拓扑排序是对有向无环图的一种排序。表示了顶点按边的方向出现的先后顺序。如果有环,则无法表示两个顶点的先后顺序。
在现实生活中,也会有不少应用例子,比如学校课程布置图,要先修完一些基础课,才可以继续修专业课。
一个简单的求拓扑排序的算法:首先要找到任意入度为0的一个顶点,删除它及所有相邻的边,再找入度为0的顶点,以此类推,直到删除所有顶点。顶点的删除顺序即为拓扑排序。
很容易得到拓扑排序的伪代码:
void TopSort(Graph g)
{
for (int i=0; i<vertexnum; i++)
{
vertex v = FindZeroIndegree(g);
if (v is not vertex)
cout <<"the graph has cycle"<<endl;
cout << v ;
foreach vertex w adjacent to v
w.indegree--;
}
}
同样以上图为例,对于该图进行拓扑排序会得到:v1 v2 v5 v4 v3 v7 v6 或者v1 v2 v5 v4 v7 v3 v6 。
仍然利用上一贴图的构建方法,进行验证。
代码实现:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
struct adjVertexNode
{
int adjVertexPosition;
adjVertexNode * next;
};
struct VertexNode
{
char data [ 2 ];
adjVertexNode * list;
int indegree;
};
struct Graph
{
VertexNode VertexNode [ MAX_VERTEX_NUM ];
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
};
void CreateGraph ( Graph & g)
{
int i , j , edgeStart , edgeEnd;
adjVertexNode * adjNode;
cout << "Please input vertex and edge num (vnum enum):" << endl;
cin >> g . vertexNum >> g . edgeNum;
cout << "Please input vertex information (v1) /n note: every vertex info end with Enter" << endl;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cin >> g . VertexNode [ i ]. data; // vertex data info.
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = NULL;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. indegree = 0;
}
cout << "input edge information(start end):" << endl;
for ( j = 0; j < g . edgeNum; j ++)
{
cin >> edgeStart >> edgeEnd;
adjNode = new adjVertexNode;
adjNode -> adjVertexPosition = edgeEnd - 1; // because array begin from 0, so it is j-1
adjNode -> next = g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list = adjNode;
//每增加一条边,则边的End顶点的入度加1
g . VertexNode [ edgeEnd - 1 ]. indegree ++;
}
}
void PrintAdjList( const Graph & g)
{
cout << "The adjacent list for graph is:" << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cout << g . VertexNode [ i ]. data << "->";
adjVertexNode * head = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
if ( head == NULL)
cout << "NULL";
while ( head != NULL)
{
cout << head -> adjVertexPosition + 1 << " ";
head = head -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
VertexNode & FindZeroIndegree( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
if ( g . VertexNode [ i ]. indegree == 0)
return g . VertexNode [ i ];
}
return g . VertexNode [ 0 ];
}
void TopSort( Graph & g)
{
cout << "The topsort is:" << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
VertexNode & v = FindZeroIndegree( g);
if ( v . indegree != NULL)
cout << "The graph has cycle, can not do topsort" << endl;
// print graph as topsort.
cout << v . data << " ";
// for each vertex w adjacent to v, --indegree
adjVertexNode * padjv = v . list;
while ( padjv != NULL)
{ //!!这个算法这里破坏了原图中的入度信息。最后入度均为1
g . VertexNode [ padjv -> adjVertexPosition ]. indegree --;
padjv = padjv -> next;
}
//避免入度信息均为零FindZeroIndegree找到删除的顶点,将删除的顶点入度置为1
v . indegree ++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void DeleteGraph( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
adjVertexNode * tmp = NULL;
while( g . VertexNode [ i ]. list != NULL)
{
tmp = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list -> next;
delete tmp;
tmp = NULL;
}
}
}
int main( int argc , const char ** argv)
{
Graph g;
CreateGraph( g);
PrintAdjList( g);
TopSort( g);
DeleteGraph( g);
return 0;
}
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
struct adjVertexNode
{
int adjVertexPosition;
adjVertexNode * next;
};
struct VertexNode
{
char data [ 2 ];
adjVertexNode * list;
int indegree;
};
struct Graph
{
VertexNode VertexNode [ MAX_VERTEX_NUM ];
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
};
void CreateGraph ( Graph & g)
{
int i , j , edgeStart , edgeEnd;
adjVertexNode * adjNode;
cout << "Please input vertex and edge num (vnum enum):" << endl;
cin >> g . vertexNum >> g . edgeNum;
cout << "Please input vertex information (v1) /n note: every vertex info end with Enter" << endl;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cin >> g . VertexNode [ i ]. data; // vertex data info.
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = NULL;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. indegree = 0;
}
cout << "input edge information(start end):" << endl;
for ( j = 0; j < g . edgeNum; j ++)
{
cin >> edgeStart >> edgeEnd;
adjNode = new adjVertexNode;
adjNode -> adjVertexPosition = edgeEnd - 1; // because array begin from 0, so it is j-1
adjNode -> next = g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list = adjNode;
//每增加一条边,则边的End顶点的入度加1
g . VertexNode [ edgeEnd - 1 ]. indegree ++;
}
}
void PrintAdjList( const Graph & g)
{
cout << "The adjacent list for graph is:" << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cout << g . VertexNode [ i ]. data << "->";
adjVertexNode * head = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
if ( head == NULL)
cout << "NULL";
while ( head != NULL)
{
cout << head -> adjVertexPosition + 1 << " ";
head = head -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
VertexNode & FindZeroIndegree( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
if ( g . VertexNode [ i ]. indegree == 0)
return g . VertexNode [ i ];
}
return g . VertexNode [ 0 ];
}
void TopSort( Graph & g)
{
cout << "The topsort is:" << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
VertexNode & v = FindZeroIndegree( g);
if ( v . indegree != NULL)
cout << "The graph has cycle, can not do topsort" << endl;
// print graph as topsort.
cout << v . data << " ";
// for each vertex w adjacent to v, --indegree
adjVertexNode * padjv = v . list;
while ( padjv != NULL)
{ //!!这个算法这里破坏了原图中的入度信息。最后入度均为1
g . VertexNode [ padjv -> adjVertexPosition ]. indegree --;
padjv = padjv -> next;
}
//避免入度信息均为零FindZeroIndegree找到删除的顶点,将删除的顶点入度置为1
v . indegree ++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void DeleteGraph( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
adjVertexNode * tmp = NULL;
while( g . VertexNode [ i ]. list != NULL)
{
tmp = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list -> next;
delete tmp;
tmp = NULL;
}
}
}
int main( int argc , const char ** argv)
{
Graph g;
CreateGraph( g);
PrintAdjList( g);
TopSort( g);
DeleteGraph( g);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
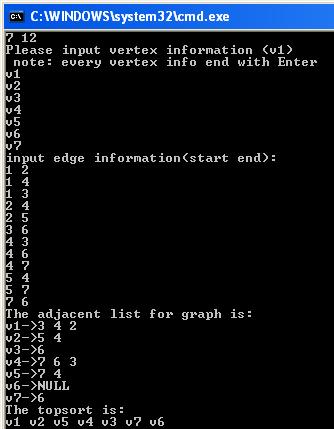
从上面的代码能发现
FindZeroIndegree的时间复杂度为O(|V|),TopSort的时间复杂度为O(|V|2)
原因在于,每次删除顶点,只有邻接点需要调整入度,但
FindZeroIndegree却是遍历了所有顶点,甚至已经删除的顶点。
更为合理的方法是将每次遍历得出的入度为0的顶点放入一个队列。
void
TopSort2(
Graph
&
g)
{
queue < VertexNode > q;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
if ( g . VertexNode [ i ]. indegree == 0)
q . push( g . VertexNode [ i ]);
}
int count = 0;
cout << "The topsort is:" << endl;
while ( ! q . empty())
{
VertexNode v = q . front();
q . pop();
cout << v . data << " ";
count ++;
adjVertexNode * padjv = v . list;
while ( padjv != NULL)
{ //!!这个算法这里破坏了原图中的入度信息。最后入度均为1
if ( --( g . VertexNode [ padjv -> adjVertexPosition ]. indegree) == 0)
q . push( g . VertexNode [ padjv -> adjVertexPosition ]);
padjv = padjv -> next;
}
}
if ( count != g . vertexNum)
cout << "The graph has cycle, can not do topsort" << endl;
}
{
queue < VertexNode > q;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
if ( g . VertexNode [ i ]. indegree == 0)
q . push( g . VertexNode [ i ]);
}
int count = 0;
cout << "The topsort is:" << endl;
while ( ! q . empty())
{
VertexNode v = q . front();
q . pop();
cout << v . data << " ";
count ++;
adjVertexNode * padjv = v . list;
while ( padjv != NULL)
{ //!!这个算法这里破坏了原图中的入度信息。最后入度均为1
if ( --( g . VertexNode [ padjv -> adjVertexPosition ]. indegree) == 0)
q . push( g . VertexNode [ padjv -> adjVertexPosition ]);
padjv = padjv -> next;
}
}
if ( count != g . vertexNum)
cout << "The graph has cycle, can not do topsort" << endl;
}
内部的while循环最多执行|E|次,即每条边执行一次。队列对每个顶点最多执行一次操作,所以新算法的时间复杂度为O(|E|+|V|). 优于O(|V|2)因为拓扑图边数最多有n(n-1)/2,即O(|E|+|V|)<=O(|V|2)





 本文深入讲解了拓扑排序的概念及其应用场景,并提供了详细的算法步骤和伪代码。通过具体实例介绍了如何实现拓扑排序,并讨论了不同算法的时间复杂度。
本文深入讲解了拓扑排序的概念及其应用场景,并提供了详细的算法步骤和伪代码。通过具体实例介绍了如何实现拓扑排序,并讨论了不同算法的时间复杂度。
















 329
329

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








