How many ways
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 4285 Accepted Submission(s): 2507
Problem Description
这是一个简单的生存游戏,你控制一个机器人从一个棋盘的起始点(1,1)走到棋盘的终点(n,m)。游戏的规则描述如下:
1.机器人一开始在棋盘的起始点并有起始点所标有的能量。
2.机器人只能向右或者向下走,并且每走一步消耗一单位能量。
3.机器人不能在原地停留。
4.当机器人选择了一条可行路径后,当他走到这条路径的终点时,他将只有终点所标记的能量。
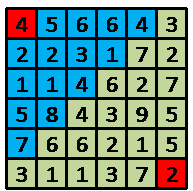
如上图,机器人一开始在(1,1)点,并拥有4单位能量,蓝色方块表示他所能到达的点,如果他在这次路径选择中选择的终点是(2,4)
点,当他到达(2,4)点时将拥有1单位的能量,并开始下一次路径选择,直到到达(6,6)点。
我们的问题是机器人有多少种方式从起点走到终点。这可能是一个很大的数,输出的结果对10000取模。
1.机器人一开始在棋盘的起始点并有起始点所标有的能量。
2.机器人只能向右或者向下走,并且每走一步消耗一单位能量。
3.机器人不能在原地停留。
4.当机器人选择了一条可行路径后,当他走到这条路径的终点时,他将只有终点所标记的能量。

如上图,机器人一开始在(1,1)点,并拥有4单位能量,蓝色方块表示他所能到达的点,如果他在这次路径选择中选择的终点是(2,4)
点,当他到达(2,4)点时将拥有1单位的能量,并开始下一次路径选择,直到到达(6,6)点。
我们的问题是机器人有多少种方式从起点走到终点。这可能是一个很大的数,输出的结果对10000取模。
Input
第一行输入一个整数T,表示数据的组数。
对于每一组数据第一行输入两个整数n,m(1 <= n,m <= 100)。表示棋盘的大小。接下来输入n行,每行m个整数e(0 <= e < 20)。
对于每一组数据第一行输入两个整数n,m(1 <= n,m <= 100)。表示棋盘的大小。接下来输入n行,每行m个整数e(0 <= e < 20)。
Output
对于每一组数据输出方式总数对10000取模的结果.
Sample Input
1 6 6 4 5 6 6 4 3 2 2 3 1 7 2 1 1 4 6 2 7 5 8 4 3 9 5 7 6 6 2 1 5 3 1 1 3 7 2
Sample Output
3948
方法一:记忆化搜索,有效地提高了暴力DFS的效率,对于重叠子问题无需再次求解,深刻理解它们的关系,同时注意初始化。不能原地不动,注意此问题。
/*------------------Header Files------------------*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
/*------------------Definitions-------------------*/
#define LL long long
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
#define MOD 10000
/*---------------------Work-----------------------*/
int maze[150][150];
int dp[150][150];
int n,m;
int DFS(int x,int y)
{
if(dp[x][y]>=0) return dp[x][y];
dp[x][y]=0;
for(int i=0;i<=maze[x][y];i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=maze[x][y];j++)
{
if(i==0&&j==0) continue;
if(i+x>=n||j+y>=m) continue;
if(i+j>maze[x][y]) continue;
dp[x][y]=(DFS(x+i,y+j)%MOD+dp[x][y]%MOD)%MOD;
}
}
return dp[x][y];
}
void work()
{
int T; cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
scanf("%d",&maze[i][j]);
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
dp[n-1][m-1]=1; //注意初始化,和过程相关
printf("%d\n",DFS(0,0));
}
}
/*------------------Main Function------------------*/
int main()
{
//freopen("test.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("cowtour.out","w",stdout);
//freopen("cowtour.in","r",stdin);
work();
return 0;
}方法二:记录dp[i][j]为到此点的所有方案数,注意初始化。之所以和前面不一样是因为一个是向前推,一个是向后推,由此也可看出DP和DFS的差异。
/*------------------Header Files------------------*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
/*------------------Definitions-------------------*/
#define LL long long
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
#define MOD 10000
/*---------------------Work-----------------------*/
int maze[150][150];
int dp[150][150];
void work()
{
int T; cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
scanf("%d",&maze[i][j]);
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[0][0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
for(int x=0;x<=maze[i][j];x++)
{
for(int y=0;y<=maze[i][j];y++)
{
if(x==0&&y==0) continue; //注意这个条件,不能待在原地
if(x+y>maze[i][j]) continue;
if(i+x>=n||j+y>=m) continue;
dp[i+x][j+y]=(dp[i][j]%MOD+dp[i+x][j+y]%MOD)%MOD;
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[n-1][m-1]);
}
}
/*------------------Main Function------------------*/
int main()
{
//freopen("test.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("cowtour.out","w",stdout);
//freopen("cowtour.in","r",stdin);
work();
return 0;
}FatMouse and Cheese
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 7190 Accepted Submission(s): 2969
Problem Description
FatMouse has stored some cheese in a city. The city can be considered as a square grid of dimension n: each grid location is labelled (p,q) where 0 <= p < n and 0 <= q < n. At each grid location Fatmouse has hid between 0 and 100 blocks of cheese in a hole. Now he's going to enjoy his favorite food.
FatMouse begins by standing at location (0,0). He eats up the cheese where he stands and then runs either horizontally or vertically to another location. The problem is that there is a super Cat named Top Killer sitting near his hole, so each time he can run at most k locations to get into the hole before being caught by Top Killer. What is worse -- after eating up the cheese at one location, FatMouse gets fatter. So in order to gain enough energy for his next run, he has to run to a location which have more blocks of cheese than those that were at the current hole.
Given n, k, and the number of blocks of cheese at each grid location, compute the maximum amount of cheese FatMouse can eat before being unable to move.
FatMouse begins by standing at location (0,0). He eats up the cheese where he stands and then runs either horizontally or vertically to another location. The problem is that there is a super Cat named Top Killer sitting near his hole, so each time he can run at most k locations to get into the hole before being caught by Top Killer. What is worse -- after eating up the cheese at one location, FatMouse gets fatter. So in order to gain enough energy for his next run, he has to run to a location which have more blocks of cheese than those that were at the current hole.
Given n, k, and the number of blocks of cheese at each grid location, compute the maximum amount of cheese FatMouse can eat before being unable to move.
Input
There are several test cases. Each test case consists of
a line containing two integers between 1 and 100: n and k
n lines, each with n numbers: the first line contains the number of blocks of cheese at locations (0,0) (0,1) ... (0,n-1); the next line contains the number of blocks of cheese at locations (1,0), (1,1), ... (1,n-1), and so on.
The input ends with a pair of -1's.
a line containing two integers between 1 and 100: n and k
n lines, each with n numbers: the first line contains the number of blocks of cheese at locations (0,0) (0,1) ... (0,n-1); the next line contains the number of blocks of cheese at locations (1,0), (1,1), ... (1,n-1), and so on.
The input ends with a pair of -1's.
Output
For each test case output in a line the single integer giving the number of blocks of cheese collected.
Sample Input
3 1 1 2 5 10 11 6 12 12 7 -1 -1
Sample Output
37
Source
记忆化搜索,有点像剪枝,只有满足dp[newx][newy]<dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy]才更新并转移状态。
/*------------------Header Files------------------*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
/*------------------Definitions-------------------*/
#define LL long long
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
#define MOD 10E9+7
#define MAX 500050
/*---------------------Work-----------------------*/
int maze[150][150];
int dp[150][150];
int n,k;
void DFS(int x,int y)
{
if(x==0&&y==0) dp[x][y]=maze[x][y];
int newx,newy;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
newx=x,newy=y+i;
if(newy<n&&dp[newx][newy]<dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy]&&maze[newx][newy]>maze[x][y])
{
dp[newx][newy]=dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy];
DFS(newx,newy);
}
newx=x,newy=y-i;
if(newy>=0&&dp[newx][newy]<dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy]&&maze[newx][newy]>maze[x][y])
{
dp[newx][newy]=dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy];
DFS(newx,newy);
}
newx=x+i,newy=y;
if(newx<n&&dp[newx][newy]<dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy]&&maze[newx][newy]>maze[x][y])
{
dp[newx][newy]=dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy];
DFS(newx,newy);
}
newx=x-i,newy=y;
if(newx>=0&&dp[newx][newy]<dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy]&&maze[newx][newy]>maze[x][y])
{
dp[newx][newy]=dp[x][y]+maze[newx][newy];
DFS(newx,newy);
}
}
}
void work()
{
while(cin>>n>>k)
{
if(n==-1&&k==-1) break;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&maze[i][j]);
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
DFS(0,0);
int Max=-INF;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
Max=max(Max,dp[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",Max);
}
}
/*------------------Main Function------------------*/
int main()
{
//freopen("test.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("cowtour.out","w",stdout);
//freopen("cowtour.in","r",stdin);
work();
return 0;
}























 1751
1751











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








