数据集选的是20_newsgroups,我按7:3分的训练集和测试集。
总的流程如下:
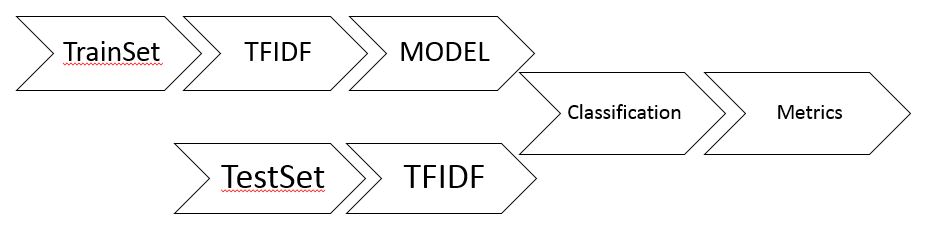
这里把数据集中的每一条文本都表示成TFTDF向量,用训练集的TFTDF向量来训练模型,用测试集的TFTDF向量进行分类测试,最后统计测试准确率。
初始化
# 设置训练集,测试集路径。
trainPath = "hdfs:///user/yy/20_newsgroups/train/*"
testPath = "hdfs:///user/yy/20_newsgroups/test/*"
# 分类时,新闻主题需要转换成数字,labelsDict将主题转换成数字
labelsDict = {'alt.atheism':0, 'comp.graphics':1, 'comp.os.ms-windows.misc':2,\
'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware':3, 'comp.sys.mac.hardware':4, 'comp.windows.x':5,\
'misc.forsale':6, 'rec.autos':7, 'rec.motorcycles':8, 'rec.sport.baseball':9,\
'rec.sport.hockey':10, 'sci.crypt':11, 'sci.electronics':12, 'sci.med':13,\
'sci.space':14, 'soc.religion.christian':15, 'talk.politics.guns':16,\
'talk.politics.mideast':17, 'talk.politics.misc':18, 'talk.religion.misc':19}
# keyTolabels则将数字再转换回主题,主要是方便自己看的
keyTolabels = {0:'alt.atheism', 1:'comp.graphics', 2:'comp.os.ms-windows.misc',\
3:'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware', 4:'comp.sys.mac.hardware', 5:'comp.windows.x',\
6:'misc.forsale', 7:'rec.autos', 8:'rec.motorcycles', 9:'rec.sport.baseball',\
10:'rec.sport.hockey', 11:'sci.crypt', 12:'sci.electronics', 13:'sci.med',\
14:'sci.space', 15:'soc.religion.christian', 16:'talk.politics.guns',\
17:'talk.politics.mideast', 18:'talk.politics.misc', 19:'talk.religion.misc'}预处理函数
完成对文档的分词,去停用词,词干提取,同义词替换的工作,需要安装一个自然语言处理的第三方库nltk。当然,每个节点都需要安装。预处理的基本步骤如下:
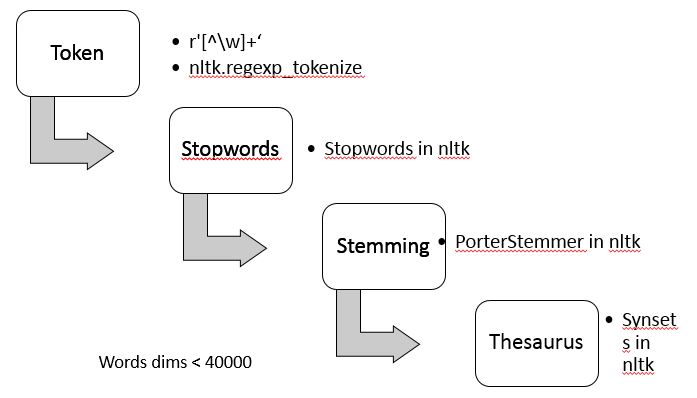
这里的同义词替换做的非常简单,只是从单词的第一个同义词集里取出第一个同义词。这么做有时会产生歧义,因为单词在不同的语义下有不同的同义词集,只取第一个同义词集即限定了仅仅使用单词的第一个语义。
def tokenlize(doc):
import nltk, re
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
r = re.compile(r'[\w]+') # 以非字母数字字符来进行分词
my_stopwords = nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('english')
porter = nltk.PorterStemmer()
newdoc = []
for word in nltk.regexp_tokenize(doc, r): # 分词
newWord = porter.stem(word.lower()) # 词干提取
if newWord in my_stopwords: # 去停用词
continue
tokenSynsets = wordnet.synsets(newWord)
newdoc.append(newWord if tokenSynsets == [] else tokenSynsets[0].lemma_names()[0]) # 同义词替换
return newdoc导入训练集
trainTokens = sc.wholeTextFiles(trainPath)\
.map(lambda (fileName, doc): doc)\
.map(lambda doc: tokenlize(doc))构建单词映射哈希表,tfidf模型
训练集和测试集都需要使用这个哈希表,它的大小根据不同单词的数量来设置,一般取2的n方,在前期数据探索的时候需要计算一下不同单词的数量。
from pyspark.mllib.feature import HashingTF
hasingTF = HashingTF(2 ** 16)
# 将训练集每个文档都映射为tf向量
trainTf = hasingTF.transform(trainTokens)
trainTf.cache()
# 构建IDF模型,训练集和测试集都用它
from pyspark.mllib.feature import IDF
idf = IDF().fit(trainTf)
# 将训练集每个tf向量转换为tfidf向量
trainTfidf = idf.transform(trainTf)
trainTfidf.cache()标注训练集
# 为训练集标注,成为最终可用的训练集,每个样本都需要放在LabeledPoint里
from pyspark.mllib.regression import LabeledPoint
trainLabels = sc.wholeTextFiles(trainPath)\
.map(lambda (path, doc): path.split('/')[-2])
train = trainLabels.zip(trainTfidf)\
.map(lambda (topic, vector): LabeledPoint(labelsDict[topic], vector))
train.cache()导入测试集
# 导入测试集并完成预处理
testTokens = sc.wholeTextFiles(testPath)\
.map(lambda (fileName, doc): doc)\
.map(lambda doc: tokenlize(doc))将测试集转换成tfidf向量
# 将测试集每个文档都映射为tf向量,和训练集用的是同一个哈希映射hasingTF
from pyspark.mllib.feature import HashingTF
testTf = hasingTF.transform(testTokens)
# 将测试集每个tf向量转换为tfidf向量,和训练集用的是同一个IDF模型idf
from pyspark.mllib.feature import IDF
testTfidf = idf.transform(testTf)标注测试集
# 为测试集标注,成为最终可用与测试的测试集
from pyspark.mllib.regression import LabeledPoint
testLabels = sc.wholeTextFiles(testPath)\
.map(lambda (path, doc): path.split('/')[-2])
test = testLabels.zip(testTfidf)\
.map(lambda (topic, vector): LabeledPoint(labelsDict[topic], vector))
testCount = test.count()训练朴素贝叶斯模型并计算准确率
from pyspark.mllib.classification import NaiveBayes
model = NaiveBayes.train(train, 0.1)
# 计算测试的准确率
predictionAndLabel = test.map(lambda p: (model.predict(p.features), p.label))
accuracy = 1.0 * predictionAndLabel.filter(lambda x: x[0] == x[1]).count() / testCount
print accuracy0.803298634582
训练多元逻辑回归模型并计算准确率
from pyspark.mllib.classification import LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS
lrModel = LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS.train(train, iterations=10, numClasses=20)
# 计算测试的准确率
predictionAndLabel = test.map(lambda p: (lrModel.predict(p.features), p.label))
accuracy = 1.0 * predictionAndLabel.filter(lambda x: x[0] == x[1]).count() / testCount
print accuracy0.812897120454
如果有兴趣,可以随便拿一份新闻组文本来测试一下,给自己一个更为直观的感受。
aTestText = """
Path: cantaloupe.srv.cs.cmu.edu!rochester!udel!bogus.sura.net!howland.reston.ans.net!ira.uka.de!math.fu-berlin.de!cs.tu-berlin.de!ossip
From: ossip@cs.tu-berlin.de (Ossip Kaehr)
Newsgroups: comp.sys.mac.hardware
Subject: SE/30 8bit card does not work with 20mb..
Date: 21 Apr 1993 23:22:22 GMT
Organization: Technical University of Berlin, Germany
Lines: 27
Message-ID: <1r4kve$6cl@news.cs.tu-berlin.de>
NNTP-Posting-Host: trillian.cs.tu-berlin.de
Mime-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=iso-8859-1
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit
Summary: HELP!
Keywords: SE/30 MODE32 System7 PDS
Hello!
I have a SE/30 and a Generation Systems 8bit PDS card for a 17"
screen.
It worked great until I upgraded from 5 to 20 mb ram.
Now with Sys7.1 and MODE32 or 32enabler it does not boot..
a tech support person said the card does not support these 32bit
fixes.
BUT: when pressing the shift key while booting (when the ext. monitor
goes black after having been grey) the system SOMETIMES boots properly!!
and then works ok with the 20mb and full graphics.
WHAT's HAPPENING???
Thanks a lot for any advice!!!
please answer by mail.
Ossip Kaehr
ossip@cs.tu-berlin.de
voice: +49.30.6226317
--
__ -------------------------------------------------------------- __
/_/\ Ossip Kaehr Hermannstrasse 32 D-1000 Berlin 44 Germany /\_\
\_\/ Tel. +49.30.6223910 or 6218814 EMail ossip@cs.tu-berlin.de \/_/
--------------------------------------------------------------
"""testTf = hasingTF.transform(tokenlize(aTestText)) # 预处理后转换为tf向量
testTfidf = idf.transform(testTf) # 再转换成tfidf向量
print keyTolabels[lrModel.predict(testTfidf)] # 预测并输出结果'comp.sys.mac.hardware'
总结spark上如何将文档转换成tfidf向量
# 构建哈希表用于映射所有单词
from pyspark.mllib.feature import HashingTF
hasingTF = HashingTF(2 ** 16) # 维数需要大于不同单词的总数
# 将文档映射为tf向量,这里的trainTokens为rdd类型
trainTf = hasingTF.transform(trainTokens)
testTf = hasingTF.transform(testTokens)
# 构建IDF模型,训练集和测试集都用它
from pyspark.mllib.feature import IDF
idf = IDF().fit(trainTf)
# 将tf向量转换为tfidf向量
trainTfidf = idf.transform(trainTf)
testTfidf = idf.transform(testTf)相关阅读
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tf%E2%80%93idf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_Language_Toolkit





















 8803
8803











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








