import java.util.HashSet;
public class Main {
static class Test {
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return 32;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
System.out.println("obj");
return true;
}
public boolean equals(Test obj) {
System.out.println("test");
// 不会访问
return false;
}
public boolean fun(Object obj) {
System.out.println("obj");
return true;
}
public boolean fun(Test obj) {
System.out.println("test");
// 不会访问
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Test> set = new HashSet<>();
Test test=new Test();
test.equals(new Test());
System.out.println("=========");
test.fun(new Test());
set.add(new Test());
set.add(new Test());
set.add(new Test());
System.out.println(set.size());
// test
// =========
// test
// obj
// obj
// 1
}
}import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static class A {
int flag = 1;
public A() {
test(flag);
}
public void test(int i) {
System.out.println("A." + flag);
}
public void test(Collection collection) {
System.out.println("A.collection");
}
public void test(List list) {
System.out.println("A.list");
}
public void test(Map list) {
System.out.println("A.Map");
}
}
private static class B extends A {
public B() {
flag++;
test(flag);
}
public void test(int i) {
System.out.println("B." + flag);
}
public void test(Collection collection) {
System.out.println("B.collection");
}
public void test(List list) {
System.out.println("B.list");
}
public void test(Map map) {
System.out.println("B.Map");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 引用类型指向的静态方法
// 对象实例指向的成员方法(重写)
A a=new B();
a.test(new HashSet());
System.out.println("=======");
a.test(new HashMap());
System.out.println("=======");
a.test(new ArrayList());
// B.1
// B.2
// B.collection
// =======
// B.Map
// =======
// B.list
}
}import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static class A {
int flag = 1;
public A() {
test(flag);
}
public void test(int i) {
System.out.println("A." + flag);
}
public void test(Collection collection) {
System.out.println("A.collection");
}
public static void test(List list) {
System.out.println("A.list");
}
public static void test(Map list) {
System.out.println("A.Map");
}
}
private static class B extends A {
public B() {
flag++;
test(flag);
}
public void test(int i) {
System.out.println("B." + flag);
}
public void test(Collection collection) {
System.out.println("B.collection");
}
public static void test(List list) {
System.out.println("B.list");
}
public static void test(Map map) {
System.out.println("B.Map");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 引用类型指向的静态方法
// 对象实例指向的成员方法(重写)
A a = new B();
a.test(new HashSet());
System.out.println("=======");
a.test(new HashMap());
System.out.println("=======");
a.test(new ArrayList());
// B.1
// B.2
// B.collection
// =======
// A.Map
// =======
// A.list
}
}import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static class A {
int flag = 1;
public A() {
test(flag);
}
public void test(int i) {
System.out.println("A." + flag);
}
public void test(Collection collection) {
System.out.println("A.collection");
}
public static void test(List list) {
System.out.println("A.list");
}
public static void test(Map list) {
System.out.println("A.Map");
}
}
private static class B extends A {
public int flag = 2;
public B() {
flag++;
test(flag);
}
public void test(int i) {
System.out.println("B." + flag);
}
public void test(Collection collection) {
System.out.println("B.collection");
}
public static void test(List list) {
System.out.println("B.list");
}
public static void test(Map map) {
System.out.println("B.Map");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 引用类型指向的静态方法
// 对象实例指向的成员方法(重写)
A a = new B();
a.test(new HashSet());
System.out.println("=======");
a.test(new HashMap());
System.out.println("=======");
a.test(new ArrayList());
System.out.println("=======");
System.out.println(a.flag);
// B.1
// B.2
// B.collection
// =======
// A.Map
// =======
// A.list
// 1
}
}总结
- 成员变量静态绑定,调用引用指向的类的成员
- 静态变量和静态方法静态绑定,调用引用指向的静态变量和方法
- 成员方法动态绑定,调用对象实际类型的方法,若存在方法重载,多个方法均符合,调用最接近实际参数类型的那个方法。
静态绑定的实现
在编译成的class文件,加载进入虚拟机的时候,静态成员和静态方法也绑定在指定类中。
动态绑定的实现
Java对象内存示例:
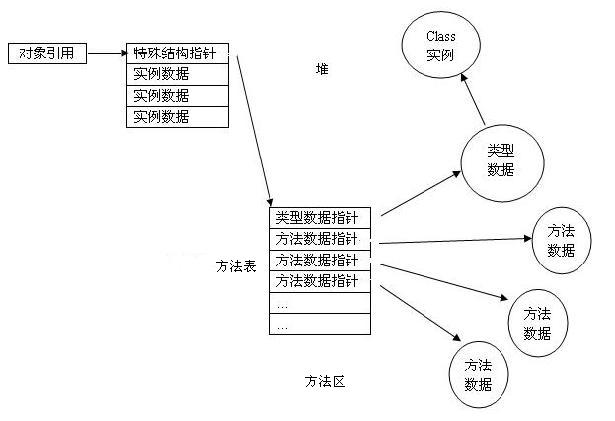
对象引用->对象实例数据+类结构指针
类结构指针->方法表(动态绑定的所有成员方法,不包含static、private等静态绑定)
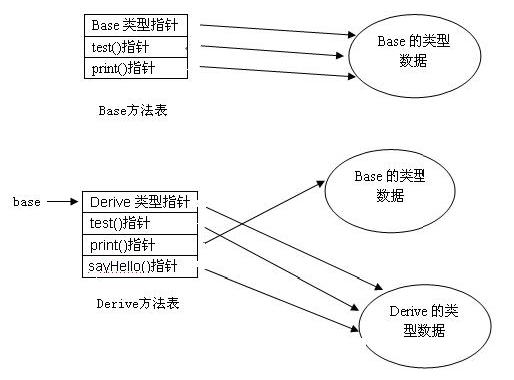
在方法表中,来自超类的方法出现在来自子类的方法之前,并且排列方法指针的顺序和方法在class文件中出现的顺序相同,这种排列顺序的例外情况是,被子类的方法覆盖的方法出现在超类中该方法第一次出现的地方。






















 178
178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








