我们曾经在《深入理解Spark 2.1 Core (一):RDD的原理与源码分析 》讲解过:
为了有效地实现容错,RDD提供了一种高度受限的共享内存,即RDD是只读的,并且只能通过其他RDD上的批量操作来创建(注:还可以由外部存储系数据集创建,如HDFS)
可知,我们在第九,第十篇博文所讲的是传统hadoop MapReduce类似的,在最初从HDFS中读取数据生成HadoopRDD的过程。而RDD可以通过其他RDD上的批量操作来创建,所以这里的HadoopRDD对于下一个生成的ShuffledRDD可以视为Map端,当然下一个生成的ShuffledRDD可以被下下个ShuffledRDD视为Map端。反过来说,下一个ShuffledRDD可以被`HadoopRDD视作Reduce端。
这篇博文,我们就来讲下Shuffle的Reduce端。其实在RDD迭代部分和第九篇博文类似,不同的是,这里调用的是rdd.ShuffledRDD.compute:
override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[(K, C)] = {
// 得到依赖
val dep = dependencies.head.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]]
// 调用getReader,传入dep.shuffleHandle 分区 上下文
// 得到Reader,调用read()
// 得到迭代器
SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader(dep.shuffleHandle, split.index, split.index + 1, context)
.read()
.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]]
}
- 1
- 3
这里调用的是shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager的getReader:
override def getReader[K, C](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
startPartition: Int,
endPartition: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleReader[K, C] = {
// 生成返回 BlockStoreShuffleReader
new BlockStoreShuffleReader(
handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[K, _, C]], startPartition, endPartition, context)
}
- 1
shuffle.BlockStoreShuffleReader.read:
override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = {
// 实例化ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator
val blockFetcherItr = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator(
context,
blockManager.shuffleClient,
blockManager,
// 通过消息发送获取 ShuffleMapTask 存储数据位置的元数据
mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition),
// 设置每次传输的大小
SparkEnv.get.conf.getSizeAsMb("spark.reducer.maxSizeInFlight", "48m") * 1024 * 1024,
// // 设置Int的大小
SparkEnv.get.conf.getInt("spark.reducer.maxReqsInFlight", Int.MaxValue))
// 基于配置的压缩和加密来包装流
val wrappedStreams = blockFetcherItr.map { case (blockId, inputStream) =>
serializerManager.wrapStream(blockId, inputStream)
}
val serializerInstance = dep.serializer.newInstance()
// 对每个流生成 k/v 迭代器
val recordIter = wrappedStreams.flatMap { wrappedStream =>
serializerInstance.deserializeStream(wrappedStream).asKeyValueIterator
}
// 每条记录读取后更新任务度量
val readMetrics = context.taskMetrics.createTempShuffleReadMetrics()
// 生成完整的迭代器
val metricIter = CompletionIterator[(Any, Any), Iterator[(Any, Any)]](
recordIter.map { record =>
readMetrics.incRecordsRead(1)
record
},
context.taskMetrics().mergeShuffleReadMetrics())
// 传入metricIter到可中断的迭代器
// 为了能取消迭代
val interruptibleIter = new InterruptibleIterator[(Any, Any)](context, metricIter)
val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
// 若需要对数据进行聚合
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
// 若需要进行Map端(对于下一个Shuffle来说)的合并
val combinedKeyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(combinedKeyValuesIterator, context)
// 若只需要进行Reduce端(对于下一个Shuffle来说)的合并
} else {
val keyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, Nothing)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(keyValuesIterator, context)
}
} else {
require(!dep.mapSideCombine, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]]
}
dep.keyOrdering match {
case Some(keyOrd: Ordering[K]) =>
// 若需要排序
// 若spark.shuffle.spill设置为否的话
// 将不会spill到磁盘
val sorter =
new ExternalSorter[K, C, C](context, ordering = Some(keyOrd), serializer = dep.serializer)
sorter.insertAll(aggregatedIter)
context.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(sorter.memoryBytesSpilled)
context.taskMetrics().incDiskBytesSpilled(sorter.diskBytesSpilled)
context.taskMetrics().incPeakExecutionMemory(sorter.peakMemoryUsedBytes)
CompletionIterator[Product2[K, C], Iterator[Product2[K, C]]](sorter.iterator, sorter.stop())
case None =>
aggregatedIter
}
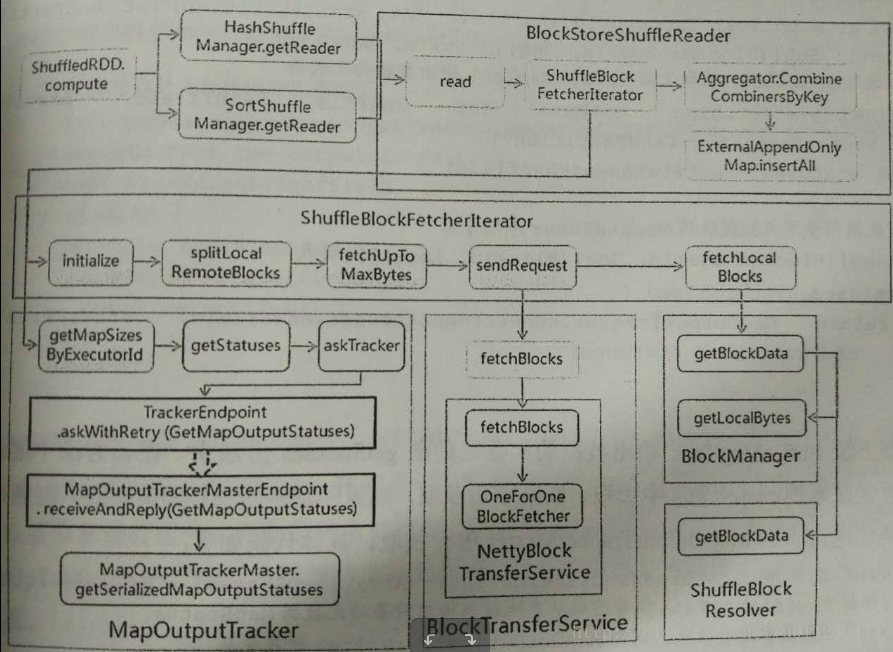
}类调用关系图:
下面我们来深入讲解下实例化ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator的过程:
// 实例化ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator
val blockFetcherItr = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator(
context,
blockManager.shuffleClient,
blockManager,
// 通过消息发送获取 ShuffleMapTask 存储数据位置的元数据
mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition),
// 设置每次传输的大小
SparkEnv.get.conf.getSizeAsMb("spark.reducer.maxSizeInFlight", "48m") * 1024 * 1024,
// // 设置Int的大小
SparkEnv.get.conf.getInt("spark.reducer.maxReqsInFlight", Int.MaxValue))
- 1
获取元数据
mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId
首先我们会调用mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId:
def getMapSizesByExecutorId(shuffleId: Int, startPartition: Int, endPartition: Int)
: Seq[(BlockManagerId, Seq[(BlockId, Long)])] = {
logDebug(s"Fetching outputs for shuffle $shuffleId, partitions $startPartition-$endPartition")
// 得到元数据
val statuses = getStatuses(shuffleId)
// 返回格式为:
// Seq[BlockManagerId,Seq[(shuffle block id, shuffle block size)]]
statuses.synchronized {
return MapOutputTracker.convertMapStatuses(shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition, statuses)
}
}
- 1
mapOutputTracker.getStatuses
private def getStatuses(shuffleId: Int): Array[MapStatus] = {
// 尝试从本地获取数据
val statuses = mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull
if (statuses == null) {
// 若本地无数据
logInfo("Don't have map outputs for shuffle " + shuffleId + ", fetching them")
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis
var fetchedStatuses: Array[MapStatus] = null
fetching.synchronized {
// 若以及有其他人也准备远程获取这数据的话
// 则等待
while (fetching.contains(shuffleId)) {
try {
fetching.wait()
} catch {
case e: InterruptedException =>
}
}
// 尝试直接获取数据
fetchedStatuses = mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull
if (fetchedStatuses == null) {
// 若还是不得不远程获取,
// 则将shuffleId加入fetching
fetching += shuffleId
}
}
if (fetchedStatuses == null) {
logInfo("Doing the fetch; tracker endpoint = " + trackerEndpoint)
try {
// 远程获取
val fetchedBytes = askTracker[Array[Byte]](GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId))
// 反序列化
fetchedStatuses = MapOutputTracker.deserializeMapStatuses(fetchedBytes)
logInfo("Got the output locations")
// 将数据加入mapStatuses
mapStatuses.put(shuffleId, fetchedStatuses)
} finally {
fetching.synchronized {
fetching -= shuffleId
fetching.notifyAll()
}
}
}
logDebug(s"Fetching map output statuses for shuffle $shuffleId took " +
s"${System.currentTimeMillis - startTime} ms")
if (fetchedStatuses != null) {
// 若直接获取,则直接返回
return fetchedStatuses
} else {
logError("Missing all output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId)
throw new MetadataFetchFailedException(
shuffleId, -1, "Missing all output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId)
}
} else {
// 若直接获取,则直接返回
return statuses
}
}
- 1
- 2
mapOutputTracker.askTracker
向trackerEndpoint发送消息GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId)
protected def askTracker[T: ClassTag](message: Any): T = {
try {
trackerEndpoint.askWithRetry[T](message)
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
logError("Error communicating with MapOutputTracker", e)
throw new SparkException("Error communicating with MapOutputTracker", e)
}
}
- 1
MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint.receiveAndReply
case GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId: Int) =>
val hostPort = context.senderAddress.hostPort
logInfo("Asked to send map output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId + " to " + hostPort)
val mapOutputStatuses = tracker.post(new GetMapOutputMessage(shuffleId, context))可以看到,这里并不是直接返回消息,而是调用tracker.post:
def post(message: GetMapOutputMessage): Unit = {
mapOutputRequests.offer(message)
}
- 1
- 2
向mapOutputRequests加入GetMapOutputMessage(shuffleId, context)消息。这里的mapOutputRequests是链式阻塞队列。
private val mapOutputRequests = new LinkedBlockingQueue[GetMapOutputMessage]
- 1
MapOutputTrackerMaster.MessageLoop.run
MessageLoop启一个线程不断的参数从mapOutputRequests读取数据:
private class MessageLoop extends Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
while (true) {
try {
val data = mapOutputRequests.take()
if (data == PoisonPill) {
mapOutputRequests.offer(PoisonPill)
return
}
val context = data.context
val shuffleId = data.shuffleId
val hostPort = context.senderAddress.hostPort
logDebug("Handling request to send map output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId +
" to " + hostPort)
// 若读到数据
// 则序列化
val mapOutputStatuses = getSerializedMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId)
// 返回数据
context.reply(mapOutputStatuses)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) => logError(e.getMessage, e)
}
}
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException => // exit
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
MapOutputTracker.convertMapStatuses
我们回到mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId中返回的MapOutputTracker.convertMapStatuses:
private def convertMapStatuses(
shuffleId: Int,
startPartition: Int,
endPartition: Int,
statuses: Array[MapStatus]): Seq[(BlockManagerId, Seq[(BlockId, Long)])] = {
assert (statuses != null)
val splitsByAddress = new HashMap[BlockManagerId, ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)]]
for ((status, mapId) <- statuses.zipWithIndex) {
if (status == null) {
val errorMessage = s"Missing an output location for shuffle $shuffleId"
logError(errorMessage)
throw new MetadataFetchFailedException(shuffleId, startPartition, errorMessage)
} else {
for (part <- startPartition until endPartition) {
// 返回的Seq中的结构是status.location,Seq[ShuffleBlockId,SizeForBlock]
splitsByAddress.getOrElseUpdate(status.location, ArrayBuffer()) +=
((ShuffleBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, part), status.getSizeForBlock(part)))
}
}
}
// 对Seq根据status.location进行排序
splitsByAddress.toSeq
}
- 1
划分本地和远程Block
让我回到new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator
storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator.initialize
当我们实例化ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator时,会调用initialize:
private[this] def initialize(): Unit = {
context.addTaskCompletionListener(_ => cleanup())
// 划分本地和远程的blocks
val remoteRequests = splitLocalRemoteBlocks()
// 把远程请求随机的添加到队列中
fetchRequests ++= Utils.randomize(remoteRequests)
assert ((0 == reqsInFlight) == (0 == bytesInFlight),
"expected reqsInFlight = 0 but found reqsInFlight = " + reqsInFlight +
", expected bytesInFlight = 0 but found bytesInFlight = " + bytesInFlight)
// 发送远程请求获取blocks
fetchUpToMaxBytes()
val numFetches = remoteRequests.size - fetchRequests.size
logInfo("Started " + numFetches + " remote fetches in" + Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTime))
// 获取本地的Blocks
fetchLocalBlocks()
logDebug("Got local blocks in " + Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTime))
}
- 1
storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator.splitLocalRemoteBlocks
private[this] def splitLocalRemoteBlocks(): ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest] = {
// 是的远程请求最大长度为 maxBytesInFlight / 5
// maxBytesInFlight: 为单次航班请求的最大字节数
// 航班: 一批请求
// 1/5 : 是为了提高请求批发度,允许5个请求分别从5个节点获取数据
val targetRequestSize = math.max(maxBytesInFlight / 5, 1L)
logDebug("maxBytesInFlight: " + maxBytesInFlight + ", targetRequestSize: " + targetRequestSize)
// 缓存需要远程请求的FetchRequest对象
val remoteRequests = new ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest]
// 总共 blocks 的数量
var totalBlocks = 0
// 我们从上文可知blocksByAddress是根据status.location进行排序的
for ((address, blockInfos) <- blocksByAddress) {
totalBlocks += blockInfos.size
if (address.executorId == blockManager.blockManagerId.executorId) {
// 若 executorId 相同 与本 blockManagerId.executorId,
// 则从本地获取
localBlocks ++= blockInfos.filter(_._2 != 0).map(_._1)
numBlocksToFetch += localBlocks.size
} else {
// 否则 远程请求
// 得到迭代器
val iterator = blockInfos.iterator
// 当前累计块的大小
var curRequestSize = 0L
// 当前累加块
// 累加: 若向一个节点频繁的请求字节很少的Block,
// 那么会造成网络阻塞
var curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)]
// iterator 中的block 都是同一节点的
while (iterator.hasNext) {
val (blockId, size) = iterator.next()
if (size > 0) {
curBlocks += ((blockId, size))
remoteBlocks += blockId
numBlocksToFetch += 1
curRequestSize += size
} else if (size < 0) {
throw new BlockException(blockId, "Negative block size " + size)
}
if (curRequestSize >= targetRequestSize) {
// 若累加到大于远程请求的尺寸
// 往remoteRequests加入FetchRequest
remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks)
curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)]
logDebug(s"Creating fetch request of $curRequestSize at $address")
curRequestSize = 0
}
}
// 增加最后的请求
if (curBlocks.nonEmpty) {
remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks)
}
}
}
logInfo(s"Getting $numBlocksToFetch non-empty blocks out of $totalBlocks blocks")
remoteRequests
}
- 1
- 8
获取Block
storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator.fetchUpToMaxBytes
我们回到storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator.initialize的fetchUpToMaxBytes()来深入讲解下如何获取远程的Block:
private def fetchUpToMaxBytes(): Unit = {
// Send fetch requests up to maxBytesInFlight
// 单次航班请求数要小于最大航班请求数
// 单次航班字节数数要小于最大航班字节数
while (fetchRequests.nonEmpty &&
(bytesInFlight == 0 ||
(reqsInFlight + 1 <= maxReqsInFlight &&
bytesInFlight + fetchRequests.front.size <= maxBytesInFlight))) {
sendRequest(fetchRequests.dequeue())
}
}
- 1
storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator.sendRequest
private[this] def sendRequest(req: FetchRequest) {
logDebug("Sending request for %d blocks (%s) from %s".format(
req.blocks.size, Utils.bytesToString(req.size), req.address.hostPort))
bytesInFlight += req.size
reqsInFlight += 1
// 可根据blockID查询block大小
val sizeMap = req.blocks.map { case (blockId, size) => (blockId.toString, size) }.toMap
val remainingBlocks = new HashSet[String]() ++= sizeMap.keys
val blockIds = req.blocks.map(_._1.toString)
val address = req.address
// 关于shuffleClient.fetchBlocks我们会在之后的博文讲解
shuffleClient.fetchBlocks(address.host, address.port, address.executorId, blockIds.toArray,
new BlockFetchingListener {
// 请求成功
override def onBlockFetchSuccess(blockId: String, buf: ManagedBuffer): Unit = {
ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator.this.synchronized {
if (!isZombie) {
buf.retain()
remainingBlocks -= blockId
results.put(new SuccessFetchResult(BlockId(blockId), address, sizeMap(blockId), buf,
remainingBlocks.isEmpty))
logDebug("remainingBlocks: " + remainingBlocks)
}
}
logTrace("Got remote block " + blockId + " after " + Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTime))
}
// 请求失败
override def onBlockFetchFailure(blockId: String, e: Throwable): Unit = {
logError(s"Failed to get block(s) from ${req.address.host}:${req.address.port}", e)
results.put(new FailureFetchResult(BlockId(blockId), address, e))
}
}
)
}
- 1
storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator.fetchLocalBlocks
我们再回过头来看获取本地blocks:
private[this] def fetchLocalBlocks() {
// 获取迭代器
val iter = localBlocks.iterator
while (iter.hasNext) {
val blockId = iter.next()
try {
// 遍历获取数据
// blockManager.getBlockData 会在后续博文讲解
val buf = blockManager.getBlockData(blockId)
shuffleMetrics.incLocalBlocksFetched(1)
shuffleMetrics.incLocalBytesRead(buf.size)
buf.retain()
results.put(new SuccessFetchResult(blockId, blockManager.blockManagerId, 0, buf, false))
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
logError(s"Error occurred while fetching local blocks", e)
results.put(new FailureFetchResult(blockId, blockManager.blockManagerId, e))
return
}
}
}




















 158
158











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








