tensorflow官方教程: 卷积神经网络CNN在数据集CIFAR-10上分类
本文主要包含如下内容:
本篇博客来自原始英文教程原始教程,你可以参照原始教程以及本篇博客进行学习。
官方原始教程中首先介绍了CIFAR-10 数据集,然后介绍了卷积神经网络模型的搭建,随后进行训练和测试网络。若不清楚的你可以自行阅读原文,这里,我们之间进入重点,讲解官方提供的相关代码。
训练测试代码
官方教程提供了 CIFAR-10 数据集以及相关训练测试代码,代码位于 models/tutorials/image/cifar10/ 中。其中包含以下文件:
cifar10_input.py 读取本地CIFAR-10二进制文件格式。
cifar10.py 构建CIFAR-10模型。
cifar10_train.py 在CPU或GPU上训练CIFAR-10模型。
cifar10_multi_gpu_train.py 在多个GPU上训练CIFAR-10模型。
cifar10_eval.py 评估CIFAR-10模型的预测性能。
其中,网络主要包含在cifar10.py中,包含模型输入、模型训练和模型预测。
针对模型输入:代码编写了 inputs() 和 distorted_inputs() 两个函数,实现了图像数据的读取和预处理操作:对数据进行了DataAugmentation(数据增强),包括了随机的水平翻转、随机剪切一块24*24的图片、设置随机的亮度和对比度以及对数据进行标准化。通过这些操作,我们可以获得更多的带噪声的样本,扩大了样本容量,对提高准确率有所帮助。具体代码见 cifar10_input.py。
针对模型预测:代码编写了前馈网络,网络结构如下表所示:
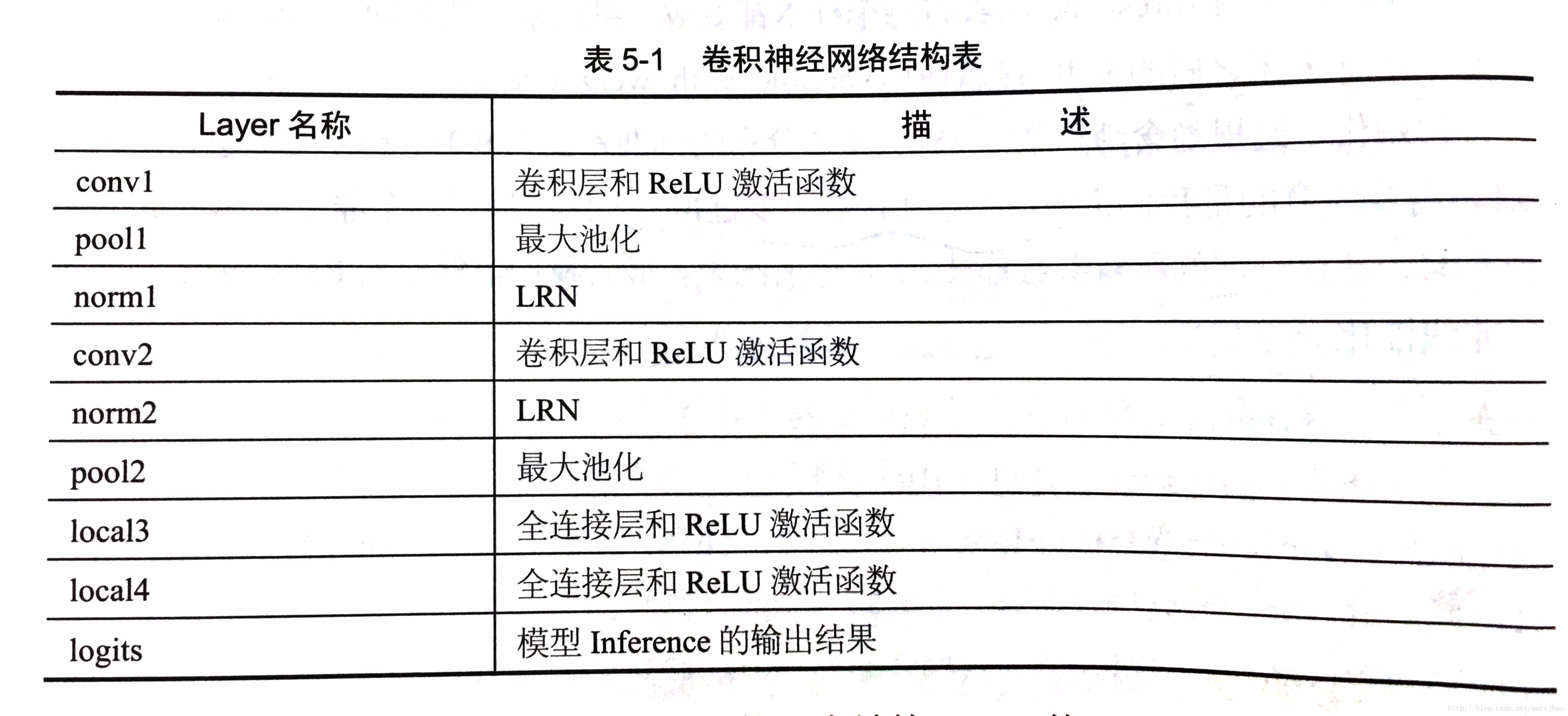
针对模型的训练:代码中定义了损失函数,运用了交叉熵损失,并且定义优化器,定义计算Top K 准确率操作。
在模型和相关训练测试代码编写完成后,我们运行相关代码,实现训练和测试:
python cifar10_train.py
python cifar10_eval.py 自拟训练代码
为了进一步学习tensorflow,我们自拟代码,实现网络的训练,可以参考博客,并结合本篇论文进行学习。
#coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import time
import cifar10,cifar10_input
max_steps = 1000000 # 最大迭代轮数
batch_size = 128 # 批大小
data_dir = '/tmp/cifar10_data/cifar-10-batches-bin' # 数据所在路径
## 初始化 weight 函数
def _variable_with_weight_decay(shape, stddev, wd):
var = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=stddev))
if wd is not None:
weight_decay = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), wd, name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', weight_decay)
return var
## 下载数据库cifar10至'/tmp/cifar10_data'
cifar10.maybe_download_and_extract()
## 进行数据增强,读取图像数据和标签
images_train, labels_train = cifar10_input.distorted_inputs(data_dir=data_dir, batch_size=batch_size)
# 裁剪图片正中间的24*24大小的区块并进行数据标准化操作
images_test, labels_test = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data=True, data_dir=data_dir, batch_size=batch_size)
# 定义placeholder
# 注意此处输入尺寸的第一个值应该是batch_size而不是None
image_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 24, 24, 3])
label_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size])
## 定义网络
## 卷积层1
weight1 = _variable_with_weight_decay(shape=[5, 5, 3, 64],stddev=5e-2,wd=0.0)
kernel1 = tf.nn.conv2d(image_holder, weight1, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
bias1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64]))
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(kernel1, bias1))
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],padding='SAME')
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75)
# 卷积层2
weight2 = _variable_with_weight_decay([5, 5, 64, 64], stddev=5e-2, wd=0.0)
kernel2 = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weight2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
bias2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(kernel2, bias2))
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75)
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# 全连接层3
reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, [batch_size, -1]) # 将每个样本reshape为一维向量
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value # 取每个样本的长度
weight3 = _variable_with_weight_decay([dim, 384], stddev=0.04, wd=0.004)
bias3 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[384]))
local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weight3) + bias3)
# 全连接层4
weight4 = _variable_with_weight_decay([384, 192], stddev=0.04, wd=0.004)
bias4 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[192]))
local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weight4) + bias4)
# 全连接层5
weight5 = _variable_with_weight_decay([192, 10],stddev=1/192.0, wd=0.0)
bias5 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[10]))
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weight5), bias5)
# 定义损失函数loss
def loss(logits, labels):
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.int64)
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels, logits=logits, name='cross_entropy_per_example')
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='cross_entropy')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', cross_entropy_mean)
return tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'), name='total_loss')
# 定义loss
loss = loss(logits, label_holder)
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-3).minimize(loss) # 定义优化器
top_k_op = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, label_holder, 1)
# 定义会话并开始迭代训练
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
# 启动图片数据增强的线程队列
tf.train.start_queue_runners()
# 迭代训练
for step in range(max_steps):
start_time = time.time()
image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_train, labels_train]) # 获取训练数据
_, loss_value = sess.run([train_op, loss],feed_dict={image_holder: image_batch,label_holder: label_batch})
duration = time.time() - start_time # 计算每次迭代需要的时间
if step % 10 == 0:
examples_per_sec = batch_size / duration # 每秒处理的样本数
sec_per_batch = float(duration) # 每批需要的时间
format_str = ('step %d, loss=%.2f (%.1f examples/sec; %.3f sec/batch)')
print(format_str % (step, loss_value, examples_per_sec, sec_per_batch))
# 在测试集上测评准确率
num_examples = 10000
import math
num_iter = int(math.ceil(num_examples / batch_size))
true_count = 0
total_sample_count = num_iter * batch_size
step = 0
while step < num_iter:
image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_test, labels_test])
predictions = sess.run([top_k_op],feed_dict={image_holder: image_batch,label_holder: label_batch})
true_count += np.sum(predictions)
step += 1
precision = true_count / total_sample_count
print('precision @ 1 =%.3f' % precision)




















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








