1、http://poj.org/problem?id=2559
2、题目大意:
给出n个矩形并排,给出他们的高度,求可以在此基础上找出一个面积最大且底边在基线上的矩形,输出最大面积
一开始用的区间DP,样例都过了,但发现dp[N][N]超内存了,看网上代码,居然是用结构体或两个一维数组表示的
3、题目:
Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 13118 | Accepted: 4238 |
Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
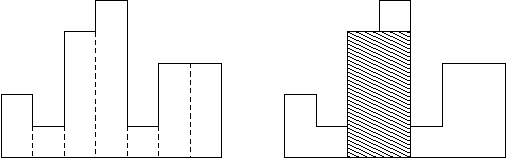
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.

Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer
n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that
1<=n<=100000. Then follow
n integers
h1,...,hn, where
0<=hi<=1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is
1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3 4 1000 1000 1000 1000 0
Sample Output
8 4000
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
Source
4、AC代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define N 100005
struct node
{
ll num;
ll left;
ll right;
} a[N];
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n==0)
break;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%lld",&a[i].num);
a[i].left=i;
a[i].right=i;
}
a[0].num=-1;
a[n+1].num=-1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
while(a[i].num<=a[a[i].left-1].num)
a[i].left=a[a[i].left-1].left;
}
for(int i=n; i>=1; i--)
{
while(a[i].num<=a[a[i].right+1].num)
a[i].right=a[a[i].right+1].right;
}
ll tmp=-1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(a[i].num*(a[i].right-a[i].left+1)>tmp)
tmp=a[i].num*(a[i].right-a[i].left+1);
}
printf("%lld\n",tmp);
}
return 0;
}区间DP做的,超内存的代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define N 100005
#define INF 1000000005
int a[N];
int dp[22005][22005];
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n==0)
break;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
dp[i][i]=a[i];
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j+i-1<=n;j++)
{
int s=j;
int e=j+i-1;
int minn=INF;
for(int k=s;k<=e;k++)
{
if(a[k]<minn)
minn=a[k];
}
dp[s][e]=max(dp[s][e],dp[s+1][e]);
dp[s][e]=max(dp[s][e],(e-s+1)*minn);
dp[s][e]=max(dp[s][e],dp[s][e-1]);
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[1][n]);
}
return 0;
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








