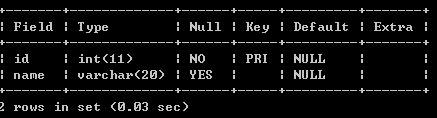
- 首先我们开始建立表吧,为了考虑后面学习的关联性,这次我创建了两张表,一张department是部门,还一张是Person,想法是department里的leaderName与Person里的name对应,但并不是外键。表的结构如下:
然后我们创建两个实体类,其实这里的注解这次项目并没用到,写上只是考虑后期可能用上:
package entity;
import annotation.Column;
import annotation.Table;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
@Table("department")
public class Department {
@Column("no")
int no;
@Column("name")
String name;
@Column("telephone")
String telephone;
Person Person;
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public Person getPerson() {
return Person;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
Person = person;
}
}
package entity;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
public class Person {
int id;
String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- 我们自己定义两个注解,分别是Table和Column让对应实体类的名字和属性与数据库的表名和字段对应:
package annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Table {
String value();
}
package annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Column {
String value();
}
- 我需要一个传入sql语句返回String类型结果的类:
package dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
public class JdbcDao {
private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/micro";
private String password = "root";
private String username = "root";
private String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Connection conn = null;
/*
* 获得连接
*/
public Connection getConnection()
{
try
{
Class.forName(driver);
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
/*
* 关闭连接
*/
public void Close(ResultSet rs,PreparedStatement p,Connection conn)
{
try
{
rs.close();
p.close();
conn.close();
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* 通过sql语句查询数据库并返回String集合
*/
public List<String> Query(String sql)
{
//获得连接
Connection conn = getConnection();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
try {
PreparedStatement p = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rt = p.executeQuery();
while(rt.next())
{
//将查询的结果拼装并将结果转换成String添加到List中
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("no:").append(rt.getInt("no")).append(" name:").append(rt.getString("name")).append(" telephone:").append(rt.getString("telephone"));
list.add(sb.toString());
}
//记得关闭连接
Close(rt, p, conn);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
}
我们可以来测试持久层的可用性(添加记录部门没展示):
/*
* 测试JdbcDao
*/
String sql = "select * from department";
JdbcDao jd = new JdbcDao();
List<String> list = jd.Query(sql);
for(String str : list)
{
System.out.println(str);
}- 好了现在轮子准备的差不多了,接下来关键是拼装我们要传入的sql语句。这个语句要从我们实例化的类的参数来构造:
- 过滤类,我们要过滤的属性拿出来,过滤的表拿出来,,格式比较类似bean:
package filter;
import annotation.Column;
import annotation.Table;
import entity.Person;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
@Table("department")
public class FilterSql {
@Column("no")
private int no;
@Column("name")
private String name;
@Column("telephone")
private String telephone;
//这里Person我们没用到,可以不写的
private Person person;
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person getPerson() {
return person;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
}
- 好了,这个时候我们思路很清晰,要写一个构造sql语句的类,通过过滤条件构造,这是这个需求的重点:
package filter;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import annotation.Column;
import annotation.Table;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
public class FilterQuery {
public String getQuery(Object filter)
{
/*
* 分几步,要利用条件进行查询,就要获得查询sql语句的数据库的表名
* 字段名与字段值
* 初始化sql
*/
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("select * from ");
/*
* 利用反射加载类
*/
try {
Class<?> c = Class.forName("filter.FilterSql");
/*
* 获得注解Table标记的表名
*/
Table table = (Table) c.getAnnotation(Table.class);
if(table != null)
{
String tableName = table.value();
sb.append(tableName);
}
/*
* 获得字段名
*/
//先利用java反射获得类的属性集合
Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields();
/*
* 遍历字段去扫描注解并获得字段名
*/
sb.append(" where 1 = 1");
for(Field f : fields)
{
/*
* 分别获取字段名,后面判断如果有设定值才返回,否则不返回到sql语句中,但是要首先判断这个属性是否有Column注解
*/
if(f.isAnnotationPresent(Column.class))
{
Column column = f.getAnnotation(Column.class);
String columnName = column.value();
/*
* 判断该字段的值是否符号要求
*/
//为了获得该属性的值得采取反射
Object columnValue = null;
String getValueMethodName = "get"+columnName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()+columnName.substring(1);
try{
Method getMethod = c.getMethod(getValueMethodName);
columnValue = getMethod.invoke(filter);
if(columnValue == null || columnValue instanceof Integer && ((Integer)columnValue) == 0)
{
continue;
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
//拼装sql
sb.append(" and ").append(columnName);
/*
* 若columnValue为字符串,拼装的时候应该加上双引号
*/
if(columnValue instanceof String)
{
/*
* 若存在","分割,应该是in ("","",...)的拼装方法
*/
if(((String)columnValue).contains(","))
{
sb.append(" in ").append("(");
//遍历所有","分割的部分
String[] strArray = ((String)columnValue).split(",");
for(String str : strArray)
{
sb.append(str).append(",");
}
//最后肯定多一个逗号,去除掉
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
sb.append(")");
}
//若没有包含",",则之间加双引号即可
else
{
sb.append(" = ").append("'").append(columnValue).append("'");
}
}
/*
* 若不是String,则直接拼装
*/
else
{
sb.append(" = ").append(columnValue);
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sb.toString();
}
}- 好了,最后我们来测试:
我还额外添加了一条记录用来测试:
package dao;
import java.util.List;
import entity.Person;
import filter.FilterQuery;
import filter.FilterSql;
/**
@author:micro_hz
2015年8月21日
*/
public class TestDao {
public static void main(String args[])
{
/*
* 测试JdbcDao
*/
// String sql = "select * from department";
// JdbcDao jd = new JdbcDao();
// List<String> list = jd.Query(sql);
//
// for(String str : list)
// {
// System.out.println(str);
// }
/*
* 测试FilterQuery
*/
/*
* 过滤条件一
*/
FilterSql f1 = new FilterSql();
f1.setNo(101);
f1.setTelephone("123,456");
FilterQuery fq = new FilterQuery();
System.out.println(fq.getQuery(f1));
/*
* 过滤条件二
*/
FilterSql f2 = new FilterSql();
f2.setPerson(new Person());
//
f2.setTelephone("123,432");
f2.setName("xiaoma");
System.out.println(fq.getQuery(f2));
/*
* 将过滤条件f1加到JdbcDao去查询
*/
JdbcDao jd = new JdbcDao();
List<String> list = jd.Query(fq.getQuery(f1));
//遍历查询的结果
for(String str : list)
{
System.out.println(str);
}
FilterSql f3 = new FilterSql();
//f3的过滤条件是存在以下电话号码的给我查出来
f3.setTelephone("2015");
String sql = fq.getQuery(f3);
System.out.println(sql);//打印查看该语句是否正确
/*
* 可以直接如下这么查询
*/
System.out.println("查询结果如下");
list = jd.Query(fq.getQuery(f3));
for(String str : list)
{
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}运行结果:
























 3224
3224

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








