大家先看看简单的应用程序截图,考虑一下如何实现。
截图如图一、图二、图三
图一 初始界面截图
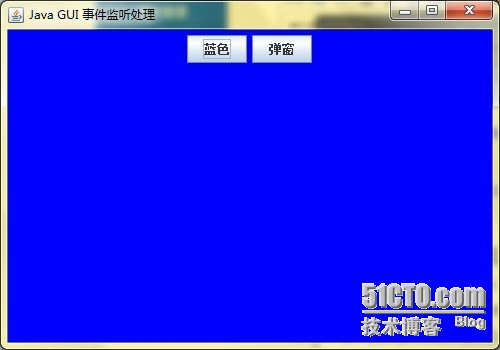
图二 蓝色按钮事件处理
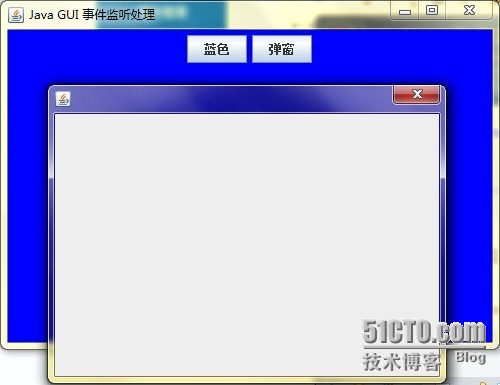
在此列举四种方法:
-
自身类实现ActionListener接口,作为事件监听器
-
通过匿名类处理
-
通过内部类处理
-
通过外部类处理
下面依次介绍:
第一种:自身类实现ActionListener接口,作为事件监听器。
这种方法是最基本的,也是初学者经常使用的,我当初即是如此。
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JDialog;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class EventListener1 extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
private JButton btBlue, btDialog;
/**
* Java事件监听处理——自身类实现ActionListener接口,作为事件监听器
*
* @author codebrother
*/
// 构造方法
public EventListener1() {
// 设置标题栏内容
setTitle("Java GUI 事件监听处理");
// 设置初始化窗口位置
setBounds(100, 100, 500, 350);
// 设置窗口布局
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
// 创建按钮对象
btBlue = new JButton("蓝色");
// 将按钮添加事件监听器
btBlue.addActionListener(this);
// 创建按钮对象
btDialog = new JButton("弹窗");
// 将按钮添加事件监听器
btDialog.addActionListener(this);
// 把按钮容器添加到JFrame容器上
add(btBlue);
add(btDialog);
// 设置窗口可视化
setVisible(true);
// 设置窗口关闭
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
// ***************************事件处理***************************
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 判断最初发生Event事件的对象
if (e.getSource() == btBlue) {
// 获得容器
Container c = getContentPane();
// 设置容器背景颜色
c.setColor.BLUE);
}
else if (e.getSource() == btDialog) {
// 创建JDialog窗口对象
JDialog dialog = new JDialog();
dialog.setBounds(300, 200, 400, 300);
dialog.setVisible(true);
}
}
// ***************************主方法***************************
public static void main(String[] args) {
new EventListener1();
}
}第二种,通过匿名类处理。
这是比较好的一种方法,我是在2011年开始使用这种方法的import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JDialog;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class EventListener2 extends JFrame {
private JButton btBlue, btDialog;
/**
* Java事件监听处理——匿名类处理
*
* @author codebrother
*/
// 构造方法
public EventListener2() {
// 设置标题栏内容
setTitle("Java GUI 事件监听处理");
// 设置初始化窗口位置
setBounds(100, 100, 500, 350);
// 设置窗口布局
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
// 创建按钮对象
btBlue = new JButton("蓝色");
// 添加事件监听器(此处即为匿名类)
btBlue.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
// 事件处理
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 获得容器,设置容器背景颜色
Container c = getContentPane();
c.setColor.BLUE);
}
});
// 创建按钮对象,并添加事件监听器
btDialog = new JButton("弹窗");
btDialog.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
// 事件处理
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 创建JDialog窗口对象
JDialog dialog = new JDialog();
dialog.setBounds(300, 200, 400, 300);
dialog.setVisible(true);
}
});
// 把按钮容器添加到JFrame容器上
add(btBlue);
add(btDialog);
// 设置窗口可视化
setVisible(true);
// 设置窗口关闭
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
// ***************************主方法***************************
public static void main(String[] args) {
new EventListener2();
}
}
第三种:通过内部类处理。
该种方法更符合面向对象编程的思想。
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JDialog;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class EventListener3 extends JFrame {
private JButton btBlue, btDialog;
/**
* Java事件监听处理——内部类处理
*
* @author codebrother
*/
// 构造方法
public EventListener3() {
// 设置标题栏内容
setTitle("Java GUI 事件监听处理");
// 设置初始化窗口位置
setBounds(100, 100, 500, 350);
// 设置窗口布局
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
// 创建按钮对象
btBlue = new JButton("蓝色");
// 添加事件监听器对象(面向对象思想)
btBlue.addActionListener(new ColorEventListener());
btDialog = new JButton("弹窗");
btDialog.addActionListener(new DialogEventListener());
// 把按钮容器添加到JFrame容器上
add(btBlue);
add(btDialog);
// 设置窗口可视化
setVisible(true);
// 设置窗口关闭
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
// 内部类ColorEventListener,实现ActionListener接口
class ColorEventListener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Container c = getContentPane();
c.setColor.BLUE);
}
}
// 内部类DialogEventListener,实现ActionListener接口
class DialogEventListener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 创建JDialog窗口对象
JDialog dialog = new JDialog();
dialog.setBounds(300, 200, 400, 300);
dialog.setVisible(true);
}
}
// ***************************主方法***************************
public static void main(String[] args) {
new EventListener3();
}
}第四种:通过外部类处理
这种我个人不常用import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JDialog;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class EventListener4 extends JFrame {
private JButton btBlue, btDialog;
/**
* Java事件监听处理——外部类处理
*
* @author codebrother
*/
// 构造方法
public EventListener4() {
// 设置标题栏内容
setTitle("Java GUI 事件监听处理");
// 设置初始化窗口位置
setBounds(100, 100, 500, 350);
// 设置窗口布局
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
// 创建按钮对象
btBlue = new JButton("蓝色");
// 将按钮添加事件监听器
btBlue.addActionListener(new ColorEventListener(this));
// 创建按钮对象
btDialog = new JButton("弹窗");
// 将按钮添加事件监听器
btDialog.addActionListener(new DialogEventListener());
// 把按钮容器添加到JFrame容器上
add(btBlue);
add(btDialog);
// 设置窗口可视化
setVisible(true);
// 设置窗口关闭
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
// ***************************主方法***************************
public static void main(String[] args) {
new EventListener4();
}
}
// 外部类ColorEventListener,实现ActionListener接口
class ColorEventListener implements ActionListener {
private EventListener4 el;
ColorEventListener(EventListener4 el) {
this.el = el;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Container c = el.getContentPane();
c.setColor.BLUE);
}
}
// 外部类DialogEventListener,实现ActionListener接口
class DialogEventListener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 创建JDialog窗口对象
JDialog dialog = new JDialog();
dialog.setBounds(300, 200, 400, 300);
dialog.setVisible(true);
}
}你可能注意到为什么我写了两个监听事件,就是加以区分这些方法的区别:
第一种的监听处理部分,如果有多个(我就写过三十多个的事件监听,包含菜单栏按钮事件监听和工具栏按钮事件监听),那就需要一个个去判断,从理论上说是影响程序速度的。
第二种和第三种比较常用,如果程序的监听事件比较少,可以用第二种,匿名类很合适。
第三种符合面向对象编程(可以设置内部类只提供自身类使用,而且方便使用自身类的资源),尤其是适合多个监听事件的处理,当然也适合第二种方法情况。
第四种是外部类,如果多个监听事件相同,就可以选用此种方法。
个人愚见:建议初学者掌握这四种方法,侧重于第二、三种。怎么学不重要,重要的是达到目的,使自己的GUI编程运用自如。多编程,多思考,提升编程思想;多看别人的代码,取其精华,有很大帮助!






















 847
847

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








