squeezenet出自2016论文SQUEEZENET:ALEXNET-LEVEL ACCURACY WITH 50X FEWER PARAMETERS AND <0.5MB MODEL SIZE,
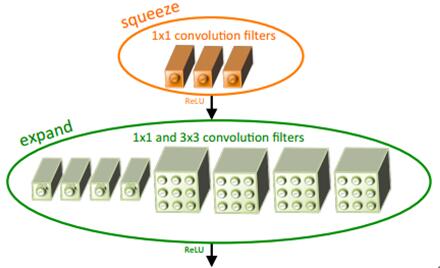
squeezenet主要提出了FireModule概念,如上图所示,一个FireModule由一个squeeze和一个expand组成,squeeze包含s个1*1的卷积核,expand包含e1个1*1的卷积核,e3个3*3的卷积核,并且满足s<e1+e3。
经过这样的一个替换,使得模型缩小了大概50倍,同时保证了准确性。
测试程序:
typedef std::pair<string, float> Prediction;
class Classifier {
public:
Classifier(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file);
std::vector<Prediction> Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N = 5);
private:
void SetMean(const string& mean_file);
std::vector<float> Predict(const cv::Mat& img);
void WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
void Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
private:
shared_ptr<Net<float> > net_;
cv::Size input_geometry_;
int num_channels_;
cv::Mat mean_;
std::vector<string> labels_;
};
Classifier::Classifier(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file) {
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::CPU);
#else
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
#endif
/* Load the network. */
net_.reset(new Net<float>(model_file, TEST));
net_->CopyTrainedLayersFrom(trained_file);
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_inputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one input.";
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_outputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one output.";
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
num_channels_ = input_layer->channels();
CHECK(num_channels_ == 3 || num_channels_ == 1)
<< "Input layer should have 1 or 3 channels.";
input_geometry_ = cv::Size(input_layer->width(), input_layer->height());
/* Load the binaryproto mean file. */
SetMean(mean_file);
/* Load labels. */
std::ifstream labels(label_file.c_str());
CHECK(labels) << "Unable to open labels file " << label_file;
string line;
while (std::getline(labels, line))
labels_.push_back(string(line));
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
CHECK_EQ(labels_.size(), output_layer->channels())
<< "Number of labels is different from the output layer dimension.";
}
static bool PairCompare(const std::pair<float, int>& lhs,
const std::pair<float, int>& rhs) {
return lhs.first > rhs.first;
}
/* Return the indices of the top N values of vector v. */
static std::vector<int> Argmax(const std::vector<float>& v, int N) {
std::vector<std::pair<float, int> > pairs;
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
pairs.push_back(std::make_pair(v[i], static_cast<int>(i)));
std::partial_sort(pairs.begin(), pairs.begin() + N, pairs.end(), PairCompare);
std::vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
result.push_back(pairs[i].second);
return result;
}
/* Return the top N predictions. */
std::vector<Prediction> Classifier::Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N) {
std::vector<float> output = Predict(img);
N = std::min<int>(labels_.size(), N);
std::vector<int> maxN = Argmax(output, N);
std::vector<Prediction> predictions;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int idx = maxN[i];
predictions.push_back(std::make_pair(labels_[idx], output[idx]));
}
return predictions;
}
/* Load the mean file in binaryproto format. */
void Classifier::SetMean(const string& mean_file) {
BlobProto blob_proto;
ReadProtoFromBinaryFileOrDie(mean_file.c_str(), &blob_proto);
/* Convert from BlobProto to Blob<float> */
Blob<float> mean_blob;
mean_blob.FromProto(blob_proto);
CHECK_EQ(mean_blob.channels(), num_channels_)
<< "Number of channels of mean file doesn't match input layer.";
/* The format of the mean file is planar 32-bit float BGR or grayscale. */
std::vector<cv::Mat> channels;
float* data = mean_blob.mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < num_channels_; ++i) {
/* Extract an individual channel. */
cv::Mat channel(mean_blob.height(), mean_blob.width(), CV_32FC1, data);
channels.push_back(channel);
data += mean_blob.height() * mean_blob.width();
}
/* Merge the separate channels into a single image. */
cv::Mat mean;
cv::merge(channels, mean);
/* Compute the global mean pixel value and create a mean image
* filled with this value. */
cv::Scalar channel_mean = cv::mean(mean);
mean_ = cv::Mat(input_geometry_, mean.type(), channel_mean);
}
std::vector<float> Classifier::Predict(const cv::Mat& img) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
input_layer->Reshape(1, num_channels_,
input_geometry_.height, input_geometry_.width);
/* Forward dimension change to all layers. */
net_->Reshape();
std::vector<cv::Mat> input_channels;
WrapInputLayer(&input_channels);
Preprocess(img, &input_channels);
net_->Forward();
/* Copy the output layer to a std::vector */
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
const float* begin = output_layer->cpu_data();
const float* end = begin + output_layer->channels();
return std::vector<float>(begin, end);
}
/* Wrap the input layer of the network in separate cv::Mat objects
* (one per channel). This way we save one memcpy operation and we
* don't need to rely on cudaMemcpy2D. The last preprocessing
* operation will write the separate channels directly to the input
* layer. */
void Classifier::WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
int width = input_layer->width();
int height = input_layer->height();
float* input_data = input_layer->mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < input_layer->channels(); ++i) {
cv::Mat channel(height, width, CV_32FC1, input_data);
input_channels->push_back(channel);
input_data += width * height;
}
}
void Classifier::Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
/* Convert the input image to the input image format of the network. */
cv::Mat sample;
if (img.channels() == 3 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
else if (img.channels() == 1 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
else
sample = img;
cv::Mat sample_resized;
if (sample.size() != input_geometry_)
cv::resize(sample, sample_resized, input_geometry_);
else
sample_resized = sample;
cv::Mat sample_float;
if (num_channels_ == 3)
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC3);
else
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat sample_normalized;
cv::subtract(sample_float, mean_, sample_normalized);
/* This operation will write the separate BGR planes directly to the
* input layer of the network because it is wrapped by the cv::Mat
* objects in input_channels. */
cv::split(sample_normalized, *input_channels);
CHECK(reinterpret_cast<float*>(input_channels->at(0).data)
== net_->input_blobs()[0]->cpu_data())
<< "Input channels are not wrapping the input layer of the network.";
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
argc = 6;
if (argc != 6) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0]
<< " deploy.prototxt network.caffemodel"
<< " mean.binaryproto labels.txt img.jpg" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
::google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);
/*string model_file = argv[1];
string trained_file = argv[2];
string mean_file = argv[3];
string label_file = argv[4];*/
/*string model_file = ".//caffenet//deploy.prototxt";
string trained_file = ".//caffenet//bvlc_reference_caffenet.caffemodel";*/
string model_file = ".//AlexNet//deploy.prototxt";
string trained_file = ".//AlexNet//bvlc_alexnet.caffemodel";
/*string model_file = ".\\SqueezeNet_v1.0\\deploy.prototxt";
string trained_file = ".\\SqueezeNet_v1.0\\squeezenet_v1.0.caffemodel";*/
string mean_file = "imagenet_mean.binaryproto";
string label_file = "synset_words.txt";
Classifier classifier(model_file, trained_file, mean_file, label_file);
//string file = argv[5];
string file = "cat.jpg";
//string file = "fish-bike.jpg";
std::cout << "---------- Prediction for "<< file << " ----------" << std::endl;
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(file, -1);
CHECK(!img.empty()) << "Unable to decode image " << file;
std::vector<Prediction> predictions = classifier.Classify(img);
end = (double)(1000 * (clock() - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
// std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(4) << gp.second <<" "<<gp.first << endl;
std::cout << "time:" << end <<"ms"<< std::endl;
/* Print the top N predictions. */
for (size_t i = 0; i < predictions.size(); ++i) {
Prediction p = predictions[i];
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(4) << p.second << " - \""
<< p.first << "\"" << std::endl;
}
cv::imshow(file, img);
cv::waitKey();
}
#else
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
LOG(FATAL) << "This example requires OpenCV; compile with USE_OPENCV.";
}
模型大小:
AlexNet模型大小:232M
caffeNet模型大小:232M
SqueezeNet_v1.0模型大小:4.76M
SqueezeNet_v1.1模型大小:4.72M
实验效果:
测试1:
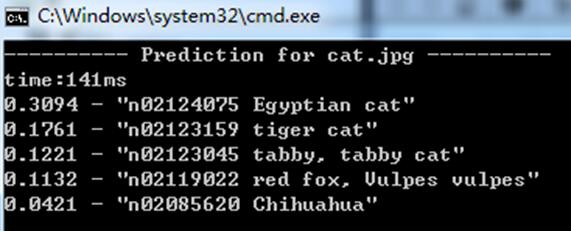
AlexNet:
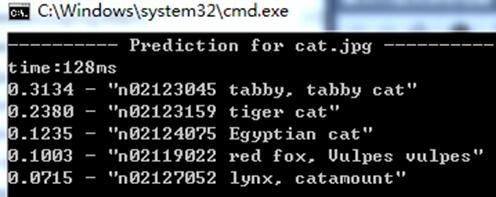
caffenet:
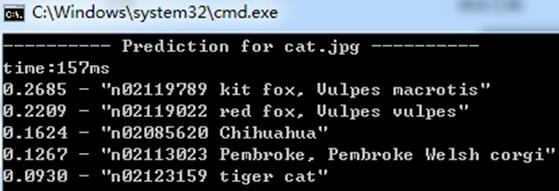
squeezenet_v1.0:
squeezenet_v1.1:
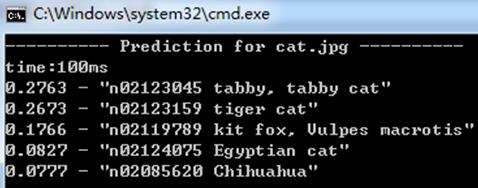
测试2:

AlexNet:
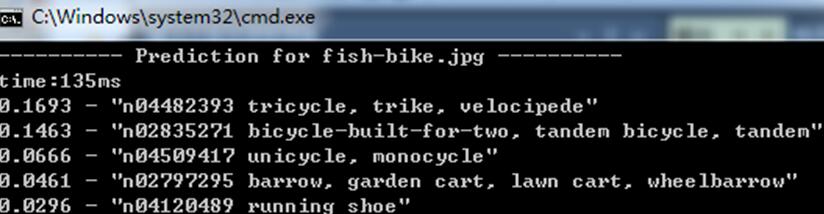
caffenet:
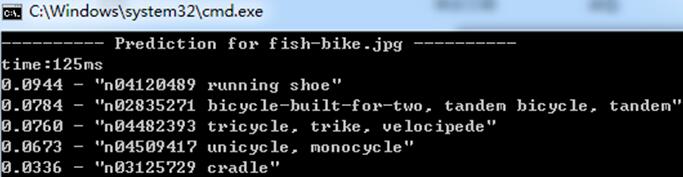
squeezenet_v1.0:
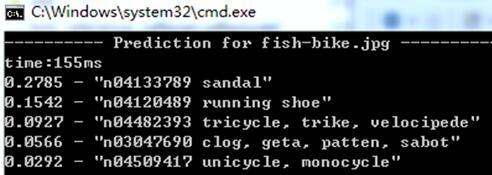
squeezenet_v1.1:
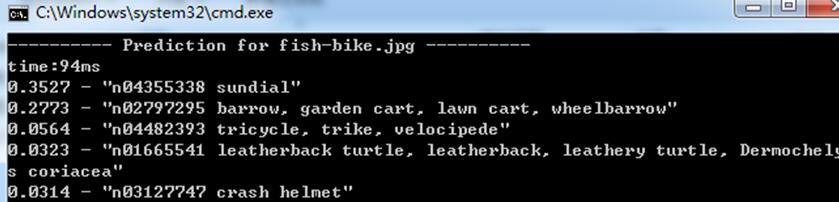





















 97
97











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








