Struts是一个为开发基于模型(Model)-视图(View)-控制器(Controller)(MVC)模式的应用架构的开源框架,是利用Java Servlet和JSP构建Web应用的一项非常有用的技术。由于Struts能充分满足应用开发的需求,简单易用,敏捷迅速,因而吸引了众多的开发人员的关注。在这个专题中我们介绍一些Struts的入门知识。
Struts开发指南之MVC架构
模型-视图-控制器(MVC)是80年代Smalltalk-80出现的一种软件设计模式,现在已经被广泛的使用。
1、模型(Model)
模型是应用程序的主体部分。模型表示业务数据,或者业务逻辑.
2、视图(View)
视图是应用程序中用户界面相关的部分,是用户看到并与之交互的界面。
3、控制器(controller)
控制器工作就是根据用户的输入,控制用户界面数据显示和更新model对象状态。
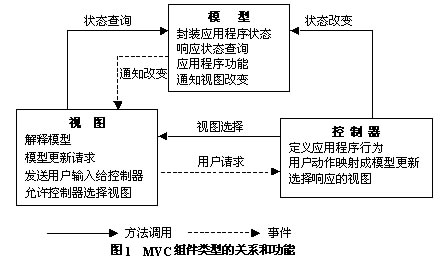
MVC 式的出现不仅实现了功能模块和显示模块的分离,同时它还提高了应用系统的可维护性、可扩展性、可移植性和组件的可复用性
早期的程序中,如果不注意对数功能和显示的解耦合,常常会导致程序的复杂及难以维护。很多VB,Delphi等RAD程序都有这种问题。甚至现在的C#,Java有时候也会出现把业务逻辑写在显示模块中的现象
管MVC设计模式很早就提出,但在Web项目的开发中引入MVC却是步履维艰。主要原因:一是在早期的Web项目的开发中,程序语言和HTML的分离一直难以实现。CGI程序以字符串输出的形式动态地生成HTML内容。后来随着脚本语言的出现,前面的方式又被倒了过来,改成将脚本语言书写的程序嵌入在HTML内容中。这两种方式有一个相同的不足之处即它们总是无法将程序语言和HTML分离。二是脚本语言的功能相对较弱,缺乏支持MVC设计模式的一些必要的技术基础。直到基于J2EE的JSP Model 2问世时才得以改观。它用JSP技术实现视图的功能,用Servlet技术实现控制器的功能,用JavaBean技术实现模型的功能
JSP Model 1 与 JSP Model 2
SUN在JSP出现早期制定了两种规范,称为Model1和Model2。虽然Model2在一定程度上实现了MVC,但是它的应用用并不尽如人意
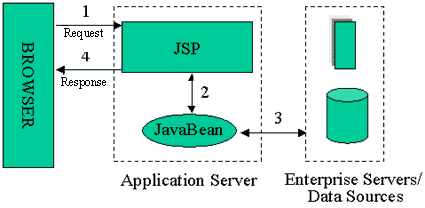
JSP Model 1
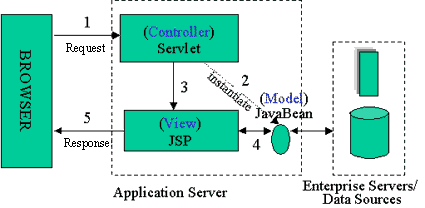
JSP Model 2
model2 容易使系统出现多个Controller,并且对页面导航的处理比较复杂
有些人觉得model2仍不够好,于是Craig R. McClanahan 2000年5月 提交了一个WEB framework给Java Community.这就是后来的Struts.
2001年7月,Struts1.0,正式发布。该项目也成为了Apache Jakarta的子项目之一
Struts 质上就是在Model2的基础上实现的一个MVC架构。它只有一个中心控制器,他采用XML定制转向的URL。采用Action来处理逻辑
Struts开发指南之安装与使用
Struts可以运行在任何一个支持JSP1.2和Servlet2.3的WEB Container中Struts将所有的请求提交到同一个中心控制器,org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet 类
web.xml配置
<servlet-name>action</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>config</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup>
<servlet-mapping>
一个标准的使用了Struts的URL样式如下:
扩展映射:http://www.my_site_name.com/mycontext/actionName.do
路径映射:http://www.my_site_name.com/mycontext/do/action_Name
| <servlet-name>action</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do或/do/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> |
Struts运行
Struts首先在Container启动的时候调用ActionServlet的init()方法。初始化各种配置。这些配置写在struts-config.xml文件中。
一个标准的struts-config文件包含如下结构:
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts-config PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 1.1//EN" "http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/dtds/struts-config_1_1.dtd"> <struts-config> <data-sources /> // 定义数据源 <form-beans /> // 定义ActionForm <global-exceptions /> // 定义全局异常 <global-forwards /> // 定义全局转向url <action-mappings /> // 定义action <controller /> // 配置Controller <message-resources /> // 配置资源文件 </struts-config> |
Struts由上述几部分组成。其中最主要的是Action和Form。下面简单叙述一下其处理过程。
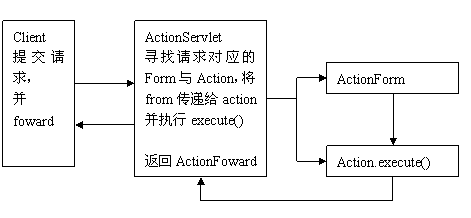
一个请求提交给ActionServlet,ActionServlet会寻找相应的Form和Action,首先将提交的request对象,映射到form中。,然后将form传递给action来进行处理。action得到form,对xml的mapping,request,response四个对象,并调用execute()方法然后返回一个forward-url(相应视图)给ActionServlet,最终返回给客户端。
我们来看一个最简单的实例
说明:实例一是最简单的Struts程序。它仅仅使用了1个form和1个action功能是将首页输入的值传递给action,经过判断后返回结果。如果是空则返回empty。代码如下:
input.jsp:
| <form method="post" action="/example.do"> 请输入值 <input type="text" name="test"/> <br><br> <input type="submit" name="Submit" > <input name="reset" type="reset" > </form> |
struts-config.xml:
| <struts-config> // 配置formbean <form-beans> <form-bean name="exampleActionForm" type="com.zotn.struts.example1.ExampleActionForm" /> </form-beans> // 配置action <action-mappings> <action name="exampleActionForm" path="/example" type="com.zotn.struts.example1.ExampleAction"> // action内部的foward <forward name="foward" path="/foward.jsp" /> </action> </action-mappings> </struts-config> |
Action:
| public class ExampleAction extends Action { public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping actionMapping, ActionForm actionForm, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { // 得到对应的form ExampleActionForm eaf = (ExampleActionForm)actionForm; // 取得输入的test String test = eaf.getTest(); // 判断并将值放入request if ("".equals(test)){ request.setAttribute("test","empty"); }else{ request.setAttribute("test",test); } // 通过mapping寻找相应的url,返回ActionFoward return actionMapping.findForward("foward"); } } |
FormBean:
| public class ExampleActionForm extends ActionForm { private String test; public String getTest() { return test; } public void setTest(String test) { this.test = test; } } |
Struts开发指南之J2EE n层结构
早期的网络系统设计常常采用三层结构。最常见的结构,就是表示( presentation )层 , 领域( domain )层 , 以及基础架构( infrastructure )层。
n层结构的提出是为了适应当前B/S模式开发WEB Application的需要而提出的。传统的Brown模型是指:表示层( Presentation ),控制 / 中介层( Controller/Mediator ),领域层( Domain ) , 数据映射层( Data Mapping ) , 和数据源层( Data Source )。它其实就是在三层架构中增加了两个中间层。控制 / 中介层位于表示层和领域层之间,数据映射层位于领域层和基础架构层之间。
J2EE规范提出了自己的n-tiers结构。
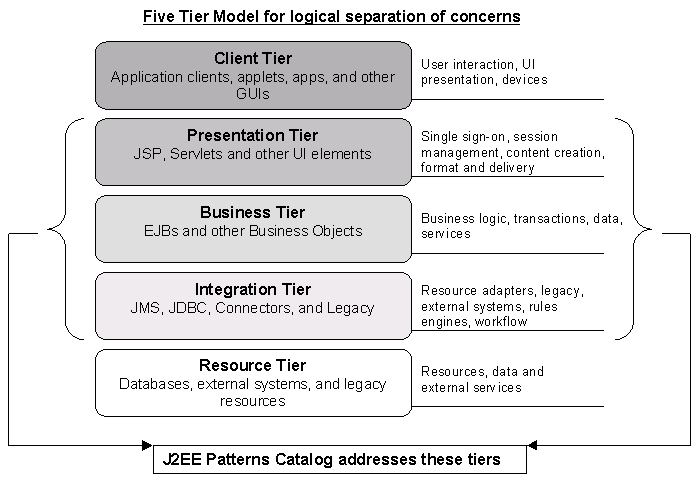
下表是几种模型的对照
| ISA | Brown | J2EE 层 | 对应程序部分 |
| 表示层 | 表示层 | 客户层 | 浏览器 HTML 页面, XSL, 手机客户端等 |
| 服务器表示层 | JSP 及 ActionForm ,XML | ||
| 控制/中介层 | Controller 控制器及 Action | ||
| 领域层 | 领域层 | 业务层 | Javabeans / SessionBean /Session Facade |
| 数据映射层 | 整合层 | EntityBean / JDO / Hibernate / JDBC | |
| 数据层 | 数据源层 | 资源层 | RDBMS 数据库 |
J2EE的基本原则之一,是使得各个层的实现解除耦合或耦合最小化。最终实现可以任意的切换某个层的实现。
例如,在数据映射层,可以采用EJB的BMP,CMP,也可以采用Hibernate等O/RMapping,或者采用JDO。这由部署的环境来决定。
Struts开发指南之工作流程
下图是Struts的工作流程,前边我们提到,所有的请求都提交给ActionServlet来处理。
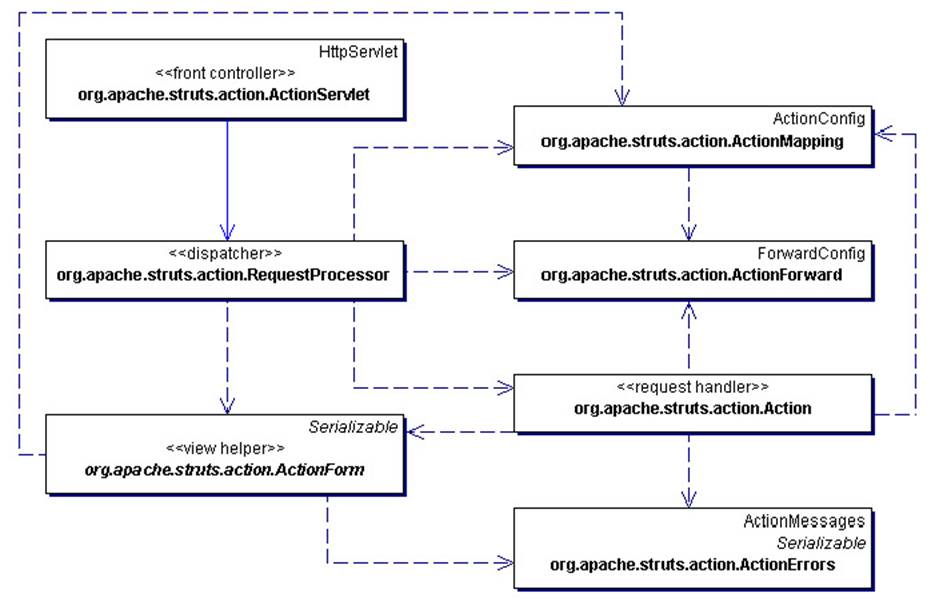
ActionServlet是一个FrontController,它是一个标准的Servlet,它将request转发给RequestProcessor来处理,
ActionMapping是ActionConfig的子类,实质上是对struts-config.xml的一个映射,从中可以取得所有的配置信息
RequestProcessor根据提交过来的url,如*.do,从ActionMapping 中得到相应的ActionForn和Action。然后将request的参数对应到ActionForm中,进行form验证。如果验证通过则调用Action的execute()方法来执行Action,最终返回ActionFoward。
ActionFoward是对mapping中一个foward的包装,对应于一个url
ActionForm使用了ViewHelper模式,是对HTML中form的一个封装。其中包含有validate方法,用于验证form数据的有效性。ActionForm是一个符合JavaBean规范的类,所有的属性都应满足get和set对应。对于一些复杂的系统,还可以采用DynaActionForm来构造动态的Form,即通过预制参数来生成Form。这样可以更灵活的扩展程序。
ActionErrors是对错误信息的包装,一旦在执行action或者form.validate中出现异常,即可产生一个ActionError并最终加入到ActionErrors。在Form验证的过程中,如果有Error发生,则会将页面重新导向至输入页,并提示错误。
Action是用于执行业务逻辑的RequsestHandler。每个Action都只建立一个instance。Action不是线程安全的,所以不应该在Action中访问特定资源。一般来说,应改使用 Business Delegate 模式来对Business tier进行访问以解除耦合。
Struts提供了多种Action供选择使用。普通的Action只能通过调用execute执行一项任务,而DispatchAction可以根据配置参数执行,而不是仅进入execute()函数,这样可以执行多种任务。如insert,update等。LookupDispatchAction可以根据提交表单按钮的名称来执行函数。
我们可以先回到刚才的例子,理解一下Struts的流程。
下面我们看Struts自带的example实例:
说明:实例二是Struts自带的example程序, 实现了登录,注册,修改功能。
代码中大量应用了struts taglib,并且采用validator插件进行form的验证。
但是代码树立了一个不好的榜样,即把大量的业务逻辑写在了action中。
部分代码如下:
登录:logon.jsp
| <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> // 声明Taglib <%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld" prefix="bean" %> <%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld" prefix="html" %> <html:html locale="true"> <head> // bean是用来从ApplicationResource中读取i18n信息 <title><bean:message key="logon.title"/></title> <html:base/> </head> <body bgcolor="white"> // 错误信息部分 <html:errors/> // 登录form,action为logion.do <html:form action="/logon" focus="username" οnsubmit="return validateLogonForm(this);"> <table border="0" width="100%"> <tr> <th align="right"> <bean:message key="prompt.username"/>: </th> <td align="left"> <html:text property="username" size="16" maxlength="18"/> </td> </tr> <tr> <th align="right"> <bean:message key="prompt.password" bundle="alternate"/>: </th> <td align="left"> <html:password property="password" size="16" maxlength="18" redisplay="false"/> </td> </tr> <tr> <td align="right"> <html:submit value="Submit"/> </td> <td align="left"> <html:reset/> </td> </tr> </table> </html:form> // Validator插件,用于form验证 <html:javascript formName="logonForm" dynamicJavascript="true" staticJavascript="false"/> <script language="Javascript1.1" src="staticJavascript.jsp"></script> </body> </html:html> |
struts-config.xml配置
| <form-beans> <!-- Logon form bean --> <form-bean name="logonForm" type="org.apache.struts.validator.DynaValidatorForm"> <form-property name="username" type="java.lang.String"/> <form-property name="password" type="java.lang.String"/> </form-bean> <!-- Subscription form bean --> <form-bean name="subscriptionForm"type="org.apache.struts.webapp.example.SubscriptionForm"/> </form-beans> <action-mappings> <!-- Edit mail subscription --> <action path="/editSubscription" type="org.apache.struts.webapp.example.EditSubscriptionAction" attribute="subscriptionForm" scope="request" validate="false"> <forward name="failure" path="/mainMenu.jsp"/> <forward name="success" path="/subscription.jsp"/> </action> ... |
subscriptionForm 是一个标准的ActionForm,其中reset方法用于清除form的值,validate方法用于验证
| public final class SubscriptionForm extends ActionForm { // The maintenance action we are performing (Create or Edit). private String action = "Create"; // Should we auto-connect at startup time? private boolean autoConnect = false; // The host name. private String host = null; private String password = null; private String type = null; private String username = null; public String getAction() { return (this.action); } public void setAction(String action) { this.action = action; } public boolean getAutoConnect() { return (this.autoConnect); } public void setAutoConnect(boolean autoConnect) { this.autoConnect = autoConnect; } public String getHost() { return (this.host); } public void setHost(String host) { this.host = host; } public String getPassword() { return (this.password); } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String getType() { return (this.type); } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public String getUsername() { return (this.username); } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } /** * Reset all properties to their default values. * * @param mapping The mapping used to select this instance * @param request The servlet request we are processing */ public void reset(ActionMapping mapping, HttpServletRequest request) { this.action = "Create"; this.autoConnect = false; this.host = null; this.password = null; this.type = null; this.username = null; } /** * Validate the properties that have been set from this HTTP request, * and return an <code>ActionErrors</code> object that encapsulates any * validation errors that have been found. If no errors are found, return * <code>null</code> or an <code>ActionErrors</code> object with no * recorded error messages. * * @param mapping The mapping used to select this instance * @param request The servlet request we are processing */ public ActionErrors validate(ActionMapping mapping, HttpServletRequest request) { ActionErrors errors = new ActionErrors(); if ((host == null) || (host.length() < 1)) errors.add("host", new ActionError("error.host.required")); if ((username == null) || (username.length() < 1)) errors.add("username", new ActionError("error.username.required")); if ((password == null) || (password.length() < 1)) errors.add("password", new ActionError("error.password.required")); if ((type == null) || (type.length() < 1)) errors.add("type", new ActionError("error.type.required")); else if (!"imap".equals(type) && !"pop3".equals(type)) errors.add("type",new ActionError("error.type.invalid", type)); return (errors); } } |
logonAction
| public final class LogonAction extends Action { /** * Process the specified HTTP request, and create the corresponding HTTP * response (or forward to another web component that will create it). * Return an <code>ActionForward</code> instance describing where and how * control should be forwarded, or <code>null</code> if the response has * already been completed. * * @param mapping The ActionMapping used to select this instance * @param form The optional ActionForm bean for this request (if any) * @param request The HTTP request we are processing * @param response The HTTP response we are creating * * @exception Exception if business logic throws an exception */ public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Extract attributes we will need Locale locale = getLocale(request); MessageResources messages = getResources(request); User user = null; // Validate the request parameters specified by the user ActionErrors errors = new ActionErrors(); String username = (String) PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(form, "username"); String password = (String) PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(form, "password"); UserDatabase database = (UserDatabase) servlet.getServletContext().getAttribute(Constants.DATABASE_KEY); if (database == null) errors.add(ActionErrors.GLOBAL_ERROR, new ActionError("error.database.missing")); else { user = getUser(database, username); if ((user != null) && !user.getPassword().equals(password)) user = null; if (user == null) errors.add(ActionErrors.GLOBAL_ERROR, new ActionError("error.password.mismatch")); } // Report any errors we have discovered back to the original form if (!errors.isEmpty()) { saveErrors(request, errors); return (mapping.getInputForward()); } // Save our logged-in user in the session HttpSession session = request.getSession(); session.setAttribute(Constants.USER_KEY, user); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("LogonAction: User '" + user.getUsername() + "' logged on in session " + session.getId()); } // Remove the obsolete form bean if (mapping.getAttribute() != null) { if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())) request.removeAttribute(mapping.getAttribute()); else session.removeAttribute(mapping.getAttribute()); } // Forward control to the specified success URI return (mapping.findForward("success")); } /** * Look up the user, throwing an exception to simulate business logic * rule exceptions. * * @param database Database in which to look up the user * @param username Username specified on the logon form * * @exception ModuleException if a business logic rule is violated */ public User getUser(UserDatabase database, String username) throws ModuleException { // Force an ArithmeticException which can be handled explicitly if ("arithmetic".equals(username)) { throw new ArithmeticException(); } // Force an application-specific exception which can be handled if ("expired".equals(username)) { throw new ExpiredPasswordException(username); } // Look up and return the specified user return ((User) database.findUser(username)); } } |





















 147
147











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








