环境准备
创建java工程
需要的jar包
- 大家也可以使用maven,参考官网
什么是Realm
在我所看的学习资料中,关于Realm的定义,写了整整一长串,但是对于初学者来说,看定义实在是太头疼了。
对于什么是Realm,我使用过之后,个人总结一下:shiro要进行身份验证,就要从realm中获取相应的身份信息来进行验证,简单来说,我们可以自行定义realm,在realm中,从数据库获取身份信息,然后和 用户输入的身份信息进行匹配。这一切都由我们自己来定义。
为什么要用Realm
在Shiro学习笔记(1)——shiro入门中,我们将身份信息(用户名/密码/角色/权限)写在配置文件中,但是实际开发中,这些身份信息应该保存在数据中,因此我们需要自定义Realm来从数据中获取身份信息,进行验证。
自定义Realm
- 定义一个MyRealm,继承
AuthorizingRealm
package com.shiro.realm;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class MyRealm1 extends AuthorizingRealm{
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class);
/**
* 获取身份信息,我们可以在这个方法中,从数据库获取该用户的权限和角色信息
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
log.info("----------doGetAuthorizationInfo方法被调用----------");
String username = (String) getAvailablePrincipal(principals);
//我们可以通过用户名从数据库获取权限/角色信息
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//权限
Set<String> s = new HashSet<String>();
s.add("printer:print");
s.add("printer:query");
info.setStringPermissions(s);
//角色
Set<String> r = new HashSet<String>();
r.add("role1");
info.setRoles(r);
return info;
}
/**
* 在这个方法中,进行身份验证
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(
AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//用户名
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
log.info("username:"+username);
//密码
String password = new String((char[])token.getCredentials());
log.info("password:"+password);
//从数据库获取用户名密码进行匹配,这里为了方面,省略数据库操作
if(!"admin".equals(username)){
throw new UnknownAccountException();
}
if(!"123".equals(password)){
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException();
}
//身份验证通过,返回一个身份信息
AuthenticationInfo aInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,password,getName());
return aInfo;
}
}
- 让我们定义的Realm起作用,就要在配置文件中配置(shiro-realm.ini)
#声明一个realm
MyRealm1=com.shiro.realm.MyRealm1
#指定securityManager的realms实现
securityManager.realms=$MyRealm1- 测试
package com.shiro.realm;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.LockedAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Main {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取SecurityManager的实例
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-realm.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
Subject currenUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//如果还未认证
if(!currenUser.isAuthenticated()){
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin","123");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currenUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("没有该用户: " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 的密码不正确!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 被锁定 ,请联系管理员");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//其他未知的异常
}
}
if(currenUser.isAuthenticated())
log.info("用户 "+currenUser.getPrincipal() +" 登录成功");
//是否有role1这个角色
if(currenUser.hasRole("role1")){
log.info("有角色role1");
}else{
log.info("没有角色role1");
}
//是否有对打印机进行打印操作的权限
if(currenUser.isPermitted("printer:print")){
log.info("可以对打印机进行打印操作");
}else {
log.info("不可以对打印机进行打印操作");
}
}
}
- 测试结果
从结果截图中,我们可以看到,自定义的Realm中的
doGetAuthorizationInfo方法被调用了两次,并且分别在currenUser.hasRole()和currenUser.isPermitted方法调用时调用
散列算法支持
一般我们存入数据库的密码都是通过加密的,比如将“原密码+盐”进行一次或多次MD5计算,shiro提供了对散列算法的支持
package com.shiro.realm;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
private String salt = "hehe";//盐
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(
AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//用户输入的用户名
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//如果数据库中没有这个用户,则返回null,登录失败
if(!username.equals("xiaozhou"))
return null;
//从数据库中查询密码
String password = "42029a889cc26562c986346114c02367";
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,
password, ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt), getName());
return info;
}
}
使用MD5的realm和一般的realm没有太多区别,唯一的区别在于:不使用散列算法(即对密码加密)的话,从数据库查询出来的密码是明文,否则查询出来的是密文,我们没法使用密文来直接比对判断密码是否正确,为了让shiro自动帮我们先加密再比对,我们要在配置文件ini中告诉shiro使用什么算法
[main]
#密码匹配器
credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher
#匹配器使用md5
credentialsMatcher.hashAlgorithmName=md5
#进行几次散列(用md5算法做几次运算)
credentialsMatcher.hashIterations=1
#realm
userRealm=com.shiro.realm.UserRealm
#该realm使用的匹配器是哪个
userRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher
#使用哪个realm
securityManager.realms=$userRealm多个Realm
有时候,我们需要进行多次身份验证,我们可以定义多个Realm,如同流水线一样,shiro会依次调用Realm
MyRealm1
package com.shiro.mutilrealm;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.shiro.realm.Main;
public class MyRealm1 extends AuthorizingRealm{
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class);
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
String username = (String) getAvailablePrincipal(principals);
//通过用户名从数据库获取权限字符串
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//权限
Set<String> s = new HashSet<String>();
s.add("printer:print");
s.add("printer:query");
info.setStringPermissions(s);
//角色
Set<String> r = new HashSet<String>();
r.add("role1");
info.setRoles(r);
return info;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(
AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("MyRealm1开始认证。。。。。。");
//用户名
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
log.info("username:"+username);
//密码
String password = new String((char[])token.getCredentials());
log.info("password:"+password);
//从数据库获取用户名密码进行匹配,这里为了方面,省略数据库操作
if(!"admin".equals(username)){
throw new UnknownAccountException();
}
if(!"123".equals(password)){
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException();
}
//身份验证通过
AuthenticationInfo aInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,password,getName());
return aInfo;
}
}
- MyRealm2和MyRealm1 代码其实基本上是一样的,直接复制一份即可。当然,如果有需求,我们可以自由地定义修改Realm。这里只做个示例而已。
配置Authenticator和AuthenticationStrategy
这两个东东是啥玩意?
上面我们配置了多个Realm进行身份验证,假设一下:MyRealm1 验证通过了,MyRealm2验证不通过怎么办,这就需要定义一个验证策略来处理这种情况。Strategy的意思就是策略。Authenticator就是验证器
配置文件(shiro-mutil-realm.ini)
#声明一个realm
MyRealm1=com.shiro.mutilrealm.MyRealm1
MyRealm2=com.shiro.mutilrealm.MyRealm2
#配置验证器
authenticator = org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator
#配置策略
# AllSuccessfulStrategy 表示 MyRealm1和MyRealm2 认证都通过才算通过
authcStrategy = org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy
#将验证器和策略关联起来
authenticator.authenticationStrategy = $authcStrategy
#配置验证器所使用的Realm
authenticator.realms=$MyRealm2,$MyRealm1
#把Authenticator设置给securityManager
securityManager.authenticator = $authenticator
##########################################################################
# 1. AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy :如果一个(或更多)Realm 验证成功,则整体的尝试被认
# 为是成功的。如果没有一个验证成功,则整体尝试失败。
# 2. FirstSuccessfulStrategy 只有第一个成功地验证的Realm 返回的信息将被使用。所有进一步
# 的Realm 将被忽略。如果没有一个验证成功,则整体尝试失败
# 3. AllSucessfulStrategy 为了整体的尝试成功,所有配置的Realm 必须验证成功。如果没有一
# 个验证成功,则整体尝试失败。
# ModularRealmAuthenticator 默认的是AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy
###########################################################################
- 验证的策略有三种,在配置文件中我用注释都写好了,就不再详细说明了
- 测试
package com.shiro.mutilrealm;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.LockedAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Main {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取SecurityManager的实例
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-mutil-realm.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
Subject currenUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//如果还未认证
if(!currenUser.isAuthenticated()){
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin","123");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currenUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("没有该用户: " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 的密码不正确!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info( token.getPrincipal() + " 被锁定 ,请联系管理员");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//其他未知的异常
}
}
if(currenUser.isAuthenticated())
log.info("用户 "+currenUser.getPrincipal() +" 登录成功");
//得到一个身份集合
PrincipalCollection principalCollection = currenUser.getPrincipals();
}
}
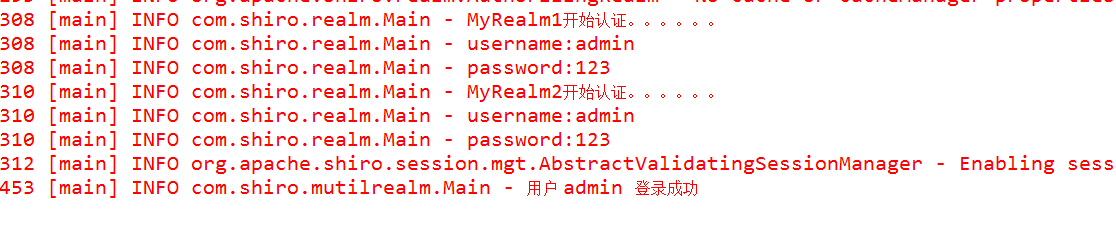
- 运行结果
结果很明显,MyRealm1和MyRealm2依次执行
自定义AuthenticationStrategy(验证策略)
- 上面我们使用了shiro自带的AuthenticationStrategy,其实我们也可以自己定义。
package com.shiro.authenticationstrategy;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AbstractAuthenticationStrategy;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.shiro.realm.Main;
public class MyAuthenticationStrategy extends AbstractAuthenticationStrategy{
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAuthenticationStrategy.class);
/**
* 所有Realm验证之前调用
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo beforeAllAttempts(
Collection<? extends Realm> realms, AuthenticationToken token)
throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============beforeAllAttempts方法被调用==================");
return super.beforeAllAttempts(realms, token);
}
/**
* 每一个Realm验证之前调用
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo beforeAttempt(Realm realm,
AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate)
throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============beforeAttempt方法被调用==================");
return super.beforeAttempt(realm, token, aggregate);
}
/**
* 每一个Realm验证之后调用
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo afterAttempt(Realm realm,
AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo singleRealmInfo,
AuthenticationInfo aggregateInfo, Throwable t)
throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============afterAttempt方法被调用==================");
return super.afterAttempt(realm, token, singleRealmInfo, aggregateInfo, t);
}
/**
* 所有Realm验证之后调用
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo afterAllAttempts(AuthenticationToken token,
AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("===============afterAllAttempts方法被调用==================");
return super.afterAllAttempts(token, aggregate);
}
}
我们所继承的 AbstractAuthenticationStrategy 中,各个方法并不是抽象的,也就是说并一定要重写,我们可以根据需求重写需要的方法即可
配置文件
要让我们自定义的AuthenticationStrategy起作用,只要将上面配置文件(shiro-mutil-realm.ini)中
authcStrategy = org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy
改为authcStrategy = com.shiro.authenticationstrategy.MyAuthenticationStrategy即可测试代码不变
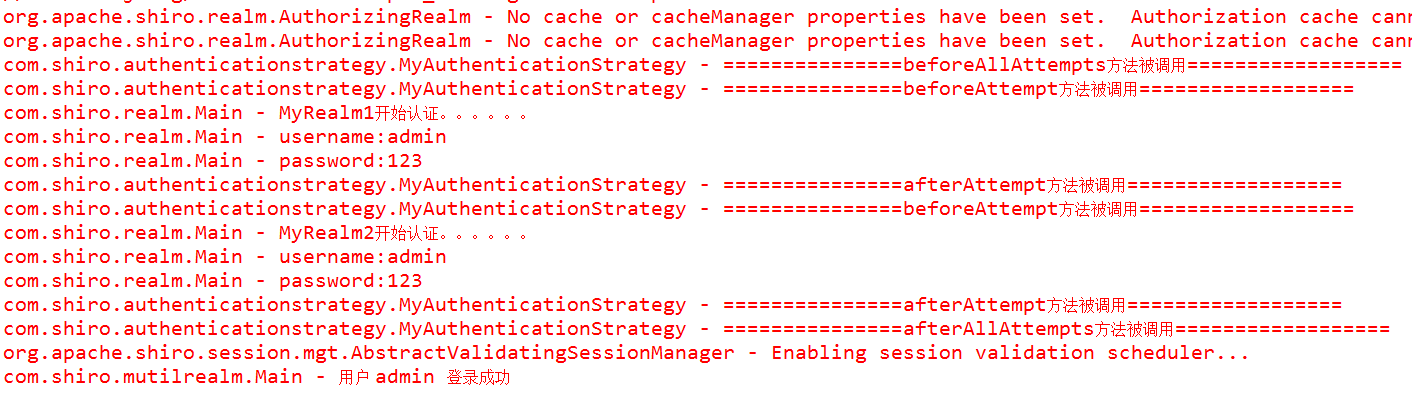
结果
从截图中也可以清除的看到自定义的策略中,各个方法被调用的顺序。有了这些,我们就可以随心所欲的根据需求进行操作了
多个Realm验证顺序
隐式排列
- 当你配置多个realm的时候,处理的顺序默认就是你配置的顺序。
- 这种情况通常就是只定义了realm,而没有配置securityManager的realms
显式排列
- 也就是显示的配置securityManager.realms,那么执行的顺序就是你配置该值的realm的顺序。
- 通常更推荐显示排列。
我们可以简单的理解为,多个Realm验证的顺序,就是我们配置的顺序





 本文详细介绍了如何自定义Realm实现Shiro身份验证,包括环境准备、Realm定义、配置Authenticator和AuthenticationStrategy、多个Realm验证顺序及自定义验证策略等内容。通过示例代码演示了Realm的实现方式及如何在配置文件中进行集成。
本文详细介绍了如何自定义Realm实现Shiro身份验证,包括环境准备、Realm定义、配置Authenticator和AuthenticationStrategy、多个Realm验证顺序及自定义验证策略等内容。通过示例代码演示了Realm的实现方式及如何在配置文件中进行集成。

















 5044
5044

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








