Android Boot loader 的 code 在 bootable/bootloader/lk 底下, LK 是 Little Kernel 的缩写, 是 andriod bootloader 的核心精神.
入口函数在 kernel/main.c 中的 kmain(), 以下就来读读这一段 code.
- void kmain( void )
- {
- // get us into some sort of thread context
- thread_init_early();
- // early arch stuff
- arch_early_init();
- // do any super early platform initialization
- platform_early_init();
- // do any super early target initialization
- target_early_init();
- dprintf(INFO, "welcome to lk/n/n" );
- // deal with any static constructors
- dprintf(SPEW, "calling constructors/n" );
- call_constructors();
- // bring up the kernel heap
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing heap/n" );
- heap_init();
- // initialize the threading system
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing threads/n" );
- thread_init();
- // initialize the dpc system
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing dpc/n" );
- dpc_init();
- // initialize kernel timers
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing timers/n" );
- timer_init();
- #if (!ENABLE_NANDWRITE)
- // create a thread to complete system initialization
- dprintf(SPEW, "creating bootstrap completion thread/n" );
- thread_resume(thread_create("bootstrap2" , &bootstrap2, NULL, DEFAULT_PRIORITY, DEFAULT_STACK_SIZE));
- // enable interrupts
- exit_critical_section();
- // become the idle thread
- thread_become_idle();
- #else
- bootstrap_nandwrite();
- #endif
- }
In include/debug.h: 我们可以看到 dprintf 的第一个参数是代表 debug level.
- /* debug levels */
- #define CRITICAL 0
- #define ALWAYS 0
- #define INFO 1
- #define SPEW 2
In include/debug.h:
- #define dprintf(level, x...) do { if ((level) <= DEBUGLEVEL) { _dprintf(x); } } while (0)
所以 dprintf 会依 DEBUGLEVEL 来判断是否输出信息.
来看第一个 call 的函数: thread_init_early, define in thread.c
- void thread_init_early( void )
- {
- int i;
- /* initialize the run queues */
- for (i=0; i < NUM_PRIORITIES; i++)
- list_initialize(&run_queue[i]);
- /* initialize the thread list */
- list_initialize(&thread_list);
- /* create a thread to cover the current running state */
- thread_t *t = &bootstrap_thread;
- init_thread_struct(t, "bootstrap" );
- /* half construct this thread, since we're already running */
- t->priority = HIGHEST_PRIORITY;
- t->state = THREAD_RUNNING;
- t->saved_critical_section_count = 1;
- list_add_head(&thread_list, &t->thread_list_node);
- current_thread = t;
- }
#define NUM_PRIORITIES 32 in include/kernel/thread.h
list_initialize() defined in include/list.h: initialized a list
- static inline void list_initialize( struct list_node *list)
- {
- list->prev = list->next = list;
- }
run_queue 是 static struct list_node run_queue[NUM_PRIORITIES]
thread_list 是 static struct list_node thread_list
再来要 call 的函数是: arch_early_init() defined in arch/arm/arch.c
- void arch_early_init( void )
- {
- /* turn off the cache */
- arch_disable_cache(UCACHE);
- /* set the vector base to our exception vectors so we dont need to double map at 0 */
- #if ARM_CPU_CORTEX_A8
- set_vector_base(MEMBASE);
- #endif
- #if ARM_WITH_MMU
- arm_mmu_init();
- platform_init_mmu_mappings();
- #endif
- /* turn the cache back on */
- arch_enable_cache(UCACHE);
- #if ARM_WITH_NEON
- /* enable cp10 and cp11 */
- uint32_t val;
- __asm__ volatile("mrc p15, 0, %0, c1, c0, 2" : "=r" (val));
- val |= (3<<22)|(3<<20);
- __asm__ volatile("mcr p15, 0, %0, c1, c0, 2" :: "r" (val));
- /* set enable bit in fpexc */
- val = (1<<30);
- __asm__ volatile("mcr p10, 7, %0, c8, c0, 0" :: "r" (val));
- #endif
- }
现代操作系统普遍采用虚拟内存管理(Virtual Memory Management)机制,这需要处理器中的MMU(Memory Management Unit,
内存管理单元)提供支持。
CPU执行单元发出的内存地址将被MMU截获,从CPU到MMU的地址称为虚拟地址(Virtual Address,以下简称VA),而MMU将这个地
址翻译成另一个地址发到CPU芯片的外部地址引脚上,也就是将VA映射成PA
MMU将VA映射到PA是以页(Page)为单位的,32位处 理器的页尺寸通常是4KB。例如,MMU可以通过一个映射项将VA的一页
0xb7001000~0xb7001fff映射到PA的一页0x2000~0x2fff,如果CPU执行单元要访问虚拟地址 0xb7001008,则实际访问到的物理地
址是0x2008。物理内存中的页称为物理页面或者页帧(Page Frame)。虚拟内存的哪个页面映射到物理内存的哪个页帧是通过页
表(Page Table)来描述的,页表保存在物理内存 中,MMU会查找页表来确定一个VA应该映射到什么PA。
操作系统和MMU是这样配合的:
1. 操作系统在初始化或分配、释放内存时会执行一些指令在物理内存中填写页表,然后用指令设置MMU,告诉MMU页表在物理内存中
的什么位置。
2. 设置好之后,CPU每次执行访问内存的指令都会自动引发MMU做查表和地址转换操作,地址转换操作由硬件自动完成,不需要用指令
控制MMU去做。
MMU除了做地址转换之外,还提供内存保护机制。各种体系结构都有用户模式(User Mode)和特权模式(Privileged Mode)之分,
操作系统可以在页表中设置每个内存页面的访问权限,有些页面不允许访问,有些页面只有在CPU处于特权模式时才允许访问,有些页面
在用户模式和特权模式都可以访问,访问权限又分为可读、可写和可执行三种。这样设定好之后,当CPU要访问一个VA时,MMU会检查
CPU当前处于用户模式还是特权模式,访问内存的目的是读数据、写数据还是取指令,如果和操作系统设定的页面权限相符,就允许访
问,把它转换成PA,否则不允许访问,产生一个异常(Exception)
常见的 segmentation fault 产生的原因:
用户程序要访问一段 VA, 经 MMU 检查后无权访问, MMU 会产生异常, CPU 从用户模式切换到特权模式, 跳转到内核代码中执行异常服务程序.
内核就会把这个异常解释为 segmentation fault, 将引发异常的程序终止.
简单的讲一下 NEON: NEON technology can accelerate multimedia and signal processing algorithms such as video encode/decode,
2D/3D graphics, gaming, audio and speech processing, image processing, telephony, and sound synthesis.
platform_early_init() defined in platform/<your-platform>/platform.c
- void platform_early_init( void )
- {
- uart_init();
- platform_init_interrupts();
- platform_init_timer();
- }
uart_init.c defined in platform/<your-platform>/uart.c 所有用到的变数,也都定义在 uart.c
- void uart_init( void )
- {
- uwr(0x0A, UART_CR); /* disable TX and RX */
- uwr(0x30, UART_CR); /* reset error status */
- uwr(0x10, UART_CR); /* reset receiver */
- uwr(0x20, UART_CR); /* reset transmitter */
- #if PLATFORM_QSD8K
- /* TCXO */
- uwr(0x06, UART_MREG);
- uwr(0xF1, UART_NREG);
- uwr(0x0F, UART_DREG);
- uwr(0x1A, UART_MNDREG);
- #else
- /* TCXO/4 */
- uwr(0xC0, UART_MREG);
- uwr(0xAF, UART_NREG);
- uwr(0x80, UART_DREG);
- uwr(0x19, UART_MNDREG);
- #endif
- uwr(0x10, UART_CR); /* reset RX */
- uwr(0x20, UART_CR); /* reset TX */
- uwr(0x30, UART_CR); /* reset error status */
- uwr(0x40, UART_CR); /* reset RX break */
- uwr(0x70, UART_CR); /* rest? */
- uwr(0xD0, UART_CR); /* reset */
- uwr(0x7BF, UART_IPR); /* stale timeout = 630 * bitrate */
- uwr(0, UART_IMR);
- uwr(115, UART_RFWR); /* RX watermark = 58 * 2 - 1 */
- uwr(10, UART_TFWR); /* TX watermark */
- uwr(0, UART_RFWR);
- uwr(UART_CSR_115200, UART_CSR);
- uwr(0, UART_IRDA);
- uwr(0x1E, UART_HCR);
- // uwr(0x7F4, UART_MR1); /* RFS/ CTS/ 500chr RFR */
- uwr(16, UART_MR1);
- uwr(0x34, UART_MR2); /* 8N1 */
- uwr(0x05, UART_CR); /* enable TX & RX */
- uart_ready = 1;
- }
platform_init_interrupts: defined in platform/msm8x60/interrupts.c
- void platform_init_interrupts( void )
- {
- platform_gic_dist_init();
- platform_gic_cpu_init();
- }
GIC 指的是 Generic Interrupt Controller. The gic-cpu and gic-dist are two subcomponents of GIC.
Devices are wired to the git-dist which is in charge of distributing interrupts to the gic-cpu (per cpu IRQ IF).
platform_init_timer(): defined in platform/<your-platform>/timer.c
- void platform_init_timer( void )
- {
- writel(0, DGT_ENABLE);
- }
DGT: Digital Game Timer: presents the countdowns of two players, it is also called chess timer or chess clock.
target_early_init(): defined in target/init.c
- /*
- * default implementations of these routines, if the target code
- * chooses not to implement.
- */
- __WEAK void target_early_init( void )
- {
- }
- __WEAK void target_init( void )
- {
- }
call_constructors() is defined in kernel/main.c:
- static void call_constructors( void )
- {
- void **ctor;
- ctor = &__ctor_list;
- while (ctor != &__ctor_end) {
- void (*func)( void );
- func = (void (*)())*ctor;
- func();
- ctor++;
- }
- }
heap_init is defined in lib/heap/heap.c:
- void heap_init( void )
- {
- LTRACE_ENTRY;
- // set the heap range
- theheap.base = ( void *)HEAP_START;
- theheap.len = HEAP_LEN;
- LTRACEF("base %p size %zd bytes/n" , theheap. base , theheap.len);
- // initialize the free list
- list_initialize(&theheap.free_list);
- // create an initial free chunk
- heap_insert_free_chunk(heap_create_free_chunk(theheap.base , theheap.len));
- // dump heap info
- // heap_dump();
- // dprintf(INFO, "running heap tests/n");
- // heap_test();
- }
thread_init is defined in kernel/thread.c but nothing coded, 先记下.
- void thread_init( void )
- {
- }
dpc_init() is defined in kernel/dpc.c:
- void dpc_init( void )
- {
- event_init(&dpc_event, false , 0);
- thread_resume(thread_create("dpc" , &dpc_thread_routine, NULL, DPC_PRIORITY, DEFAULT_STACK_SIZE));
- }
dpc 为 Delayed Procedure Call 延迟过程调用的缩写.
timer_init() is defined in kernel/timer.c:
- void timer_init( void )
- {
- list_initialize(&timer_queue);
- /* register for a periodic timer tick */
- platform_set_periodic_timer(timer_tick, NULL, 10); /* 10ms */
- }
执行 thread_resume 或是 bootstrap_nandwrite
- #if (!ENABLE_NANDWRITE)
- // create a thread to complete system initialization
- dprintf(SPEW, "creating bootstrap completion thread/n" );
- thread_resume(thread_create("bootstrap2" , &bootstrap2, NULL, DEFAULT_PRIORITY, DEFAULT_STACK_SIZE));
- // enable interrupts
- exit_critical_section();
- // become the idle thread
- thread_become_idle();
- #else
- bootstrap_nandwrite();
- #endif
In kermel/main.c:
- static int bootstrap2( void *arg)
- {
- dprintf(SPEW, "top of bootstrap2()/n" );
- arch_init();
- // initialize the rest of the platform
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing platform/n" );
- platform_init();
- // initialize the target
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing target/n" );
- target_init();
- dprintf(SPEW, "calling apps_init()/n" );
- apps_init();
- return 0;
- }
- #if (ENABLE_NANDWRITE)
- void bootstrap_nandwrite( void )
- {
- dprintf(SPEW, "top of bootstrap2()/n" );
- arch_init();
- // initialize the rest of the platform
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing platform/n" );
- platform_init();
- // initialize the target
- dprintf(SPEW, "initializing target/n" );
- target_init();
- dprintf(SPEW, "calling nandwrite_init()/n" );
- nandwrite_init();
- return 0;
- }
- #endif
continue to see apps_init(): app/app.c:void apps_init(void)
- #include <app.h>
- #include <kernel/thread.h>
- extern const struct app_descriptor __apps_start;
- extern const struct app_descriptor __apps_end;
- static void start_app( const struct app_descriptor *app);
- /* one time setup */
- void apps_init( void )
- {
- const struct app_descriptor *app;
- /* call all the init routines */
- for (app = &__apps_start; app != &__apps_end; app++) {
- if (app->init)
- app->init(app);
- }
- /* start any that want to start on boot */
- for (app = &__apps_start; app != &__apps_end; app++) {
- if (app->entry && (app->flags & APP_FLAG_DONT_START_ON_BOOT) == 0) {
- start_app(app);
- }
- }
- }
- static int app_thread_entry( void *arg)
- {
- const struct app_descriptor *app = ( const struct app_descriptor *)arg;
- app->entry(app, NULL);
- return 0;
- }
- static void start_app( const struct app_descriptor *app)
- {
- printf("starting app %s/n" , app->name);
- thread_resume(thread_create(app->name, &app_thread_entry, (void *)app, DEFAULT_PRIORITY, DEFAULT_STACK_SIZE));
- }
至于会有那些 app 被放入 boot thread section, 则定义在 include/app.h 中的 APP_START(appname)
- #define APP_START(appname) struct app_descriptor _app_##appname __SECTION(".apps") = { .name = #appname,
- #define APP_END };
在 app 中只要像 app/aboot/aboot.c 指定就会在 bootloader bootup 时放入 thread section 中被执行.
- APP_START(aboot)
- .init = aboot_init,
- APP_END
在我的 bootloader 中有 app/aboot/aboot.c, app/tests/tests.c, app/shell/shell.c, 及 app/stringtests/string_tests.c 皆有此声明.
接下来关注: aboot.c 中的 aboot_init()
- void aboot_init( const struct app_descriptor *app)
- {
- unsigned reboot_mode = 0;
- unsigned disp_init = 0;
- unsigned usb_init = 0;
- //test_ram();
- /* Setup page size information for nand/emmc reads */
- if (target_is_emmc_boot())
- {
- page_size = 2048;
- page_mask = page_size - 1;
- }
- else
- {
- page_size = flash_page_size();
- page_mask = page_size - 1;
- }
- /* Display splash screen if enabled */
- #if DISPLAY_SPLASH_SCREEN
- display_init();
- dprintf(INFO, "Diplay initialized/n" );
- disp_init = 1;
- diplay_image_on_screen();
- #endif
- /* Check if we should do something other than booting up */
- if (keys_get_state(KEY_HOME) != 0)
- boot_into_recovery = 1;
- if (keys_get_state(KEY_BACK) != 0)
- goto fastboot;
- if (keys_get_state(KEY_CLEAR) != 0)
- goto fastboot;
- #if NO_KEYPAD_DRIVER
- /* With no keypad implementation, check the status of USB connection. */
- /* If USB is connected then go into fastboot mode. */
- usb_init = 1;
- udc_init(&surf_udc_device);
- if (usb_cable_status())
- goto fastboot;
- #endif
- init_vol_key();
- if (voldown_press())
- goto fastboot;
- reboot_mode = check_reboot_mode();
- if (reboot_mode == RECOVERY_MODE) {
- boot_into_recovery = 1;
- } else if (reboot_mode == FASTBOOT_MODE) {
- goto fastboot;
- }
- if (target_is_emmc_boot())
- {
- boot_linux_from_mmc();
- }
- else
- {
- recovery_init();
- boot_linux_from_flash();
- }
- dprintf(CRITICAL, "ERROR: Could not do normal boot. Reverting "
- "to fastboot mode./n" );
- fastboot:
- if (!usb_init)
- udc_init(&surf_udc_device);
- fastboot_register("boot" , cmd_boot);
- if (target_is_emmc_boot())
- {
- fastboot_register("flash:" , cmd_flash_mmc);
- fastboot_register("erase:" , cmd_erase_mmc);
- }
- else
- {
- fastboot_register("flash:" , cmd_flash);
- fastboot_register("erase:" , cmd_erase);
- }
- fastboot_register("continue" , cmd_continue);
- fastboot_register("reboot" , cmd_reboot);
- fastboot_register("reboot-bootloader" , cmd_reboot_bootloader);
- fastboot_publish("product" , TARGET(BOARD));
- fastboot_publish("kernel" , "lk" );
- fastboot_init(target_get_scratch_address(), 120 * 1024 * 1024);
- udc_start();
- target_battery_charging_enable(1, 0);
- }
target_is_emmc_boot() is defined in target/init.c: _EMMC_BOOT 是 compiler 时的 flags
- __WEAK int target_is_emmc_boot( void )
- {
- #if _EMMC_BOOT
- return 1;
- #else
- return 0;
- #endif
- }
check_reboot_mode is defined in target/<your-platform>/init.c:
- unsigned check_reboot_mode( void )
- {
- unsigned restart_reason = 0;
- void *restart_reason_addr = 0x401FFFFC;
- /* Read reboot reason and scrub it */
- restart_reason = readl(restart_reason_addr);
- writel(0x00, restart_reason_addr);
- return restart_reason;
- }
reboot mode in bootloader:
- #define RECOVERY_MODE 0x77665502
- #define FASTBOOT_MODE 0x77665500
再来就会执行 boot_linux_from_mmc():
- int boot_linux_from_mmc( void )
- {
- struct boot_img_hdr *hdr = ( void *) buf;
- struct boot_img_hdr *uhdr;
- unsigned offset = 0;
- unsigned long long ptn = 0;
- unsigned n = 0;
- const char *cmdline;
- uhdr = (struct boot_img_hdr *)EMMC_BOOT_IMG_HEADER_ADDR;
- if (!memcmp(uhdr->magic, BOOT_MAGIC, BOOT_MAGIC_SIZE)) {
- dprintf(INFO, "Unified boot method!/n" );
- hdr = uhdr;
- goto unified_boot;
- }
- if (!boot_into_recovery)
- {
- ptn = mmc_ptn_offset("boot" );
- if (ptn == 0) {
- dprintf(CRITICAL, "ERROR: No boot partition found/n" );
- return -1;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- ptn = mmc_ptn_offset("recovery" );
- if (ptn == 0) {
- dprintf(CRITICAL, "ERROR: No recovery partition found/n" );
- return -1;
- }
- }
- if (mmc_read(ptn + offset, (unsigned int *)buf, page_size)) {
- dprintf(CRITICAL, "ERROR: Cannot read boot image header/n" );
- return -1;
- }
- if (memcmp(hdr->magic, BOOT_MAGIC, BOOT_MAGIC_SIZE)) {
- dprintf(CRITICAL, "ERROR: Invaled boot image header/n" );
- return -1;
- }
- if (hdr->page_size && (hdr->page_size != page_size)) {
- page_size = hdr->page_size;
- page_mask = page_size - 1;
- }
- offset += page_size;
- n = ROUND_TO_PAGE(hdr->kernel_size, page_mask);
- if (mmc_read(ptn + offset, ( void *)hdr->kernel_addr, n)) {
- dprintf(CRITICAL, "ERROR: Cannot read kernel image/n" );
- return -1;
- }
- offset += n;
- n = ROUND_TO_PAGE(hdr->ramdisk_size, page_mask);
- if (mmc_read(ptn + offset, ( void *)hdr->ramdisk_addr, n)) {
- dprintf(CRITICAL, "ERROR: Cannot read ramdisk image/n" );
- return -1;
- }
- offset += n;
- unified_boot:
- dprintf(INFO, "/nkernel @ %x (%d bytes)/n" , hdr->kernel_addr,
- hdr->kernel_size);
- dprintf(INFO, "ramdisk @ %x (%d bytes)/n" , hdr->ramdisk_addr,
- hdr->ramdisk_size);
- if (hdr->cmdline[0]) {
- cmdline = (char *) hdr->cmdline;
- } else {
- cmdline = DEFAULT_CMDLINE;
- }
- dprintf(INFO, "cmdline = '%s'/n" , cmdline);
- dprintf(INFO, "/nBooting Linux/n" );
- boot_linux((void *)hdr->kernel_addr, ( void *)TAGS_ADDR,
- (const char *)cmdline, board_machtype(),
- (void *)hdr->ramdisk_addr, hdr->ramdisk_size);
- return 0;
- }
mmc_read() is defined in platform/<your-platform>/mmc.c:
- unsigned int mmc_read (unsigned long long data_addr, unsigned int * out , unsigned int data_len)
- {
- int val = 0;
- val = mmc_boot_read_from_card( &mmc_host, &mmc_card, data_addr, data_len, out );
- return val;
- }
boot_linux(): 启动 Linux, 看看函数定义
- void boot_linux( void *kernel, unsigned *tags,
- const char *cmdline, unsigned machtype,
- void *ramdisk, unsigned ramdisk_size)
- {
- unsigned *ptr = tags;
- unsigned pcount = 0;
- void (*entry)(unsigned,unsigned,unsigned*) = kernel;
- struct ptable *ptable;
- int cmdline_len = 0;
- int have_cmdline = 0;
- int pause_at_bootup = 0;
- /* CORE */
- *ptr++ = 2;
- *ptr++ = 0x54410001;
- if (ramdisk_size) {
- *ptr++ = 4;
- *ptr++ = 0x54420005;
- *ptr++ = (unsigned)ramdisk;
- *ptr++ = ramdisk_size;
- }
- ptr = target_atag_mem(ptr);
- if (!target_is_emmc_boot()) {
- /* Skip NAND partition ATAGS for eMMC boot */
- if ((ptable = flash_get_ptable()) && (ptable->count != 0)) {
- int i;
- for (i=0; i < ptable->count; i++) {
- struct ptentry *ptn;
- ptn = ptable_get(ptable, i);
- if (ptn->type == TYPE_APPS_PARTITION)
- pcount++;
- }
- *ptr++ = 2 + (pcount * (sizeof ( struct atag_ptbl_entry) /
- sizeof (unsigned)));
- *ptr++ = 0x4d534d70;
- for (i = 0; i < ptable->count; ++i)
- ptentry_to_tag(&ptr, ptable_get(ptable, i));
- }
- }
- if (cmdline && cmdline[0]) {
- cmdline_len = strlen(cmdline);
- have_cmdline = 1;
- }
- if (target_is_emmc_boot()) {
- cmdline_len += strlen(emmc_cmdline);
- }
- if (target_pause_for_battery_charge()) {
- pause_at_bootup = 1;
- cmdline_len += strlen(battchg_pause);
- }
- if (cmdline_len > 0) {
- const char *src;
- char *dst;
- unsigned n;
- /* include terminating 0 and round up to a word multiple */
- n = (cmdline_len + 4) & (~3);
- *ptr++ = (n / 4) + 2;
- *ptr++ = 0x54410009;
- dst = (char *)ptr;
- if (have_cmdline) {
- src = cmdline;
- while ((*dst++ = *src++));
- }
- if (target_is_emmc_boot()) {
- src = emmc_cmdline;
- if (have_cmdline) --dst;
- have_cmdline = 1;
- while ((*dst++ = *src++));
- }
- if (pause_at_bootup) {
- src = battchg_pause;
- if (have_cmdline) --dst;
- while ((*dst++ = *src++));
- }
- ptr += (n / 4);
- }
- /* END */
- *ptr++ = 0;
- *ptr++ = 0;
- dprintf(INFO, "booting linux @ %p, ramdisk @ %p (%d)/n" ,
- kernel, ramdisk, ramdisk_size);
- if (cmdline)
- dprintf(INFO, "cmdline: %s/n" , cmdline);
- enter_critical_section();
- platform_uninit_timer();
- arch_disable_cache(UCACHE);
- arch_disable_mmu();
- #if DISPLAY_SPLASH_SCREEN
- display_shutdown();
- #endif
- entry(0, machtype, tags);
- }
配合 boot.img 来看会比较好理解.
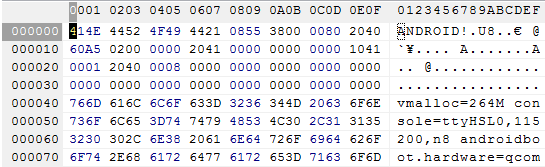
由此可知 boot_img_hdr 中 各成员值为:
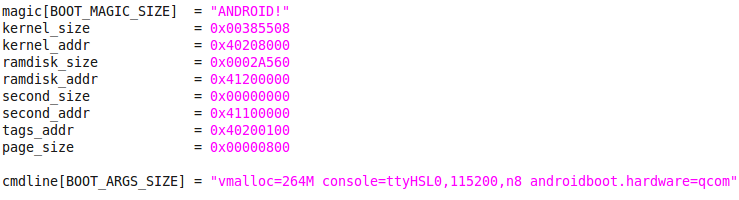

TAGS_ADDR 如上 target/<your-platform>/rules.mk 所定义的 : 0x40200100, 所 以 boot_linux(), 就是传入TAGS_ADDR,
然后将资料写入 tag, tag 的结构如下所示.
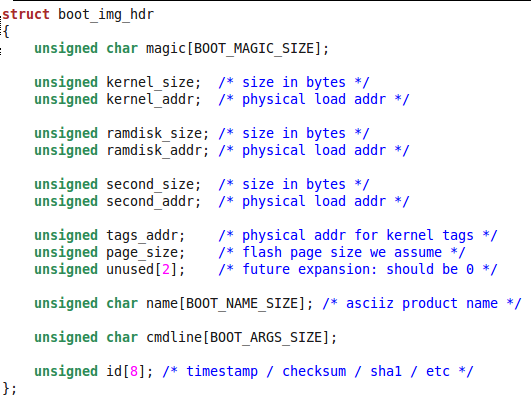
然后进入到 kernel 的入口函数: entry(0, machtype, tags)























 329
329











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








