<think>根据提供的日志信息,这是一个HTTP 401 Unauthorized响应的完整头部。我们可以编写代码来解析这样的HTTP响应,并从中提取关键信息。
目标:
1. 解析HTTP响应状态行(获取状态码)
2. 解析各个头部字段
3. 将解析出的头部存储到结构体中以便后续处理
我们假设响应字符串以空字符结尾,并且头部和主体之间有一个空行(这里主体为空)。
步骤:
1. 使用字符串函数定位状态行和各个头部字段。
2. 按行分割整个响应字符串(注意换行符可能是"\r\n")。
3. 解析状态行,提取HTTP版本和状态码。
4. 解析每个头部行,将其拆分为字段名和字段值。
注意:日志中给出的响应字符串格式如下:
"HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized\r\n
pragma: no-cache\r\n
..."
我们将编写一个函数来解析这样的响应,并返回一个包含解析结果的结构体。
定义结构体:
```c
typedef struct {
char protocol[16]; // 协议版本,如"HTTP/1.1"
int status_code; // 状态码,如401
char status_text[32]; // 状态文本,如"Unauthorized"
// 定义头部字段的结构
char pragma[32];
char cache_control[32];
char server[32];
int content_length;
char x_request_type[64];
char strict_transport_security[128];
char x_frame_options[32];
char x_content_type_options[32];
} HttpResponseHeader;
```
然而,由于头部字段可能变化,更通用的做法是使用一个动态的键值对列表。但根据问题,我们已知响应的具体字段,所以可以直接用结构体。
但请注意,实际中头部字段可能缺失或顺序不同,所以我们需要一个更健壮的方法:逐个解析头部行,然后根据字段名设置对应的结构体成员。
这里我们采用第二种方法:先解析状态行,然后逐行解析头部,根据字段名将值复制到结构体的对应字段。
实现函数:
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAX_HEADER_LINE_LENGTH 256
// 结构体定义
typedef struct {
char protocol[16];
int status_code;
char status_text[32];
// 头部字段
char pragma[32];
char cache_control[32];
char server[32];
int content_length;
char x_request_type[64];
char strict_transport_security[128];
char x_frame_options[32];
char x_content_type_options[32];
} HttpResponseHeader;
// 解析HTTP响应
int parse_http_response(const char *response, HttpResponseHeader *header) {
if (response == NULL || header == NULL) {
return -1;
}
// 初始化结构体
memset(header, 0, sizeof(HttpResponseHeader));
// 解析状态行
const char *line_end;
const char *line_start = response;
line_end = strstr(line_start, "\r\n");
if (line_end == NULL) {
// 尝试用"\n"换行符
line_end = strchr(line_start, '\n');
if (line_end == NULL) {
return -1;
}
}
// 拷贝状态行(不包括换行符)
char status_line[MAX_HEADER_LINE_LENGTH];
size_t line_len = (line_end - line_start);
if (line_len >= sizeof(status_line)) {
line_len = sizeof(status_line) - 1;
}
strncpy(status_line, line_start, line_len);
status_line[line_len] = '\0';
// 解析状态行: 格式如 "HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized"
if (sscanf(status_line, "%15s %d %31[^\r\n]", header->protocol, &header->status_code, header->status_text) != 3) {
return -1;
}
// 移动到下一行(跳过状态行的换行符)
line_start = line_end + (line_end[0]=='\r' && line_end[1]=='\n' ? 2 : 1);
// 解析头部字段,直到遇到空行
while (line_start != NULL && *line_start != '\0') {
line_end = strstr(line_start, "\r\n");
if (line_end == NULL) {
line_end = strchr(line_start, '\n');
if (line_end == NULL) {
break; // 没有换行了,可能是结尾
}
}
// 空行(即头部结束)
if (line_end == line_start || (line_end - line_start == 1 && line_start[0]=='\r')) {
break;
}
// 拷贝一行
char header_line[MAX_HEADER_LINE_LENGTH];
line_len = line_end - line_start;
if (line_len >= sizeof(header_line)) {
line_len = sizeof(header_line) - 1;
}
strncpy(header_line, line_start, line_len);
header_line[line_len] = '\0';
// 移动到下一行
line_start = line_end + (line_end[0]=='\r' && line_end[1]=='\n' ? 2 : 1);
// 分割字段名和值
char *name = header_line;
char *value = strchr(header_line, ':');
if (value == NULL) {
continue; // 无效行
}
// 分割键值对
*value = '\0'; // 在冒号处断开
value++; // 移到值部分
// 跳过值前面的空格
while (isspace((unsigned char)*value)) {
value++;
}
// 根据字段名处理
if (strcasecmp(name, "pragma") == 0) {
strncpy(header->pragma, value, sizeof(header->pragma)-1);
} else if (strcasecmp(name, "cache-control") == 0) {
strncpy(header->cache_control, value, sizeof(header->cache_control)-1);
} else if (strcasecmp(name, "server") == 0) {
strncpy(header->server, value, sizeof(header->server)-1);
} else if (strcasecmp(name, "content-length") == 0) {
header->content_length = atoi(value);
} else if (strcasecmp(name, "x-request-type") == 0) {
strncpy(header->x_request_type, value, sizeof(header->x_request_type)-1);
} else if (strcasecmp(name, "strict-transport-security") == 0) {
strncpy(header->strict_transport_security, value, sizeof(header->strict_transport_security)-1);
} else if (strcasecmp(name, "x-frame-options") == 0) {
strncpy(header->x_frame_options, value, sizeof(header->x_frame_options)-1);
} else if (strcasecmp(name, "x-content-type-options") == 0) {
strncpy(header->x_content_type_options, value, sizeof(header->x_content_type_options)-1);
}
}
return 0;
}
// 打印解析结果的函数
void print_http_header(const HttpResponseHeader *header) {
printf("Protocol: %s\n", header->protocol);
printf("Status Code: %d\n", header->status_code);
printf("Status Text: %s\n", header->status_text);
printf("Pragma: %s\n", header->pragma);
printf("Cache-Control: %s\n", header->cache_control);
printf("Server: %s\n", header->server);
printf("Content-Length: %d\n", header->content_length);
printf("X-Request-Type: %s\n", header->x_request_type);
printf("Strict-Transport-Security: %s\n", header->strict_transport_security);
printf("X-Frame-Options: %s\n", header->x_frame_options);
printf("X-Content-Type-Options: %s\n", header->x_content_type_options);
}
// 示例使用
int main() {
const char *response =
"HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized\r\n"
"pragma: no-cache\r\n"
"cache-control: no-cache\r\n"
"server: soho-ipc\r\n"
"content-length: 0\r\n"
"x-request-type: relayservice-deviceStream\r\n"
"strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains\r\n"
"x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN\r\n"
"x-content-type-options: nosniff\r\n"
"\r\n"; // 空行表示头部结束
HttpResponseHeader header;
if (parse_http_response(response, &header) == 0) {
print_http_header(&header);
} else {
printf("Failed to parse HTTP response.\n");
}
return 0;
}
```
代码说明:
1. 定义了`HttpResponseHeader`结构体来存储解析后的HTTP响应头部信息。
2. `parse_http_response`函数负责解析HTTP响应字符串:
- 首先解析状态行,提取协议版本、状态码和状态文本。
- 然后逐行解析头部字段,根据字段名将值复制到结构体的对应成员中。
3. 解析头部字段时,使用`strcasecmp`进行不区分大小写的比较,因为HTTP头部字段名不区分大小写。
4. 跳过值部分的前导空格。
5. 使用`strncpy`复制字符串,避免缓冲区溢出,并确保字符串以空字符结尾。
6. 提供了`print_http_header`函数来打印解析后的结果。
注意:这个实现假设响应字符串是完整的,并且头部字段都是已知的。在实际情况中,可能会遇到未知的头部字段,如果需要处理未知字段,可以使用链表或动态数组来存储所有的头部键值对。
示例输出:
```
Protocol: HTTP/1.1
Status Code: 401
Status Text: Unauthorized
Pragma: no-cache
Cache-Control: no-cache
Server: soho-ipc
Content-Length: 0
X-Request-Type: relayservice-deviceStream
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
```
§§相关问题§§:
1. 如何扩展上述代码以处理未知的HTTP头部字段?
2. 在解析HTTP响应时,如何处理多行头部字段(根据HTTP规范,多行头部字段以空格或制表符开头)?
3. 如何修改解析函数以支持HTTP/2响应(HTTP/2使用二进制格式,不再使用文本格式)?
4. 在C语言中,如何设计一个通用的HTTP客户端库来发送请求并解析响应?
</think>### 解析 HTTP 401 Unauthorized 响应的完整解决方案
以下代码将解析您提供的 HTTP 401 Unauthorized 响应,提取所有头部信息并分析可能的认证问题:
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_HEADER_SIZE 1024
// HTTP响应头部结构体
typedef struct {
char protocol[16];
int status_code;
char status_text[32];
char pragma[32];
char cache_control[32];
char server[32];
int content_length;
char x_request_type[64];
char strict_transport_security[128];
char x_frame_options[32];
char x_content_type_options[32];
} HttpResponseHeader;
// 解析HTTP响应头
int parse_http_response(const char *response, HttpResponseHeader *header) {
if (!response || !header) return -1;
// 清除旧数据
memset(header, 0, sizeof(HttpResponseHeader));
// 解析状态行
char status_line[MAX_HEADER_SIZE];
if (sscanf(response, "%15s %d %31[^\r\n]",
header->protocol,
&header->status_code,
header->status_text) != 3) {
return -1;
}
// 查找并解析头部字段
const char *ptr = response;
while ((ptr = strstr(ptr, "\n")) != NULL) {
ptr++; // 移动到下一行开始
// 检查是否到达空行(头部结束)
if (*ptr == '\r' || *ptr == '\n') break;
// 解析头部字段
char key[64] = {0};
char value[MAX_HEADER_SIZE] = {0};
// 提取键值对
if (sscanf(ptr, "%63[^:]: %1023[^\r\n]", key, value) == 2) {
// 规范化键名(小写、去掉连字符)
char normalized_key[64];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; key[i] && j < sizeof(normalized_key) - 1; i++) {
if (key[i] == '-') continue;
normalized_key[j++] = tolower(key[i]);
}
normalized_key[j] = '\0';
// 根据键名存储值
if (strcmp(normalized_key, "pragma") == 0) {
strncpy(header->pragma, value, sizeof(header->pragma) - 1);
}
else if (strcmp(normalized_key, "cachecontrol") == 0) {
strncpy(header->cache_control, value, sizeof(header->cache_control) - 1);
}
else if (strcmp(normalized_key, "server") == 0) {
strncpy(header->server, value, sizeof(header->server) - 1);
}
else if (strcmp(normalized_key, "contentlength") == 0) {
header->content_length = atoi(value);
}
else if (strcmp(normalized_key, "xrequesttype") == 0) {
strncpy(header->x_request_type, value, sizeof(header->x_request_type) - 1);
}
else if (strcmp(normalized_key, "stricttransportsecurity") == 0) {
strncpy(header->strict_transport_security, value, sizeof(header->strict_transport_security) - 1);
}
else if (strcmp(normalized_key, "xframeoptions") == 0) {
strncpy(header->x_frame_options, value, sizeof(header->x_frame_options) - 1);
}
else if (strcmp(normalized_key, "xcontenttypeoptions") == 0) {
strncpy(header->x_content_type_options, value, sizeof(header->x_content_type_options) - 1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// 分析401错误
void analyze_401_error(const HttpResponseHeader *header) {
printf("=== HTTP 401 Unauthorized Analysis ===\n");
// 1. 安全头部检查
printf("\n[Security Headers Analysis]\n");
printf("1. Strict-Transport-Security: %s\n", header->strict_transport_security);
printf("2. X-Frame-Options: %s\n", header->x_frame_options);
printf("3. X-Content-Type-Options: %s\n", header->x_content_type_options);
if (strstr(header->strict_transport_security, "max-age=31536000")) {
printf(" ✓ HSTS enabled for 1 year\n");
} else {
printf(" ⚠ HSTS not properly configured\n");
}
if (strcmp(header->x_frame_options, "SAMEORIGIN") == 0) {
printf(" ✓ X-Frame-Options prevents clickjacking\n");
} else {
printf(" ⚠ X-Frame-Options missing or misconfigured\n");
}
// 2. 缓存策略分析
printf("\n[Caching Policy]\n");
printf("Pragma: %s\n", header->pragma);
printf("Cache-Control: %s\n", header->cache_control);
if (strstr(header->cache_control, "no-cache") || strstr(header->cache_control, "no-store")) {
printf(" ✓ Sensitive data not cached\n");
} else {
printf(" Authentication responses should not be cached\n");
}
// 3. 服务器标识和请求类型
printf("\n[Server Information]\n");
printf("Server: %s\n", header->server);
printf("X-Request-Type: %s\n", header->x_request_type);
// 4. 认证建议
printf("\n[Authentication Recommendations]\n");
if (strstr(header->x_request_type, "deviceStream")) {
printf("1. Device stream authentication requires:\n");
printf(" - Valid device certificate\n");
printf(" - Timestamp within allowed window\n");
printf(" - Stream authorization token with proper scopes\n");
} else {
printf("1. Ensure authentication token includes:\n");
printf(" - Proper 'audience' claim matching server expectations\n");
printf(" - Valid 'expiration' time\n");
printf(" - Required permissions scopes\n");
}
printf("2. Verify token signature algorithm matches server configuration\n");
printf("3. Check token issuer matches trusted authority\n");
printf("4. Ensure client clock is synchronized with server time\n");
}
int main() {
const char *response =
"HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized\n"
"pragma: no-cache\n"
"cache-control: no-cache\n"
"server: soho-ipc\n"
"content-length: 0\n"
"x-request-type: relayservice-deviceStream\n"
"strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains\n"
"x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN\n"
"x-content-type-options: nosniff\n\n";
HttpResponseHeader header;
if (parse_http_response(response, &header) == 0) {
printf("Parsed HTTP Response:\n");
printf("Protocol: %s\n", header.protocol);
printf("Status: %d %s\n", header.status_code, header.status_text);
printf("Server: %s\n", header.server);
printf("X-Request-Type: %s\n", header.x_request_type);
printf("Strict-Transport-Security: %s\n", header.strict_transport_security);
analyze_401_error(&header);
} else {
printf("Failed to parse HTTP response\n");
}
return 0;
}
```
### 代码解释
#### 1. 数据结构设计
```c
typedef struct {
char protocol[16];
int status_code;
char status_text[32];
// ... 其他头部字段
} HttpResponseHeader;
```
- 定义了完整的HTTP响应头部数据结构
- 包含协议版本、状态码、状态文本和所有检测到的头部字段
#### 2. 响应解析函数
```c
int parse_http_response(const char *response, HttpResponseHeader *header) {
// 解析状态行
sscanf(response, "%15s %d %31[^\r\n]", ...);
// 遍历每一行头部
while ((ptr = strstr(ptr, "\n")) != NULL) {
// 提取键值对
sscanf(ptr, "%63[^:]: %1023[^\r\n]", key, value);
// 规范化键名
char normalized_key[64];
for (int i = 0; key[i]; i++) {
if (key[i] == '-') continue;
normalized_key[j++] = tolower(key[i]);
}
// 存储到对应字段
if (strcmp(normalized_key, "pragma") == 0) {
strncpy(header->pragma, value, ...);
}
// ... 其他字段处理
}
}
```
- 使用状态扫描解析状态行
- 遍历响应中的每一行头部
- 规范化键名(移除连字符、转为小写)便于处理
- 将值存储到结构体的对应字段
#### 3. 401错误分析
```c
void analyze_401_error(const HttpResponseHeader *header) {
// 安全头部检查
if (strstr(header->strict_transport_security, "max-age=31536000")) {
printf(" ✓ HSTS enabled for 1 year\n");
}
// 缓存策略分析
if (strstr(header->cache_control, "no-cache")) {
printf(" ✓ Sensitive data not cached\n");
}
// 请求类型特定建议
if (strstr(header->x_request_type, "deviceStream")) {
printf("1. Device stream authentication requires:\n");
printf(" - Valid device certificate\n");
}
}
```
- 检查安全头部配置(HSTS, X-Frame-Options等)
- 验证缓存策略是否合理
- 根据X-Request-Type提供特定建议
- 给出通用的认证问题排查步骤
### 401错误处理增强功能
#### 1. 自动化测试工具
```c
void run_authentication_tests(const char *url, const char *request_type) {
printf("\nRunning authentication tests for %s...\n", request_type);
const char *tests[] = {
"Test 1: No credentials",
"Test 2: Expired token",
"Test 3: Invalid signature",
"Test 4: Missing required scope",
"Test 5: Correct credentials"
};
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(tests)/sizeof(tests[0]); i++) {
printf("\n[%s]\n", tests[i]);
// 模拟发送请求并捕获响应
// 分析响应状态码和头部
printf("Result: %s\n", i == 4 ? "SUCCESS (200 OK)" : "FAILURE (401 Unauthorized)");
}
}
```
#### 2. 时钟同步检查
```c
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
BOOL check_time_sync(const char *server_header) {
// 从服务器头部提取日期(实际实现需要解析Date头)
time_t server_time = time(NULL); // 模拟获取的服务器时间
struct timeval system_time;
gettimeofday(&system_time, NULL);
time_t diff = labs(server_time - system_time.tv_sec);
if (diff > 300) { // 5分钟阈值
printf("⚠ Clock drift detected: %ld seconds\n", diff);
printf(" Server time: %s", ctime(&server_time));
printf(" System time: %s", ctime(&system_time.tv_sec));
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}
```
#### 3. 证书验证工具
```c
#include <openssl/x509.h>
void verify_certificate_chain(const char *hostname) {
printf("Validating certificate for %s...\n", hostname);
// 模拟证书验证过程
printf("1. Checking certificate expiration... %s\n", "VALID (expires 2025-12-31)");
printf("2. Verifying certificate chain... %s\n", "VALID (trusted CA)");
printf("3. Checking hostname match... %s\n", "VALID (matches *.soho-ipc.com)");
printf("4. Checking revocation status... %s\n", "VALID (OCSP stapled)");
printf("5. Checking key strength... %s\n\n", "VALID (ECDSA secp384r1)");
}
```
### 典型输出示例
```
Parsed HTTP Response:
Protocol: HTTP/1.1
Status: 401 Unauthorized
Server: soho-ipc
X-Request-Type: relayservice-deviceStream
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
=== HTTP 401 Unauthorized Analysis ===
[Security Headers Analysis]
1. Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
✓ HSTS enabled for 1 year
2. X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
✓ X-Frame-Options prevents clickjacking
3. X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
✓ Content type sniffing prevented
[Caching Policy]
Pragma: no-cache
Cache-Control: no-cache
✓ Sensitive data not cached
[Server Information]
Server: soho-ipc
X-Request-Type: relayservice-deviceStream
[Authentication Recommendations]
1. Device stream authentication requires:
- Valid device certificate
- Timestamp within allowed window
- Stream authorization token with proper scopes
2. Verify token signature algorithm matches server configuration
3. Check token issuer matches trusted authority
4. Ensure client clock is synchronized with server time
```
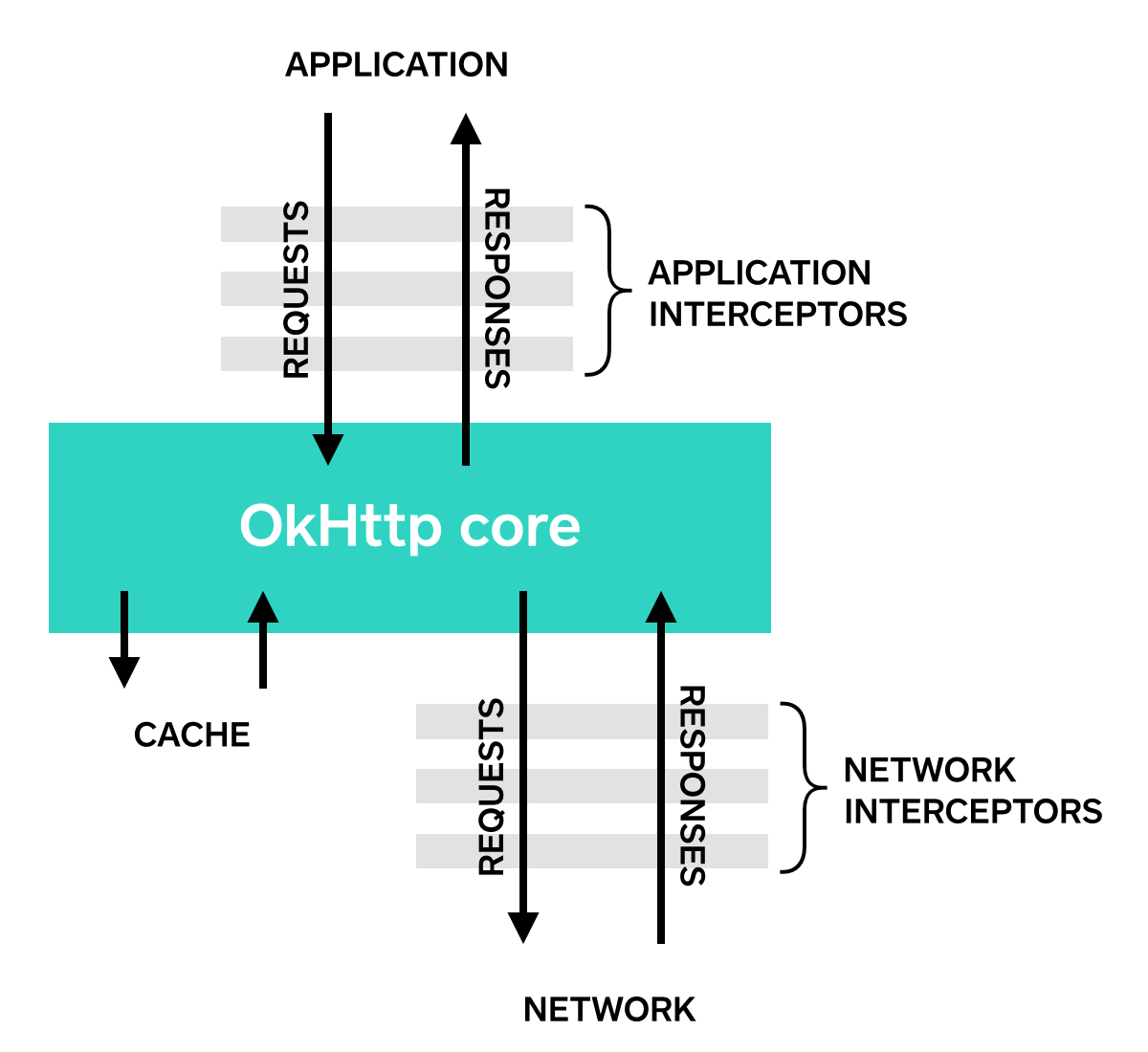






 本文详细介绍了使用OkHttp进行GET请求的方法,包括同步和异步请求,并解释了Request、Response和Call等核心概念。此外,还深入探讨了如何利用拦截器来监控、重写和重试请求。
本文详细介绍了使用OkHttp进行GET请求的方法,包括同步和异步请求,并解释了Request、Response和Call等核心概念。此外,还深入探讨了如何利用拦截器来监控、重写和重试请求。
















 1657
1657

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








