(1)——线程互斥的基本使用(Synchronized)
package com.test;
/**
*
* @Description 线程的互斥实例
* @author CCQ
* @date 2017年7月29日 下午11:23:05
*
*/
public class TraditionalThreadSynchronized {
final Outputer outputer = new Outputer();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TraditionalThreadSynchronized().init();
}
public void init() {
// 线程1
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(true){
outputer.output6("********");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}) {
}.start();
// 线程2
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(true){
outputer.output5("-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}) {
}.start();
}
static class Outputer {
//synchronized,在name字符串上加锁是不能解决问题的,因为每一个name都新的变量,所有不能保证代码块中的代码是同步的
public void output1(String name) {
synchronized (name) {
for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//可以保证同步,保证是同一把锁
public void output2(String name) {
String xxx = "";
synchronized (xxx) {
for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//this代表当前的对象
public void output3(String name) {
synchronized (this) {
for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//在方法上加锁
public synchronized void output4(String name) {
for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
//在静态方法上加锁
public static synchronized void output5(String name) {
for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
//Outputer.class注意,为了保证和静态方法是一个锁对象,需要取Outputer.class
public void output6(String name) {
synchronized (Outputer.class) {
for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
(2)线程同步通信基本使用(wait,notify)
package com.test;
/**
*
* @Description 线程通信
* @author CCQ
* @date 2017年7月30日 下午2:17:33
*
*/
public class TraditionalThreadCommunication {
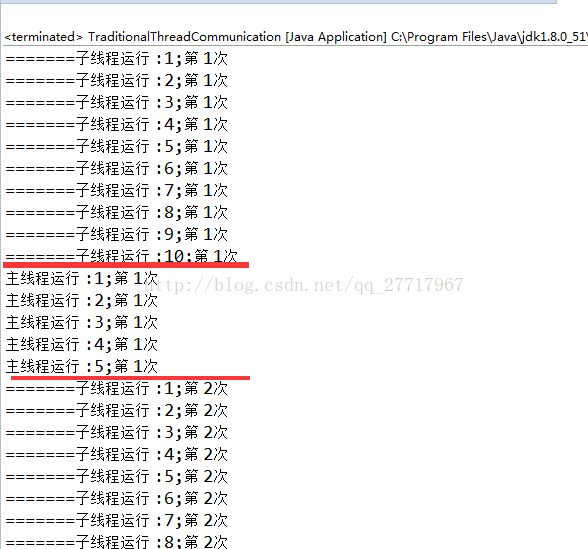
//需求:子线程先运行10次,然后主线程运行5次;然后子线程在运行10次,然后主线程在运行5次
//然后循环3次
public static void main(String[] args) {
Business business = new Business();
new Thread(
new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for(int i = 1;i<=3;i++){
business.sub(i);
}
}
}
){}.start();
for(int i = 1;i<=3;i++){
business.main(i);
}
}
}
class Business{
//定义一个标志位,当flag为true执行子线程,为false执行主线程
private boolean flag = true;
//子线程 添加一个锁
public synchronized void sub(int i){
while(!flag){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for(int j=1;j<=10;j++){
System.out.println("=======子线程运行 :" + j + ";第 " +i+ "次");
}
//设置标志位false
flag = false;
//唤醒主线程
this.notify();
}
//主线程,添加锁
public synchronized void main(int i){
while(flag){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for(int j=1;j<=5;j++){
System.out.println("主线程运行 :" + j + ";第 " +i+ "次");
}
//设置标志位true
flag = true;
//唤醒子线程
this.notify();
}
}
运行结果:





















 1510
1510











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








