Link:
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1317
XYZZY
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4368 Accepted Submission(s): 1234
Problem Description
It has recently been discovered how to run open-source software on the Y-Crate gaming device. A number of enterprising designers
have developed Advent-style games for deployment on the Y-Crate. Your job is to test a number of these designs to see which are
winnable.
Each game consists of a set of up to 100 rooms. One of the rooms is the start and one of the rooms is the finish. Each room has
an energy value between -100 and +100. One-way doorways interconnect pairs of rooms.
The player begins in the start room with 100 energy points. She may pass through any doorway that connects the room she is in
to another room, thus entering the other room. The energy value of this room is added to the player's energy. This process
continues until she wins by entering the finish room or dies by running out of energy (or quits in frustration). During her
adventure the player may enter the same room several times, receiving its energy each time.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each test case begins with n, the number of rooms. The rooms are
numbered from 1 (the start room) to n (the finish room). Input for the n rooms follows. The input for each room consists of
one or more lines containing:
the energy value for room i
the number of doorways leaving room i
a list of the rooms that are reachable by the doorways leaving room i
The start and finish rooms will always have enery level 0. A line containing -1 follows the last test case.
Output
In one line for each case, output "winnable" if it is possible for the player to win, otherwise output "hopeless".
Sample Input
5
0 1 2
-60 1 3
-60 1 4
20 1 5
0 0
5
0 1 2
20 1 3
-60 1 4
-60 1 5
0 0
5
0 1 2
21 1 3
-60 1 4
-60 1 5
0 0
5
0 1 2
20 2 1 3
-60 1 4
-60 1 5
0 0
-1
Sample Output
hopeless
hopeless
winnable
winnable
Source
University of Waterloo Local Contest 2003.09.27
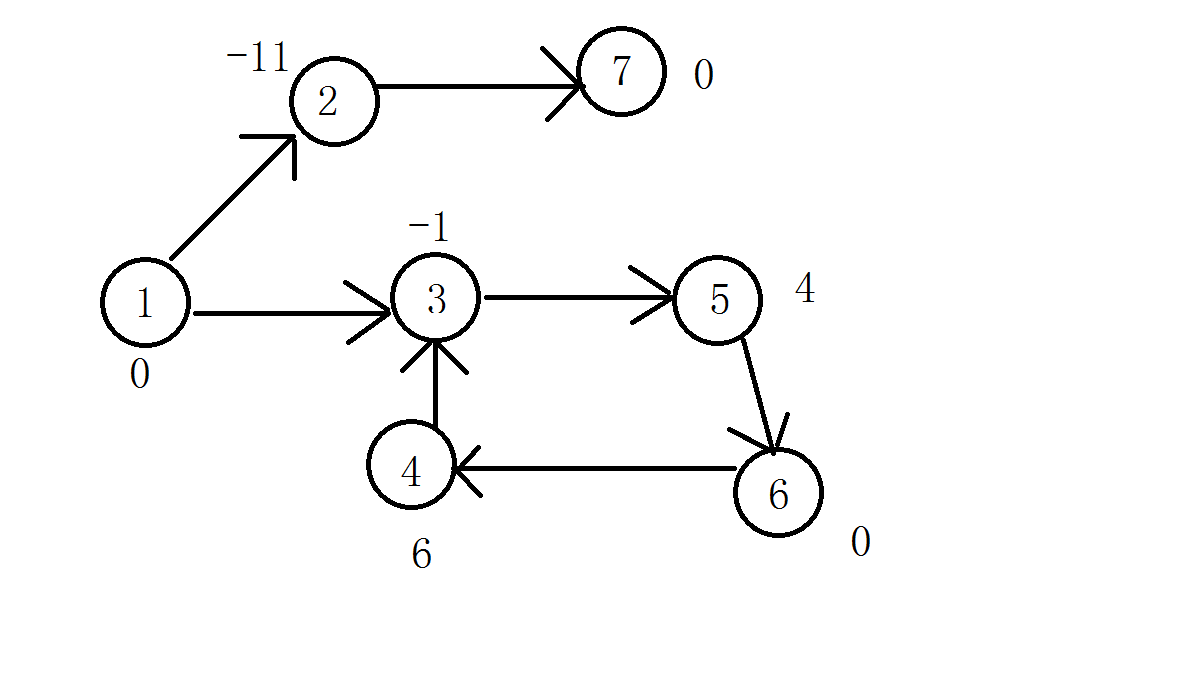
解释
上图我们分别考虑n=6和n=7两种情况这两种特例。
我们考虑一下首先必须从1可以到达n,暂且不考虑能量问题,也就是说首先1,n必须连通,然后我们考虑如果是无环的话,必须到达
n点能量仍然保持正数。如果有环,负环的话我们完全可以不用考虑,如果有正环并且可以到达,那么只要环上的点可以到达n,那么必然可以,我们
便想到了Bellman-Ford算法和Floyd算法。
Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn(105);
const int INF(0x3f3f3f3f);
int map[maxn][maxn];/******用于判断图上的任意两个端点是否连通*******/
int n;
int room_energy[maxn];
int edge_index;/*****存储这个图开始时给出的边的个数******/
struct edge
{
int from,to;
} edges[maxn*maxn];
void init()
{
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
map[i][i]=1;
edge_index=0;
}
void input()
{
int cnt_next,_next;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",room_energy+i,&cnt_next);
while(cnt_next--)
{
scanf("%d",&_next);
map[i][_next]=1;
++edge_index;
edges[edge_index].from=i;
edges[edge_index].to=_next;
}
}
}
void floyd()/******Floyd算法用于判定任意两点的连通**********/
{
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)/******Floyd算法注意i,j,k的位置,不能颠倒*******/
{
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
for(int k=1; k<=n; k++)
{
map[i][j]=map[i][j]||(map[i][k]&&map[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
bool bellman_ford()
{
int dis[maxn];
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++)
{
dis[i]=-INF;
}
dis[1]=100;
int from,to;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=edge_index; j++)
{
from=edges[j].from;
to=edges[j].to;
/****注意此处dis[from]+room_energy[to]>0的意思是还没有run out of energy****/
if(dis[to]<dis[from]+room_energy[to]&&dis[from]+room_energy[to]>0)
{
dis[to]=dis[from]+room_energy[to];
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=edge_index; i++)
{
from=edges[i].from;
to=edges[i].to;
if(dis[to]<dis[from]+room_energy[to]&&dis[from]+room_energy[to]>0&&map[to][n])
return 1;/*****若有环的地方可以与终点连通那么必然可以******/
}
return dis[n]>0;/****没遇到环但是能量没有耗光****/
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n),n!=-1)
{
init();
input();
floyd();
if(!map[1][n])/********如果开始点与最后的点都不连通,那么必定不可能**********/
{
puts("hopeless");
continue;
}
if(bellman_ford())
puts("winnable");
else
puts("hopeless");
}
return 0;
}






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








