今天小编在这里给大家详细介绍下Linux里面的木操作函数,这里全都是干货哦哦哦。各位小主赶紧来这里瞧瞧哦哦哦。走过路过千万不要错过。
一、chdir 函数
1、作用:修改当前进程的路径
2、函数原型:
#include <unistd.h>
int chdir(const char *path);
二、getcwd 函数
1、作用:获取当前进程工作目录
2、函数原型:
#include <unistd.h>
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
char *getwd(char *buf);
注:一般情况下 chdir 函数 和 getcwd 函数配合在一起使用
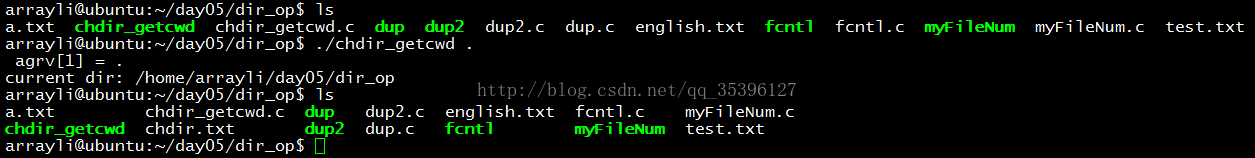
chdir 函数和 getcwd 函数的运用:
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[] )
{
if( argc<2 )
{
perror("./a.out filepath");
exit(1);
}
printf(" agrv[1] = %s\n",argv[1]);
// 修改当前的路径
int ret =chdir(argv[1]);
if( ret == -1 )
{
perror("chdir");
exit(1);
}
// 在这里通过在改变后的目录下创建一个新的文件,来证明目录已经改变
int fd = open("chdir.txt",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0644);
if( fd == -1 )
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
close(fd);
// 获取改变目录后的目录名
char buf[100]={0};
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("current dir: %s\n",buf);
return 0;
}
三、rmdir 函数
1、作用:删除一个目录
2、函数原型:
#include <unistd.h>
int rmdir(const char *pathname);
1、作用:创建一个目录
2、函数原型:
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
五、opendir 函数
1、作用:打开一个目录
2、函数原型:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
DIR *fdopendir(int fd);
(1)、DIR结构体指针,该结构是一个内部结构,保存所打开的目录的信息,作用于类似于FILE结构。
(2)、函数出错,返回NULL
六、readdir 函数
1、作用:读目录
2、函数原型:
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
返回一个记录项
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */ // 目录进入点的 inode
off_t d_off; /* not an offset; see NOTES */ // 目录文件头开始至此目录进入点的位移
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */ // d_name 长度
unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported // d_name 所指的文件夹
by all filesystem types */
char d_name[256]; /* filename */ // 文件名
};
d_tyep 有 8 种类型:
(1)、 DT_BLK This is a block device. 块设备
(2)、 DT_CHR This is a character device. 字符设备
(3)、 DT_DIR This is a directory. 目录
(4)、 DT_FIFO This is a named pipe (FIFO). 管道
(5)、 DT_LNK This is a symbolic link. 软链接
(6)、 DT_REG This is a regular file. 普通文件
(7)、 DT_SOCK This is a UNIX domain socket. 套接字
(8)、 DT_UNKNOWN The file type is unknown. 未知类型
七、closedir 函数
1、作用:关闭一个目录
2、函数原型:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
若函数执行成功,返回0;若失败,返回 -1.
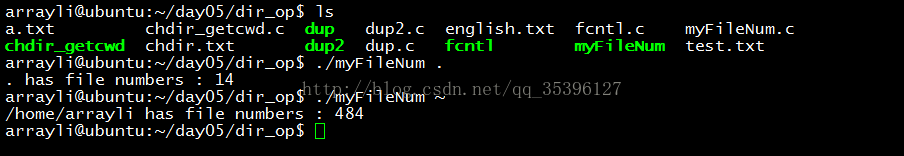
opendir、readdir、closedir 三个函数 的综合运用:
#include<unistd.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
// 获取 root 目录下的文件个数
int get_file_count(char *root)
{
// open dir
DIR * dir = NULL;
dir = opendir(root);
if( NULL == dir )
{
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
// 遍历当前打开的目录
struct dirent* ptr = NULL;
char path[1024]={0};
int total = 0;
while( (ptr = readdir(dir) )!= NULL)
{
// 过滤掉 . 和 ..
if( strcmp(ptr->d_name,".") == 0 || strcmp(ptr->d_name,"..") == 0 )
{
continue;
}
// 如果是目录,递归读目录
if(ptr->d_type == DT_DIR)
{
sprintf(path,"%s/%s",root,ptr->d_name);
total += get_file_count(path);
}
// 如果是普通文件
if( ptr->d_type == DT_REG )
{
total++;
}
}
// 关闭目录
closedir(dir);
return total;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if( argc<2 )
{
perror("./a.out dir\n");
exit(1);
}
// 获取文件个数
int count = get_file_count(argv[1]);
printf("%s has file numbers : %d\n",argv[1],count);
return 0;
}
八、dup 和 dup2 函数
1、作用:复制现有的文件描述符
2、函数原型:
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
(1)、dup 返回的是文件描述符中没有被占用的
(2)、dup2 分两种情况讨论下:
(a)、oldfd----->newfd 如果 newfd 是一个被打开的文件描述符,在拷贝前会先关掉 newfd
(b)、oldfd------>newfd是同一个文件描述符,不会关掉 newfd , 直接返回 oldfd
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd =open("a.txt",O_RDWR);
if( fd == -1 )
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
printf("file open fd = %d\n",fd);
// 找到进程文件描述符表 ======= 第一个========== 可用的文件描述符
// 将参数指定的文件复制到该描述后 返回这个描述符
int ret = dup(fd);
if( fd == -1 )
{
perror("dup");
exit(1);
}
printf(" dup fd = %d\n",ret);
char *buf = "你是猴子请来的救兵吗??\n";
char *buf1 = "你大爷的,我是程序猿!!!\n";
write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));
write(ret,buf1,strlen(buf1));
close(fd);
return 0;
}
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd =open("english.txt",O_RDWR);
if( fd == -1 )
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
int fd1 =open("a.txt",O_RDWR);
if( fd1 == -1 )
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
printf("fd = %d\n",fd);
printf("fd1 = %d\n",fd1);
int ret = dup2(fd1, fd);
if( ret == -1 )
{
perror("dup2");
exit(1);
}
printf(" current fd = %d\n",ret);
char *buf = "主要看气质 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!\n";
write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));
write(fd1,"hello world!",12);
close(fd);
close(fd1);
return 0;
}
九、fcntl 函数
1、作用:改变已经打开文件的属性
2、函数原型:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ ); 这是一个可变长参数的函数
(1)、复制一个现有的描述符--------cmd F_DUPFD
(2)、 获得 / 设置文件状态标价--------cmd( 参数设置如下 )
(a)、F_GETFD
(b)、F_STFD
(3)、获得 / 设置文件标记状态-------- cmd
(a)、
O_RDONLY 只读打开
O_WRONLY 只写打开
O_RDWR 读写打开
O_EXEC 执行打开
O_SEARCH 搜索打开
O_APPEND 追加打开
O_NONBLOCK 非阻塞模式
(b)、F_SETFL
O_APPEND
O_NONBLOCK
(4)、 获得 / 设置异步 I / O 所有权-------- cmd
(a)、F_GETOWN
(b)、F_SETOWN
(5)、获得 / 设置记录锁-------- cmd
(a)、F_GETLK
(b)、F_SETLK
(c)、SETLKW
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
int flag;
int fd;
// 测试字符串
char *p = "我们是一个由中国特使社会主义的国家!!!!!";
char *q ="呵呵,社会主义好哇";
// 以只写方式打开文件
fd = open("test.txt",O_WRONLY);
if( fd == -1 )
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
// 输入新的内容,该内容会覆盖原来的内容
if( write(fd,p,strlen(p)) == -1 )
{
perror("write");
exit(1);
}
// 使用 F_GETFL 命令得到文件状态标志
int flags = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL,0);
if( flags == -1 )
{
perror("fcntl");
exit(1);
}
// 将文件状态标志添加 “追加写” 选项
flag |= O_APPEND;
// 将文件状态修改为追加写
if( fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,flag) == -1 )
{
perror("fcntl");
exit(1);
}
// 再次输入新的内容,该内容会追加到旧内容对的后面
if( write(fd,q,strlen(q)) == -1 )
{
perror("write again");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
本文介绍的所有文件操作函数的运用,代码在我的 GitHub 上,把链接分享给大家:
https://github.com/ARRAYLI/LinuxCode/tree/master
相信您看完博客收获不少吧,那就给我点赞吧,谢谢谢哦哦。





















 582
582











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








