Android系统源码阅读(14):Zygote和System进程的启动
再不学习我们就老了
0. Zygote有什么卵用?
Zygote是进程孵化器,Android系统中其他服务进程都是拷贝于它。Zygote在设计模式中对应于prototype,这样做的好处是可以通过拷贝Zygote来快速创建一个进程。
1. Zygote脚本启动
在开机时,init进程会调用如下脚本启动进程。
system/core/rootdir/init.zygote32_64.rc :
service zygote /system/bin/app_process32 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasksservice表明该进程是作为一个服务来启动的,--start-system-server指明了该进程启动后,需要启动system服务。该进程对应的端口权限660,名字为zygote,其它进程可以通过该端口和它进行通信。
1.1 init进程创建新的app_process
在init进程中,启动service进程的过程如下。
system/core/init/init.cpp :
void service_start(struct service *svc, const char *dynamic_args)
//...
NOTICE("Starting service '%s'...\n", svc->name);
//创建新进程
pid_t pid = fork();
//在新建的进程中
if (pid == 0) {
struct socketinfo *si;
struct svcenvinfo *ei;
char tmp[32];
int fd, sz;
//依次创建service中的socket
for (si = svc->sockets; si; si = si->next) {
int socket_type = (
!strcmp(si->type, "stream") ? SOCK_STREAM :
(!strcmp(si->type, "dgram") ? SOCK_DGRAM : SOCK_SEQPACKET));
//创建socket
int s = create_socket(si->name, socket_type,
si->perm, si->uid, si->gid, si->socketcon ?: scon);
if (s >= 0) {
//发布socket
publish_socket(si->name, s);
}
}
//...
//将参数拷贝进svc结构体中
if (!dynamic_args) {
//没有参数的情况
//svc->args[0]对应于/system/bin/app_process32
//下一步会加载该程序,并且传入参数
if (execve(svc->args[0], (char**) svc->args, (char**) ENV) < 0) {
ERROR("cannot execve('%s'): %s\n", svc->args[0], strerror(errno));
}
} else {
char *arg_ptrs[INIT_PARSER_MAXARGS+1];
int arg_idx = svc->nargs;
char *tmp = strdup(dynamic_args);
char *next = tmp;
char *bword;
/* Copy the static arguments */
memcpy(arg_ptrs, svc->args, (svc->nargs * sizeof(char *)));
while((bword = strsep(&next, " "))) {
arg_ptrs[arg_idx++] = bword;
if (arg_idx == INIT_PARSER_MAXARGS)
break;
}
arg_ptrs[arg_idx] = NULL;
execve(svc->args[0], (char**) arg_ptrs, (char**) ENV);
}
_exit(127);
}
//...
}1.2 socket创建和发布
下面主要分析一下create_socket和publish_socket两个函数,来说明zygote的socket如何创建的。
创建socket。
system/core/init/util.cpp :
/*
* create_socket - creates a Unix domain socket in ANDROID_SOCKET_DIR
* ("/dev/socket") as dictated in init.rc. This socket is inherited by the
* daemon. We communicate the file descriptor's value via the environment
* variable ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV_PREFIX<name> ("ANDROID_SOCKET_foo").
*/
int create_socket(const char *name, int type, mode_t perm, uid_t uid,
gid_t gid, const char *socketcon)
{
struct sockaddr_un addr;
int fd, ret;
char *filecon;
if (socketcon)
setsockcreatecon(socketcon);
//创建一个socket
fd = socket(PF_UNIX, type, 0);
if (fd < 0) {
ERROR("Failed to open socket '%s': %s\n", name, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if (socketcon)
setsockcreatecon(NULL);
//创建一个socket地址addr
memset(&addr, 0 , sizeof(addr));
addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
//设置地址的文件位置,这里就是/dev/socket/zygote
snprintf(addr.sun_path, sizeof(addr.sun_path), ANDROID_SOCKET_DIR"/%s",
name);
ret = unlink(addr.sun_path);
if (ret != 0 && errno != ENOENT) {
ERROR("Failed to unlink old socket '%s': %s\n", name, strerror(errno));
goto out_close;
}
filecon = NULL;
if (sehandle) {
ret = selabel_lookup(sehandle, &filecon, addr.sun_path, S_IFSOCK);
if (ret == 0)
setfscreatecon(filecon);
}
//将想要存储socket的文件地址addr和socket文件描述符fd绑定起来
ret = bind(fd, (struct sockaddr *) &addr, sizeof (addr));
if (ret) {
ERROR("Failed to bind socket '%s': %s\n", name, strerror(errno));
goto out_unlink;
}
setfscreatecon(NULL);
freecon(filecon);
//设置用户组root system
chown(addr.sun_path, uid, gid);
//设置权限660
chmod(addr.sun_path, perm);
INFO("Created socket '%s' with mode '%o', user '%d', group '%d'\n",
addr.sun_path, perm, uid, gid);
return fd;
out_unlink:
unlink(addr.sun_path);
out_close:
close(fd);
return -1;
}发布socket。
static void publish_socket(const char *name, int fd)
{
//前缀为ANDROID_SOCKET_
char key[64] = ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV_PREFIX;
char val[64];
//拼接出key
strlcpy(key + sizeof(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV_PREFIX) - 1,
name,
sizeof(key) - sizeof(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV_PREFIX));
//将fd写入val
snprintf(val, sizeof(val), "%d", fd);
//将key,value写入环境变量中,以便其他进程访问
add_environment(key, val);
/* make sure we don't close-on-exec */
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, 0);
}2. Zygote进程启动过程
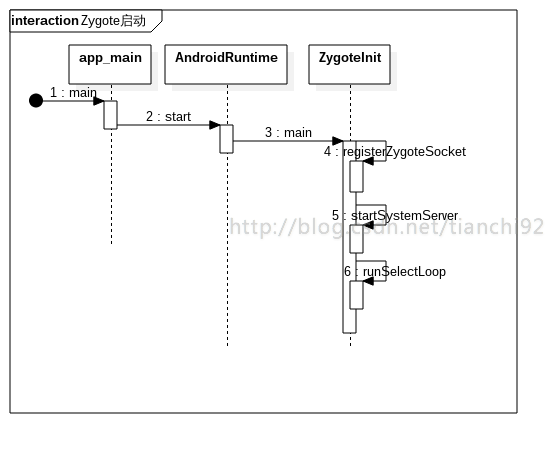
Zygote 进程的启动从app_process的main函数开始。
2.1 app_process.main
判断需要启动的进程的种类。
frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp :
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
//针对旧内核做的处理...
//创建AppRuntime对象
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
// Everything up to '--' or first non '-' arg goes to the vm.
//
// The first argument after the VM args is the "parent dir", which
// is currently unused.
//
// After the parent dir, we expect one or more the following internal
// arguments :
// 不同的进程类型
// --zygote : Start in zygote mode
// --start-system-server : Start the system server.
// --application : Start in application (stand alone, non zygote) mode.
// --nice-name : The nice name for this process.
//
// For non zygote starts, these arguments will be followed by
// the main class name. All remaining arguments are passed to
// the main method of this class.
//
// For zygote starts, all remaining arguments are passed to the zygote.
// main function.
//
// Note that we must copy argument string values since we will rewrite the
// entire argument block when we apply the nice name to argv0.
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
if (argv[i][0] != '-') {
break;
}
if (argv[i][1] == '-' && argv[i][2] == 0) {
++i; // Skip --.
break;
}
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
}
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
//判断需要创建何种类型的进程
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
//这里是Zygote进程
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
//同时需要开启SystemServer
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
Vector<String8> args;
if (!className.isEmpty()) {
// We're not in zygote mode, the only argument we need to pass
// to RuntimeInit is the application argument.
//
// The Remainder of args get passed to startup class main(). Make
// copies of them before we overwrite them with the process name.
args.add(application ? String8("application") : String8("tool"));
runtime.setClassNameAndArgs(className, argc - i, argv + i);
} else {
// We're in zygote mode.
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
if (startSystemServer) {
//作为参数传递给Zygote进程
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
//...
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
}
}
if (!niceName.isEmpty()) {
//这里进程名字就是zygote
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string());
set_process_name(niceName.string());
}
if (zygote) {
//启动Zygote,接下来会主要分析start函数
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
}
}2.2 AndroidRuntime.start
创建虚拟机,运行java函数。
frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp :
/*
* Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine
* and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class
* named by "className".
*
* Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
* options string.
*/
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
//创建一个虚拟机实例
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
//注册JNI方法
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* 将参数转化为java对象
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
//找到main函数
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
//调用com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit类的main函数
//参数放在strArray里
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}2.3 ZygoteInit.main
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygoteinit.java :
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
//解析参数
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
//注册Socket,创建一个socket服务端
registerZygoteSocket(socketName);
//...
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gcAndFinalize();
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);
if (startSystemServer) {
//启动系统服务
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
//循环等待其他服务向zygote socket发送请求
runSelectLoop(abiList);
closeServerSocket();
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}2.4 ZygoteInit.registerZygoteSocket
创建了zygote socket的server端。
/**
* Registers a server socket for zygote command connections
*
* @throws RuntimeException when open fails
*/
private static void registerZygoteSocket(String socketName) {
if (sServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
//拼接出socket名称ANDROID_SOCKET_zygote
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName;
try {
//环境变量中在上面存储了该key下对应的value
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);
//获取socket的文件描述符
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(fullSocketName + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
//创建socket server,并且保留在一个静态变量sServerSocket中
sServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}2.5 ZygoteInit.startSystemServer
从zygote中fork一个新的进程来单独处理system server。
/**
* Prepare the arguments and fork for the system server process.
*/
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName)
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
//...
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer", //这就是System server的类名
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
//从zygote中fork出一个进程
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
//在子进程中启动System server,在第3节中详细分析
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
//父进程返回
return true;
}2.6 ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop
Zygote启动无限循环,等待请求。
/**
* Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as
* they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's
* worth at a time.
*
* @throws MethodAndArgsCaller in a child process when a main() should
* be executed.
*/
private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
//一个zygote socket文件描述符
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true) {
//将现有的fd先存入pollFds
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
//一次循环最多让一个peer接入,但是可能会处理多个peer的请求
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
//是否有请求写入,没有就继续
continue;
}
if (i == 0) {
//有人在zygote上写入请求,获得该peer
//这一步只是peer和zygote建立连接,peer还未发送具体请求
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
//将其加入文件描述符fds中,该peer会向其对应的fd写入请求
//这一步不会处理,因为该peer没有在pollFds中
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
//有peer向其fd写入请求,这里开始处理这个请求,处理完毕后删除
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce();
if (done) {
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}3. System进程的启动
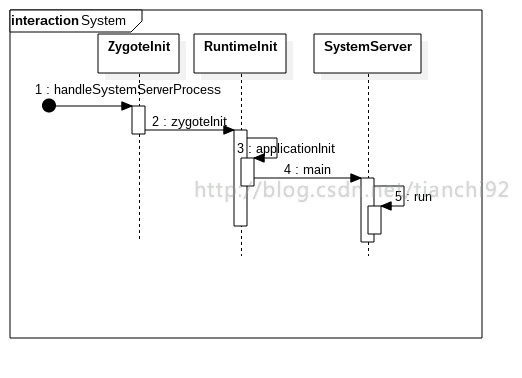
接着2.5,Zygote fork出一个新的进程来启动System server。接下来看在这个新进程中如何启动的System server。
3.1 ZygoteInit.handleSystemServerProcess
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java :
/**
* Finish remaining work for the newly forked system server process.
*/
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
//因为fork了Zygote的进程,所以会复制它的socket
//SystemServer用不着这个socket,先关了再说
closeServerSocket();
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
//设置进程名
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
//获取system server类的路径
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);
}
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
String[] args = parsedArgs.remainingArgs;
// If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
// existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
// correctly when we exec a new process.
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
System.arraycopy(parsedArgs.remainingArgs, 0, amendedArgs, 2, parsedArgs.remainingArgs.length);
}
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
} else {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
cl = new PathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* 进一步启动System server
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}3.2 RuntimeInit.zygoteInit
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java :
/**
* The main function called when started through the zygote process. This
* could be unified with main(), if the native code in nativeFinishInit()
* were rationalized with Zygote startup.<p>
*
* Current recognized args:
* <ul>
* <li> <code> [--] <start class name> <args>
* </ul>
*
* @param targetSdkVersion target SDK version
* @param argv arg strings
*/
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "RuntimeInit");
redirectLogStreams();
//做一些基本的初始化,比如时间、log等
commonInit();
//进入native部分,将来章节再讲
nativeZygoteInit();
//进一步启动system
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}3.3 RuntimeInit.applicationInit
这一步开始调用SystemServer的main函数。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java :
private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid
// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
final Arguments args;
try {
args = new Arguments(argv);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
Slog.e(TAG, ex.getMessage());
// let the process exit
return;
}
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
//启动需要启动的类的main函数,这里就是com.android.server.SystemServer
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}3.4 SystemServer.main
这里直接new了一个SystemServer,然后调用它的run函数。
3.5 SystemService.run
这一步开始依次启动各种service。
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java :
private void run() {
//...
//设置系统时间、语言等
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
//...
//一些虚拟机内存,堆栈的设置
//该线程就是主线程
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
//...
//创建SystemServiceManager
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Start services.
try {
//开始依次启动各种服务,下一节详细解释
startBootstrapServices();
startCoreServices();
startOtherServices();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//...
}
//永远的循环..
// Loop forever.
Looper.loop();
}3.6 各种service启动
startBootstrapServices
这里面启动的服务有:Installer,ActivityManagerService,PowerManagerService,LightsService,DisplayManagerService,PackageManagerService,SensorService(非具体)。
这些service有的会创建自己独立的ServiceThread,是HandlerThread的子类,它们有着自己的looper循环。startService函数将所有的service的启动过程统一管理,抽象为注册、启动两步骤。
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java :
/**
* Starts the small tangle of critical services that are needed to get
* the system off the ground. These services have complex mutual dependencies
* which is why we initialize them all in one place here. Unless your service
* is also entwined in these dependencies, it should be initialized in one of
* the other functions.
*/
private void startBootstrapServices() {
// Wait for installd to finish starting up so that it has a chance to
// create critical directories such as /data/user with the appropriate
// permissions. We need this to complete before we initialize other services.
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
// Activity manager runs the show.
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
// Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it.
// Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready
// to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify
// the permissions for those calls).
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
// Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager
// initialize power management features.
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
// Manages LEDs and display backlight so we need it to bring up the display.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
// Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager
// starts up.
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
// We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager.
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
// Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt");
if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
} else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
}
// Start the package manager.
Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
Slog.i(TAG, "User Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.USER_SERVICE, UserManagerService.getInstance());
// Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
// Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
// The sensor service needs access to package manager service, app ops
// service, and permissions service, therefore we start it after them.
startSensorService();
}startCoreServices
这一步启动的serivce有:BatteryService,UsageStatsService,WebViewUpdateService。
/**
* Starts some essential services that are not tangled up in the bootstrap process.
*/
private void startCoreServices() {
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
// Tracks application usage stats.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
// Update after UsageStatsService is available, needed before performBootDexOpt.
mPackageManagerService.getUsageStatsIfNoPackageUsageInfo();
// Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
}startOtherService
这一步启动service又多又杂,主要有如下这些,其它还有不再一一列举。
AccountManagerService accountManager = null;
ContentService contentService = null;
VibratorService vibrator = null;
IAlarmManager alarm = null;
IMountService mountService = null;
NetworkManagementService networkManagement = null;
NetworkStatsService networkStats = null;
NetworkPolicyManagerService networkPolicy = null;
ConnectivityService connectivity = null;
NetworkScoreService networkScore = null;
NsdService serviceDiscovery= null;
WindowManagerService wm = null;
UsbService usb = null;
SerialService serial = null;
NetworkTimeUpdateService networkTimeUpdater = null;
CommonTimeManagementService commonTimeMgmtService = null;
InputManagerService inputManager = null;
TelephonyRegistry telephonyRegistry = null;
ConsumerIrService consumerIr = null;
AudioService audioService = null;
MmsServiceBroker mmsService = null;
EntropyMixer entropyMixer = null;
CameraService cameraService = null;4. 总结
写到这里,有点凌乱,太多的进程和线程在这一过程中被创建。我用下图来梳理这部分进程之间的关系,希望让你一目了然吧。










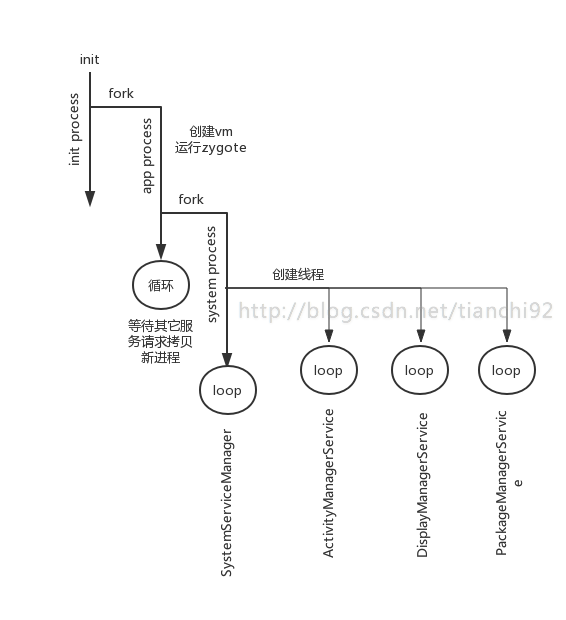













 432
432











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








