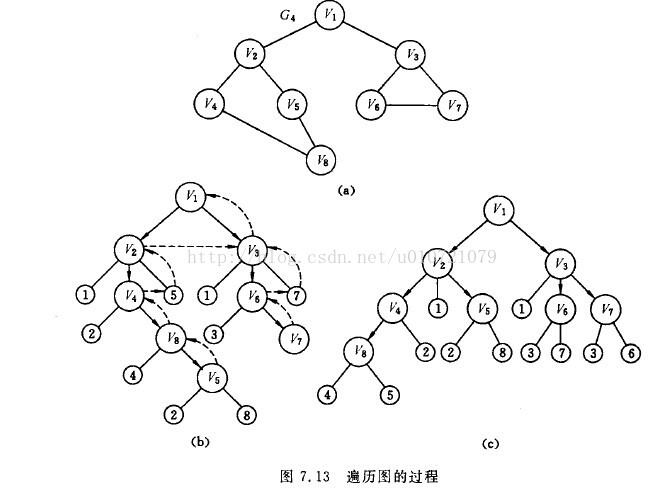
广度优先搜索(Breadth_first Search):假设从图中的顶点v出发,在访问了v之后依次访问v的各个为曾访问过的邻接点,然后分别从这些邻接点出发依次访问它们的邻接点,并使“先被访问的顶点的邻接点”先于"后被访问的顶点的邻接点"被访问,直至图中所有已被访问的顶点的邻接点都被访问到。若此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则另选图中一个未曾被访问的顶点作起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。换句话说,广度优先搜索遍历图的过程是以v为起始点,由近至远,依次访问和v有路径相通且路径长度为1,2,3……的顶点。
如图:
广度优先搜索顶点访问序列为:v1、v2、v3、v4、v5、v6、v7、v8
深度优先搜索顶点访问序列为:v1、v2、v4、v8、v5、v3、v6、v7
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<string.h>
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
#define MAX_NAME 5 //顶点字符串的最大长度
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20 //顶点的最大长度
#define MAXQSIZE 100 //队列的最大长度
#define OK 1
#define FALSE -1
typedef char VertexType[MAX_NAME];
typedef int QElemType;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef struct ArcNode
{
int adjvex;
struct ArcNode *nextarc;
InfoType *info;
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode
{
VertexType data; //data是一个含有五个字符的字符串数组
ArcNode *firstarc;
}VNode,AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct
{
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum,arcnum;
int king;
}ALGraph;
typedef struct SqQueue
{
QElemType *base;
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
int LocateVex(ALGraph &G, VertexType &u) //返回顶点u在vertices中的位置
{
for(int i = 0;i < G.vexnum; ++i)
{
if(strcmp(G.vertices[i].data,u) == 0)
return i;
}
return FALSE ;
}
int CreateDG( ALGraph &G )
{
int i,j,k;
VertexType v1,v2;
cout <<"开始构造有向图:\n请输入图的顶点的个数:";
scanf("%d",&G.vexnum);
cout << "请输入图的边的数目:";
scanf("%d",&G.arcnum);
cout <<"请输入所有的顶点:\n";
for(i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
{
scanf("%s",G.vertices[i].data);
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
cout <<"请输入弧,例如 v1-->v2\n";
for(k = 0; k < G.arcnum; ++k)
{
cout << "请输入第" << k+1 << "条弧的弧尾";
cin >> v1;
cout << "请输入第" << k+1 << "条弧的弧头";
cin >> v2;
i = LocateVex(G,v1);
j = LocateVex(G,v2);
ArcNode *p;
p = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!p)
{
cout << "溢出!";
return 0;
}
p->adjvex = j;
p->nextarc = G.vertices[i].firstarc; //单链表的逆序构造,即输入的第一个结点会成为最后一个结点
G.vertices[i].firstarc = p;
p->info = NULL;
} // for end
return OK;
} /// CreateDG() end;
int InitQueue( SqQueue &Q )
{
Q.base = (QElemType *)malloc(MAXQSIZE*sizeof(QElemType));
if(!Q.base)
{
cout << endl << "溢出!";
return 0;
}
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
return OK;
}
int EnQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType e) //插入元素e为新的队尾元素
{
if((Q.rear + 1) % MAXQSIZE == Q.front )
{
cout << "Error! The SqQeueu is full!";
return 0;
}
Q.base[Q.rear] = e;
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1 ) %MAXQSIZE;
return OK;
} // EnQueue() end
int QueueEmpty(SqQueue Q)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear)
return (OK);
else
return (0);
} //QueueEmpty() end
int DeQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType &e )
{
if(Q.front == Q.rear )
{
cout << endl << "Error! It's empty.";
return 0;
}
e = Q.base[Q.front];
Q.front = (Q.front + 1 )%MAXQSIZE;
return e;
} //DeQueue() end
void BFSTraverse(ALGraph G)
{
int i,v ,u;
ArcNode *p;
SqQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q); //辅助队列Q
int visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
for( i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i) //访问标志数组visited
visited[i] = 0;
for(v = 0; v < G.vexnum; ++v)
{
if(visited[v] == 0)
{
visited[v] = 1;
cout << G.vertices[v].data << "-->";
EnQueue(Q, v) ; //进入队列 first in first out
while(!QueueEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(Q, u); //出队列
for(p = G.vertices[u].firstarc; p!=NULL; p=p->nextarc) //先遍历v1的所有的邻接顶点w1、w2、w3,
{ //遍历的过程中w1最先进入队列接着到w2然后到w3
if(visited[p->adjvex] == 0) //然后进入下一个while循环,w1最先出队列,也就是最先访问w1的邻接顶点
{
visited[p->adjvex] = 1;
cout << G.vertices[p->adjvex].data << "-->";
EnQueue(Q, p->adjvex) ; //进入队列
}// end if
} // end for
} // end while
} // end if
} // end for
}
void DestoryALGraph(ALGraph &G)
{
ArcNode *q = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
{
for(ArcNode *p = G.vertices[i].firstarc; p != NULL; )
{
q = p;
p = p->nextarc;
delete [] q;
}
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
}
void main()
{ ALGraph G;
cout<<endl<<endl<<"BFSTraverse3.cpp";
cout<<endl<<"==============="<<endl;
CreateDG(G);
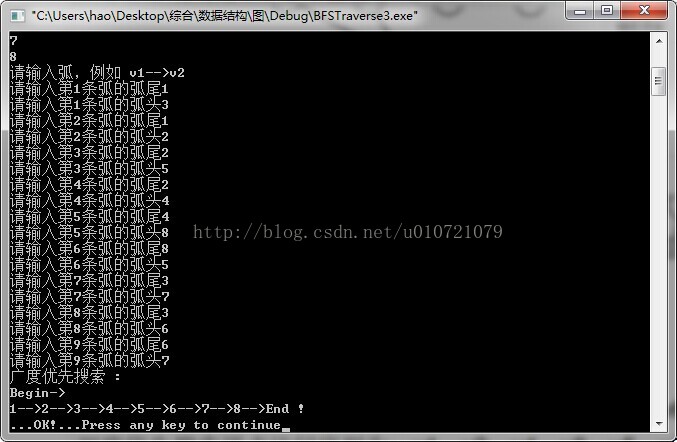
cout<<"广度优先搜索 :";
cout<<endl<<"Begin->\n";
BFSTraverse(G);
DestoryALGraph(G);
cout<<"End !"<<endl<<"...OK!...";
}
void BFSTraverse(ALGraph G)
{
int i,v ,u;
ArcNode *p;
SqQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q); //辅助队列Q
int visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
for( i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i) //访问标志数组visited
visited[i] = 0;
for(v = 0; v < G.vexnum; ++v)
{
if(visited[v] == 0)
{
visited[v] = 1;
cout << G.vertices[v].data << "-->";
EnQueue(Q, v) ; //进入队列 first in first out
while(!QueueEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(Q, u); //出队列
for(p = G.vertices[u].firstarc; p!=NULL; p=p->nextarc) //先遍历v1的所有的邻接顶点w1、w2、w3,
{ //遍历的过程中w1最先进入队列接着到w2然后到w3
if(visited[p->adjvex] == 0) //然后进入下一个while循环,w1最先出队列,也就是最先访问w1的邻接顶点
{
visited[p->adjvex] = 1;
cout << G.vertices[p->adjvex].data << "-->";
EnQueue(Q, p->adjvex) ; //进入队列
}// end if
} // end for
} // end while
} // end if
} // end for
}























 989
989











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








