HPILN: a feature learning framework for cross-modality person re-identification
当前的问题及概述:
提出了一种新的特征学习框架:hard pentaplet loss和identity loss network (HPILN),(HPILN)。在该框架中,对现有的单模态再识别模型进行了修正以适应交叉模态场景,并采用专门设计的hard pentaplet loss和identity loss来提高修正后的交叉模态再识别模型的准确性。
模型及loss:
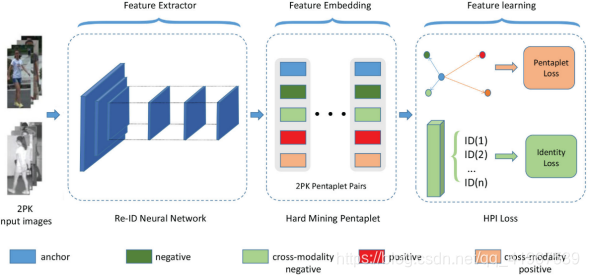
本文提出了基于特征学习框架的RGB-IR识别的HP loss模型。该框架包括三个主要部分:(i)提取RGB和IR图像共同特征的Re-ID neural network;(ii)硬采矿抽样(hard mining sampling)法,得到the hardest pentaplet pair集合;(iii)特征学习的HPI loss,包括pentaplet loss 和 identity loss。其中,第二部分的2PK为训练批大小。在每个训练批次中,随机选取P个个体,每个个体随机选取K张RGB图像和K张IR图像。
1.Re-ID neural network
大多数的Re-ID模型至少有两个完全连通的层(简称FC-1和FC-2),其中FC-2用于身份丢失,FC-1的输出作为特征嵌入,见下图,通过基于度量学习的ranking loss进行监督。Cross entropy loss及其变体通常用作identity loss,而ranking loss通常使用基于度量学习的损失函数,如HT loss。联合训练的identity和ranking loss可以学习更多的判别特征嵌入。
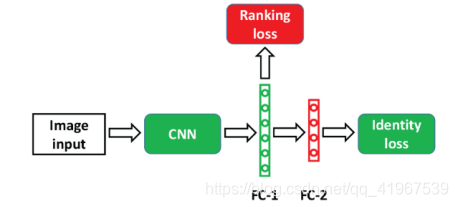
本文在该模块进行了两个地方的改进:i是identity loss通常使用softmax loss来表示,ii 设计了一个新的ranking loss称为HP loss:
2.HP loss
2.1HT loss
HT loss是triplet loss的变体,其中xa为anchor image,xp为positive image,xn为negative image,用CNN提取特征,两幅图的欧氏距离为:
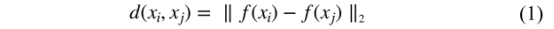
triplet loss为:
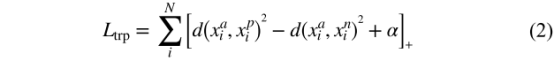
在HT loss中,有p和identity person,每个mini batch随机抽取K张图像,从而共有 PK个图像,The hardest positive sample和anchor 的欧式距离为max,the negative sample和anchor的欧氏距离为min,即选择the hardest triplet(三元组),从而HT loss:
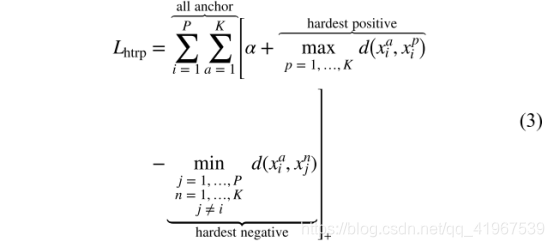
2.2HP loss:
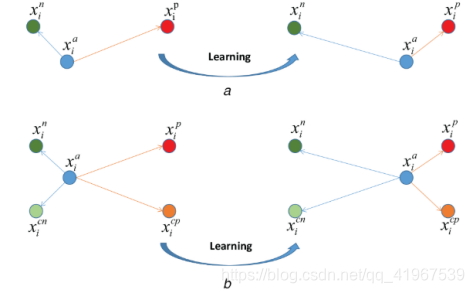
从上图可以看出,图a为HT loss,目的是最小化anchor xa和positive xp之间的距离,最大化anchor xa和negative xn之间的距离,图b为HP loss,既包含了HT loss的任务外,还加入了最小化cross-modality positive xcp和最大化cross-modality negative xcn,图a为选择the hardest triplet(三元组),图b为选择the hardest pentaplet (五元组)。
所以,HP loss包含两部分,原理同HT loss:
hard global triplet (HGT) loss:
a hard cross-modality triplet (HCT) loss:
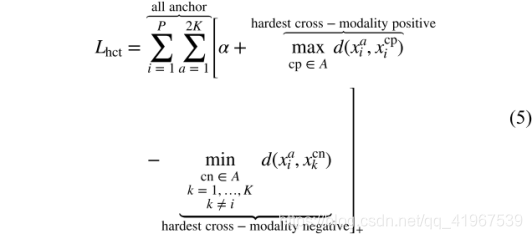
总loss,HP loss:
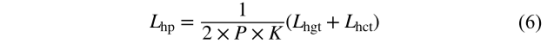
2.3HP with identity loss
HP loss作为本文的ranking loss,在本文中,同样identity loss采用的是softmax loss:
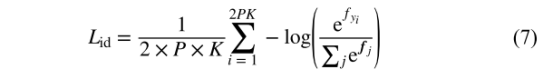
本文中总loss为:
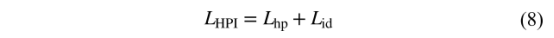
实验:
数据集:SYSU-MM01
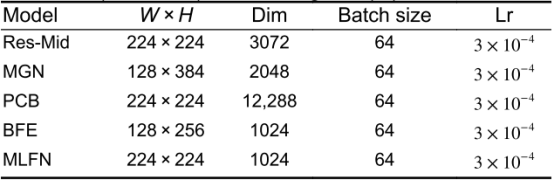
不同特征提取方法的训练参数:
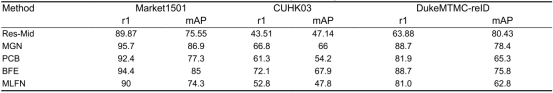
不同特征提取方法在Market1501, CUHK03, and DukeMTMC-reID数据集的比较:
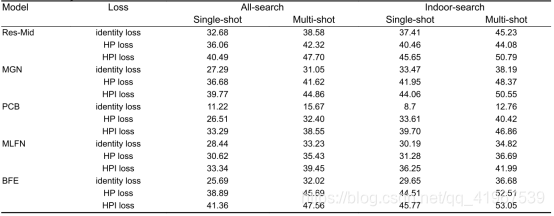
不同特征提取方法在SYSU-MM01数据集上的rank 1%的比较:
用CAM方法关注不同特征提取操作的attention:
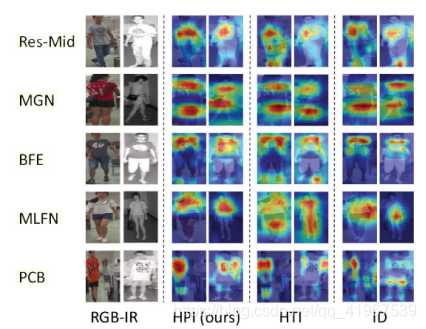
其中:
Res-Mid:The devil is in the middle: exploiting mid-level representations for cross-domain instance matching(2017)
MGN:Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification(2018)
PCB:Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline) (2018)
MLFN:Multi-level factorisation net for person re-identification(2018)
BFE :Batch feature erasing for person re- identification and beyond(2018)
不同现有的性能比较:
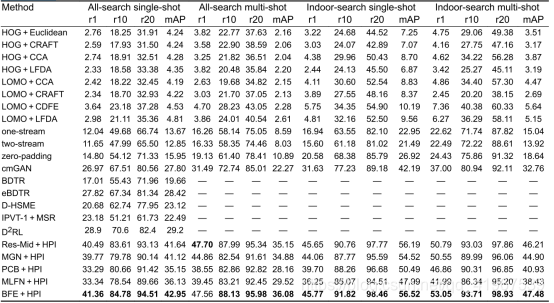
Cross-module ReID method:
zero-padding:RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification(2017)
cmGAN:Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training(2018)
bi-directional dual-constrained top-ranking (BDTR):Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking(2018)
inter-channel pair between the visible-lightand thermal images + multi-scale Retinex (IPVT-1 + MSR):Person re-identification between visible and thermal camera images based on deep residual CNN using single input(2019)
D2RL:Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification(2019)
bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking (eBDTR):‘Bi-directional center-constrained top- ranking for visible thermal person re-identification(2020)
D-hypersphere manifold embedding (HSME):HSME: hypersphere manifold embedding for visible thermal person re-identification(2019)
one-stream and two-stream networks:RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification(2017)
Other method:
handcrafted features such as Histograms of Oriented Gradient (HOG):Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection(2005)
and Local Maximal Occurrence (LOMO) :Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning(2015)
cross-domain models such as Common Discriminant Feature Extraction (CDFE) :Inter-modality face recognition(2006)
and Camera coRrelation Aware Feature augmenTation (CRAFT):Person re-identification by camera correlation aware feature augmentation(2018)
canonical correlation analysis (CCA) :A new approach to cross-modal multimedia retrieval(2010)
metric learning method Local Fisher Discriminant Analysis (LFDA):Local fisher discriminant analysis for pedestrian re-identification(2013)























 1813
1813











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








